Are you fascinated by the enduring charm of early Indian architecture, particularly the intricate beauty of Hindu temples and cave temples? Are you eager to unlock the secrets of Indian temple architecture and explore these majestic structures that have withstood centuries?
Welcome to our exploration of “Ancient Indian Art and Architecture,” where we explore centuries-old mysteries with a deep appreciation for their significance.
In this article, we will:
- Uncover the distinctive features of Hindu temple architecture, including styles such as Dravidian and Nagara.
- Explore the meticulous craftsmanship displayed in cave and rock-cut architecture.
- Discuss the evolution of artistic expressions through sculpture, pottery, and painting in ancient India.
Ready to begin an adventure through time and culture? Join us as we unravel the beauty and complexity of ancient Indian art and architecture, offering insights that inspire and educate.

Architectural Styles and Features in Ancient India
Ancient Indian architecture is known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse architectural styles. The architectural styles of ancient India evolved over time, influenced by various factors such as geography, climate, religion, and culture. In this section, we will explore some of the most prominent architectural styles and features of ancient India.
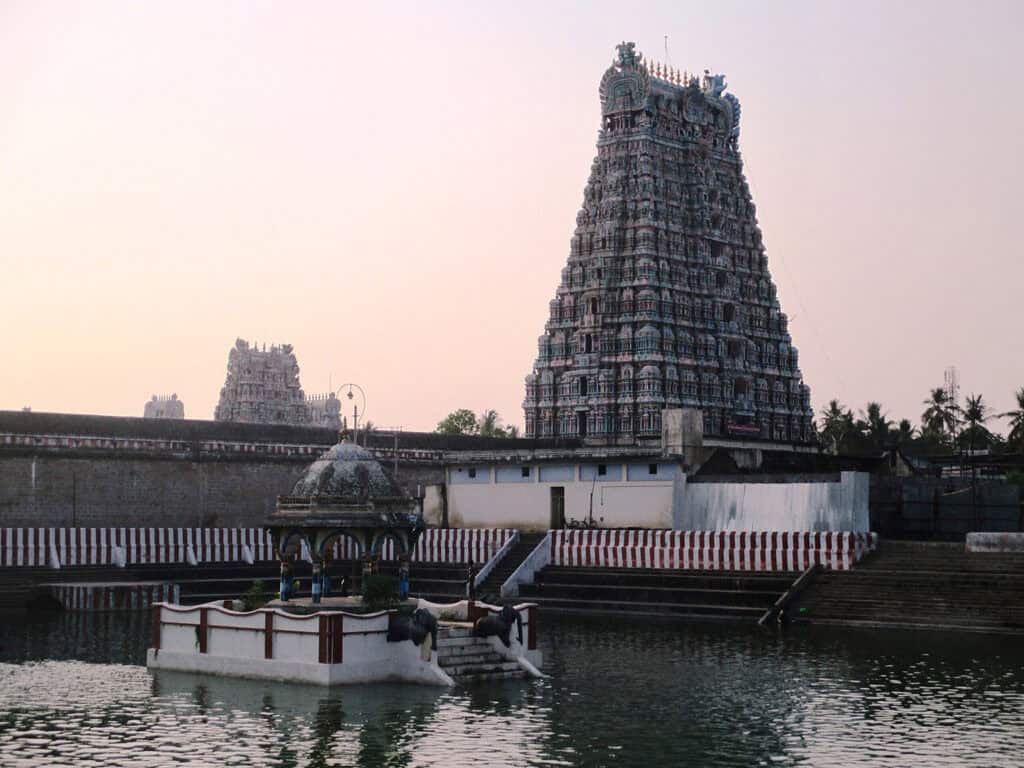
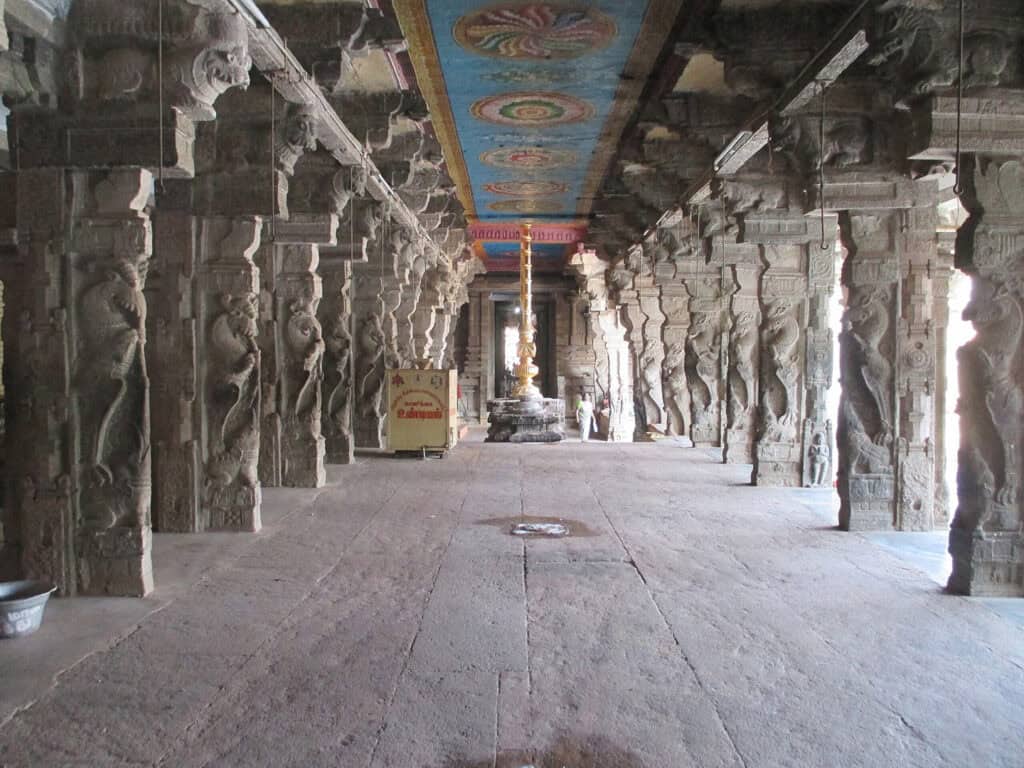
1. Dravidian Architecture
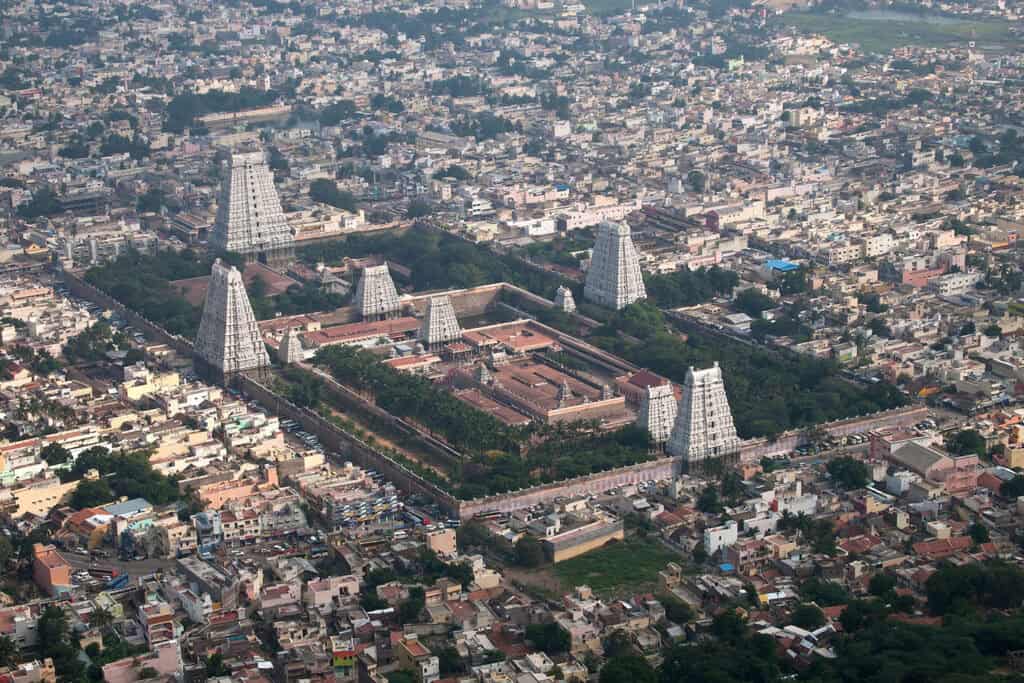

Vyacheslav Argenberg
Dravidian architecture is a style of architecture that originated in the southern part of India, particularly in the state of Tamil Nadu. It is characterized by its pyramid-shaped towers, known as gopurams, which are adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures. Some of the most famous examples of Dravidian architecture include the Rajagopalaswamy Temple.


2. Nagara Style
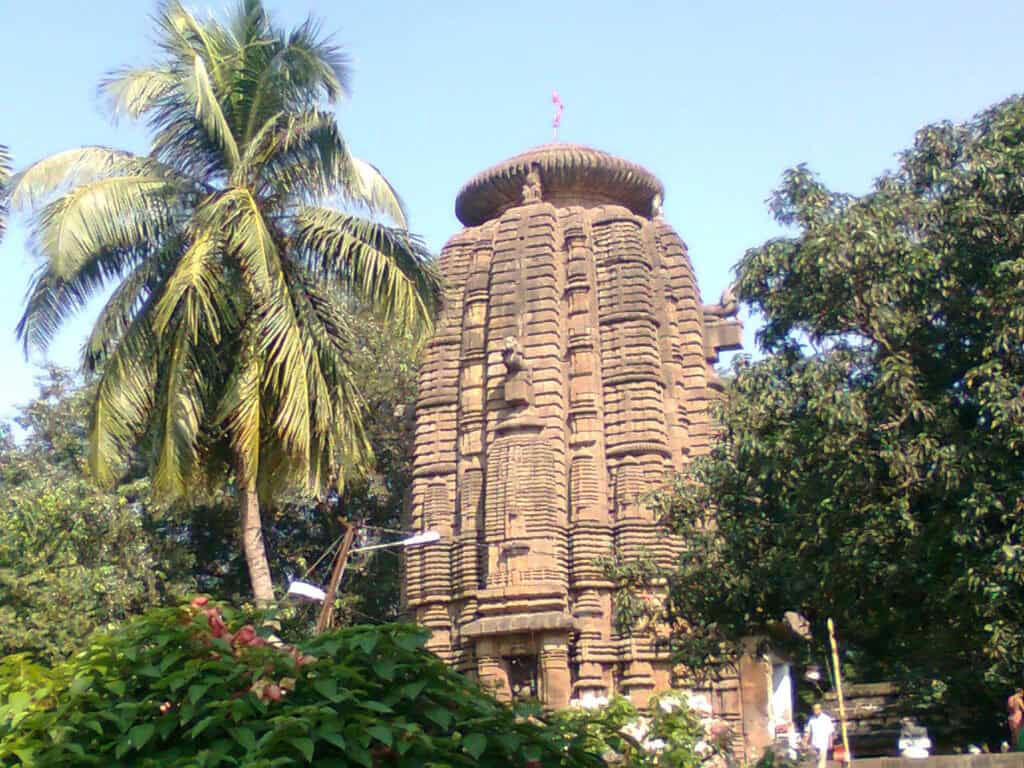

The Nagara style of architecture originated in northern India. It is characterized by its curvilinear towers, known as shikharas, and its intricate carvings and sculptures. Some of the most famous examples of Nagara style architecture include the Rameshwar Deula and Rajarani Temple.
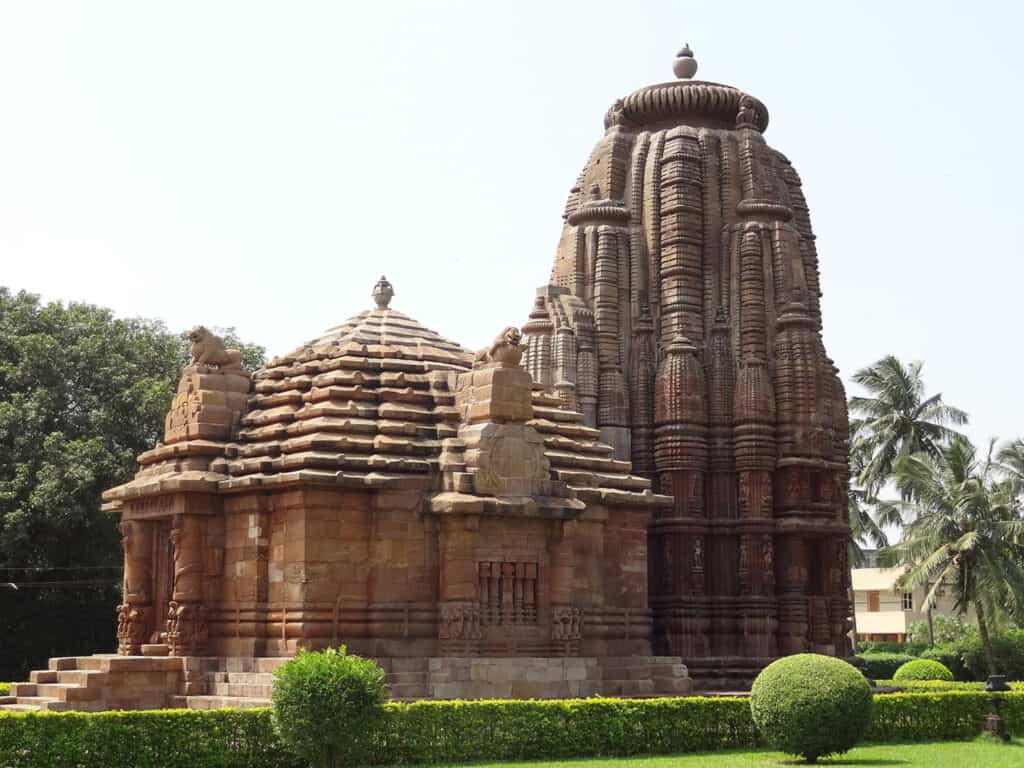

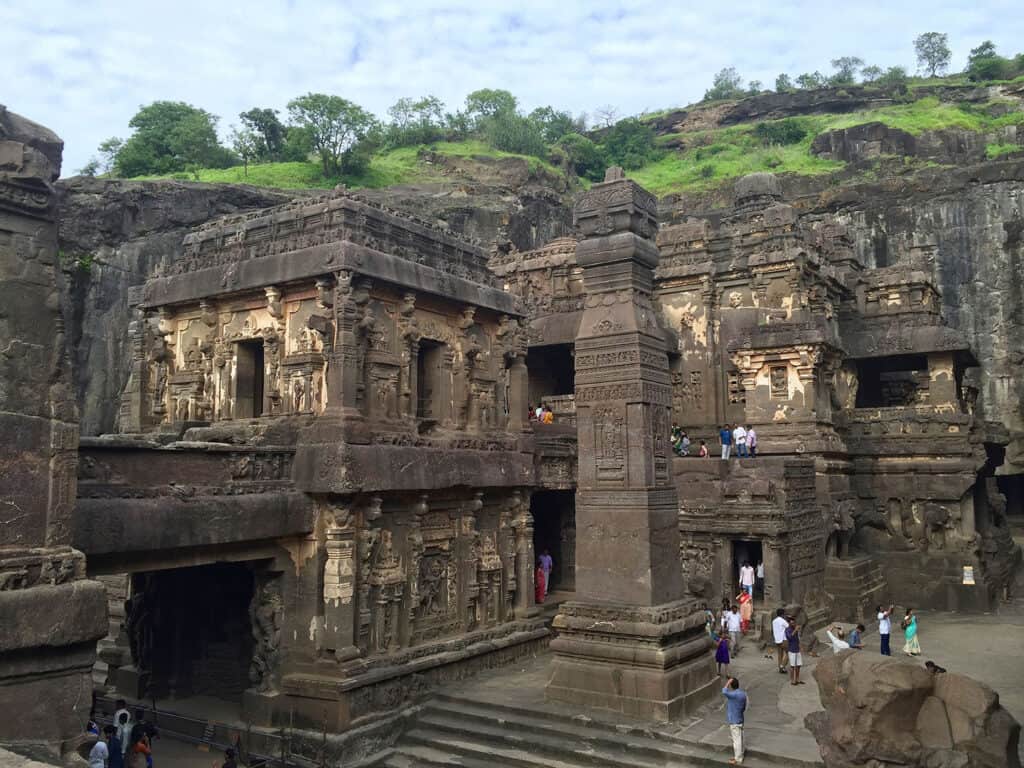
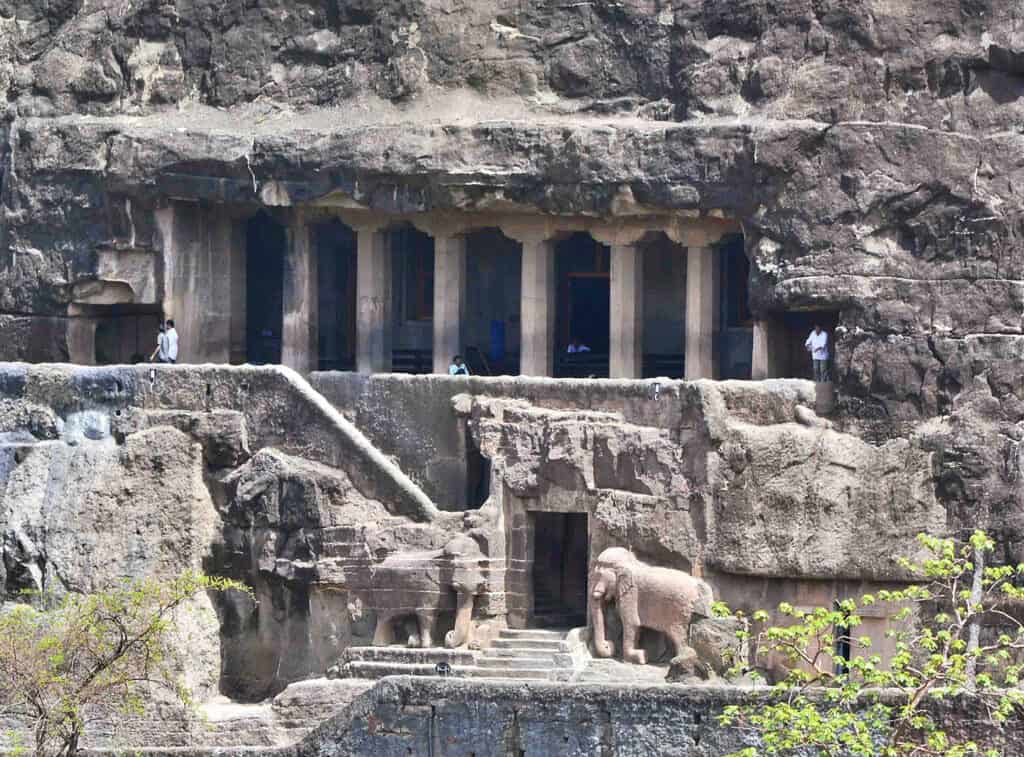
3. Cave Architecture and Rock Cut

Cave architecture is a unique style of architecture that originated in ancient India. The caves were carved out of rocks and used as temples or monasteries. The most famous examples of cave architecture are the Ajanta.
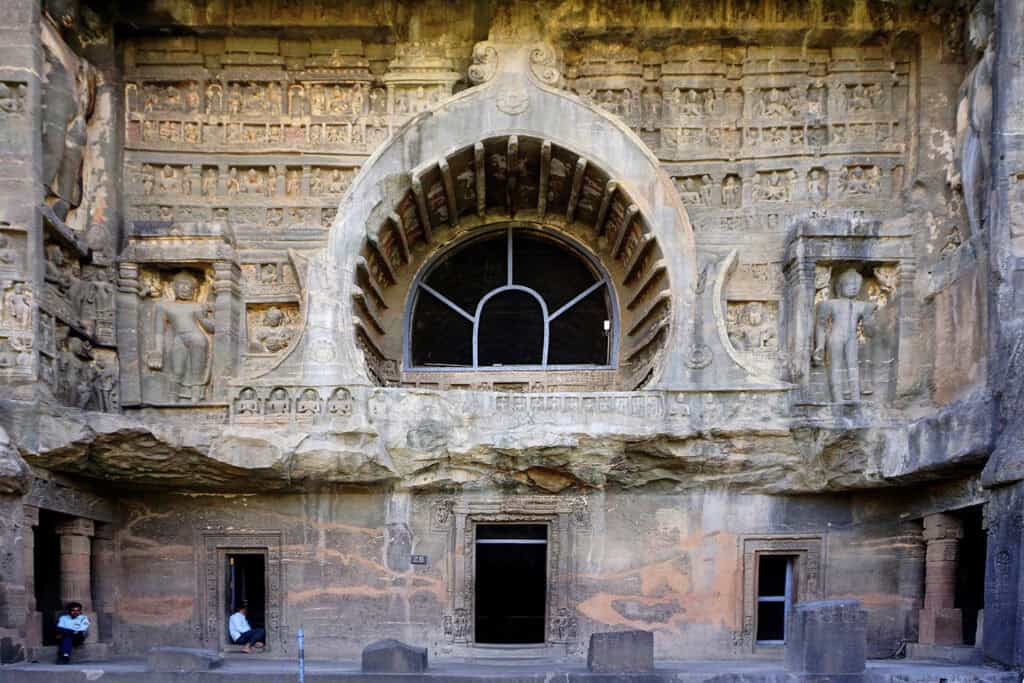
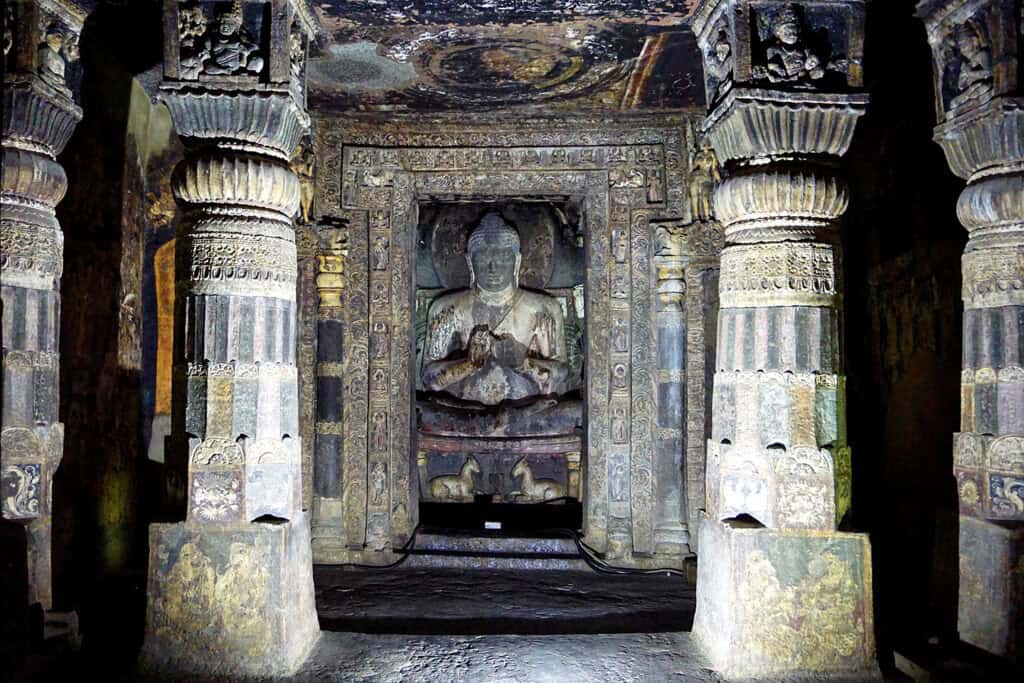


Rock-cut architecture is another unique style of architecture that originated in ancient India. It involves carving temples, monasteries, and other structures out of solid rock. The earliest instances of Indian rock-cut architecture, the Barabar caves, date from about the 3rd to the 2nd century BCE.
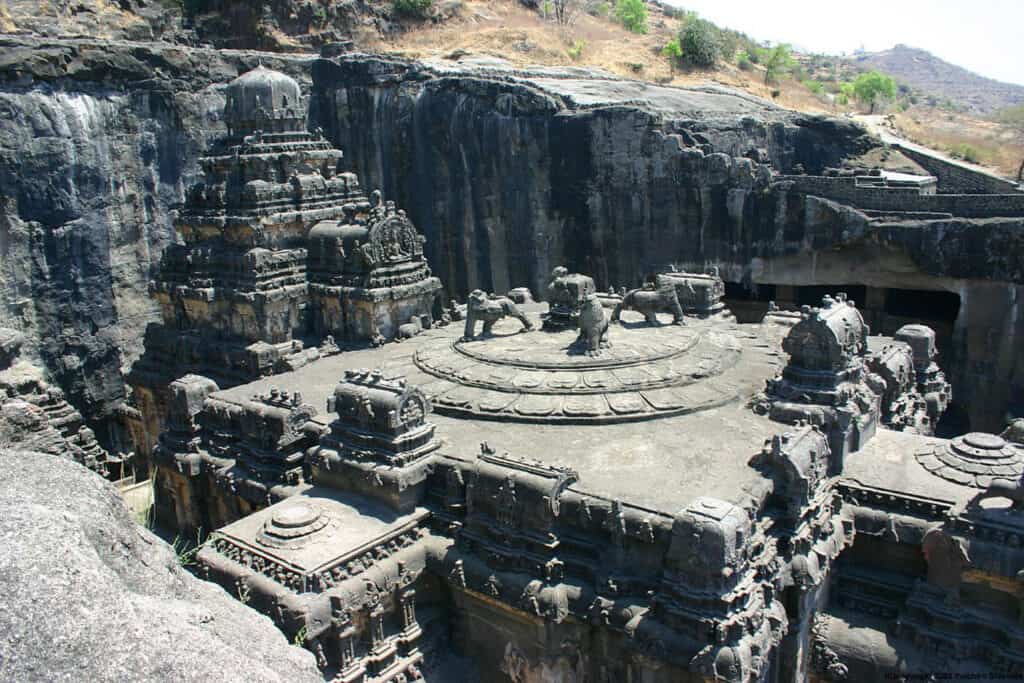


5. Walled and Moated Cities
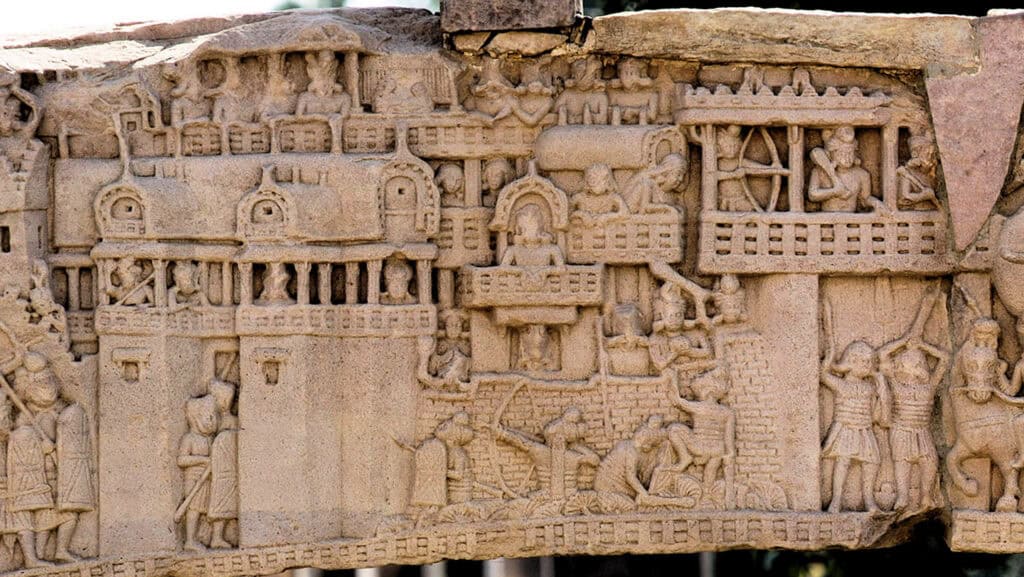

These cities were surrounded by walls and moats to protect them from invaders. Some of the most famous examples of walled and moated cities in ancient India include Kushinagar and Rajagriha.
Art in Ancient India
Art in ancient India was an integral part of the country’s rich and diverse cultural heritage. The art of ancient India can be traced back to the Indus Valley Civilization, which existed from 3500 BCE to 2600 BCE.
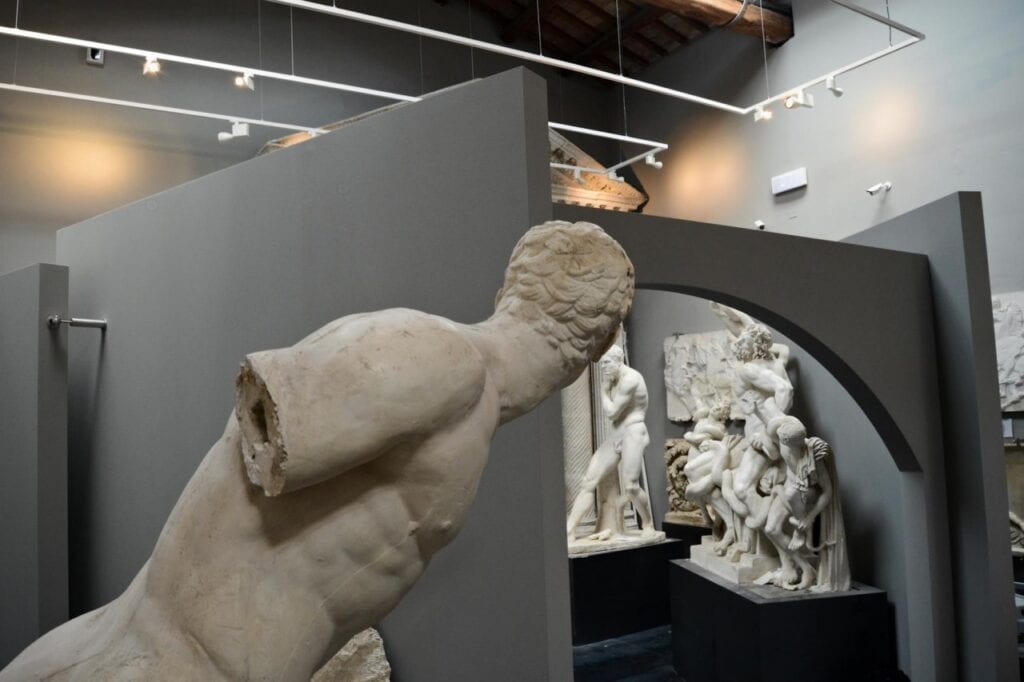
1. Sculpture
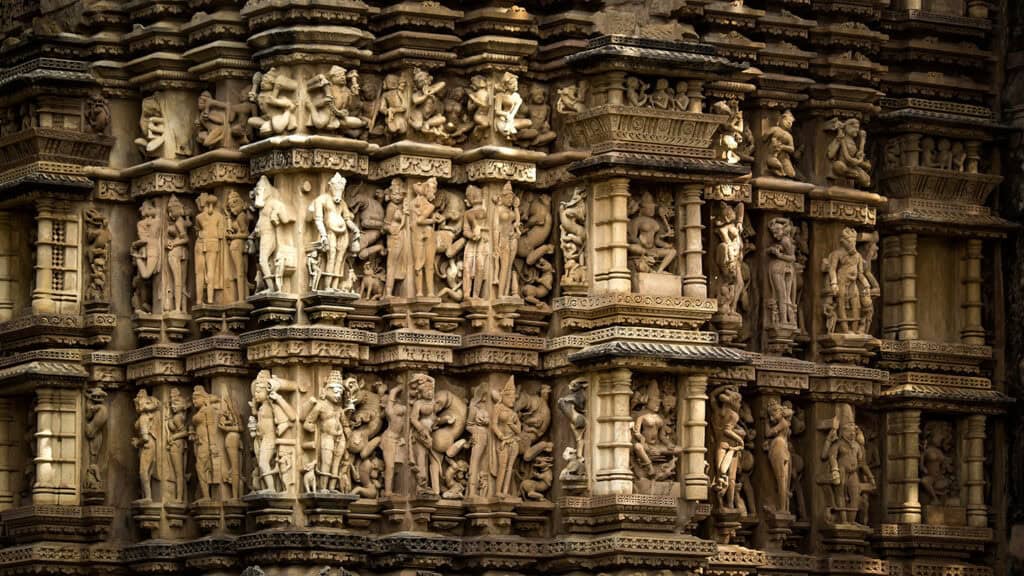

Sculpture was one of the most important forms of art in ancient India. The sculptures were made from a variety of materials, including stone, bronze, and terracotta.
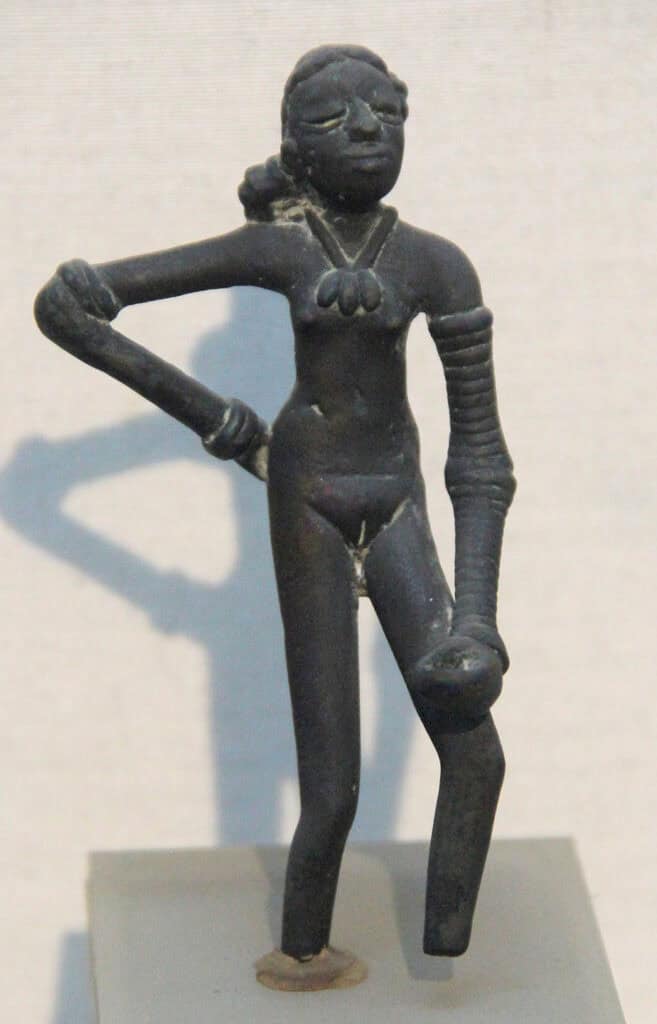

The earliest recorded sculptures in the Indian subcontinent date back to the Indus Valley civilization, which flourished between 3300 and 1700 BCE. Among these, the renowned small bronze sculpture known as the Dancing Girl stands out.
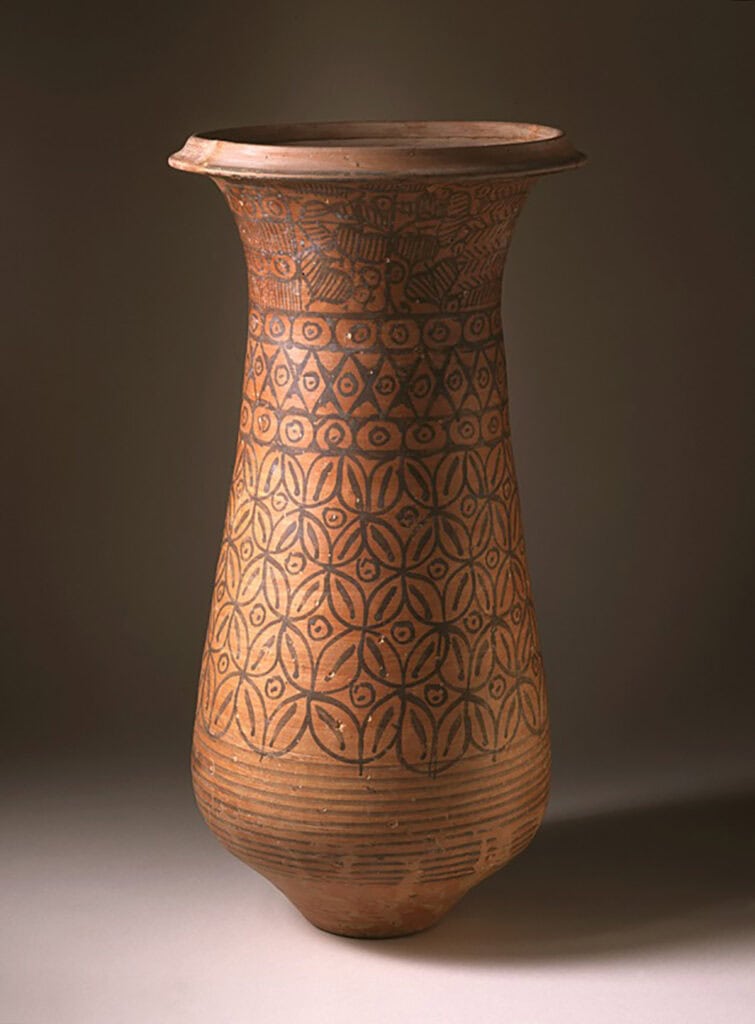
2. Pottery
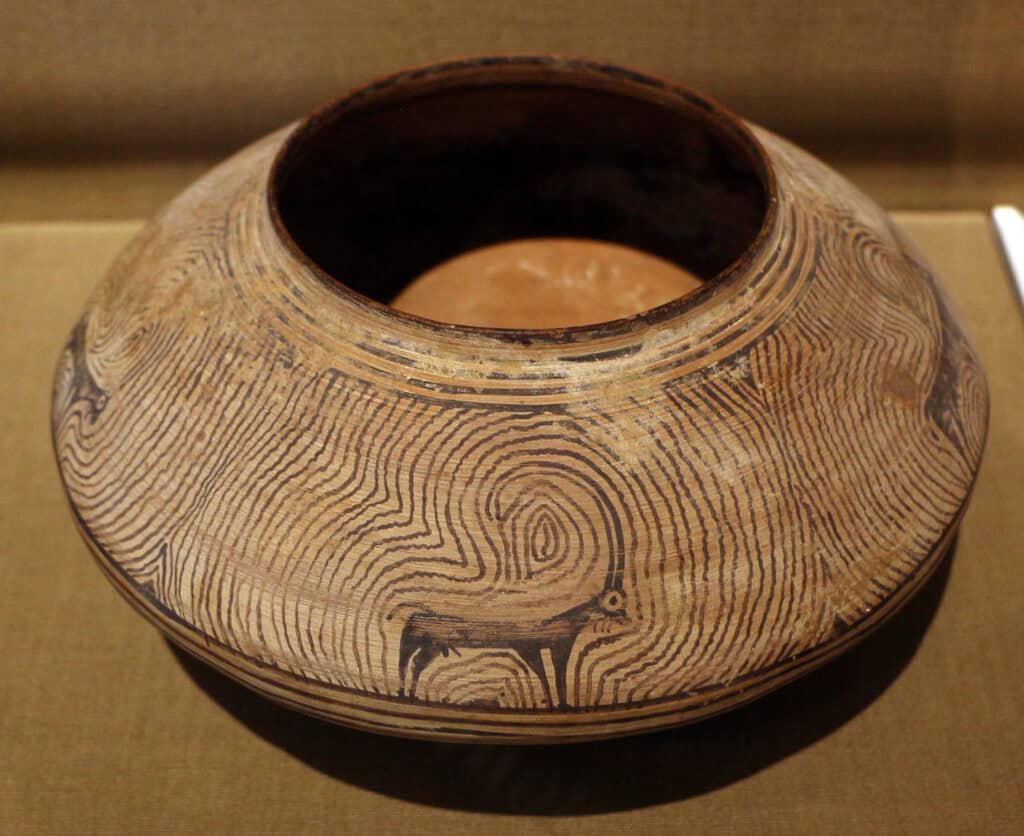

Pottery and decorative arts were also an important part of ancient Indian art. The beginnings of pottery in India date back to the early Mesolithic age. During this period, people crafted rudimentary handmade pottery, including bowls, jars, and vessels, in a variety of colors like red, orange, brown, black, and cream.

3. Painting
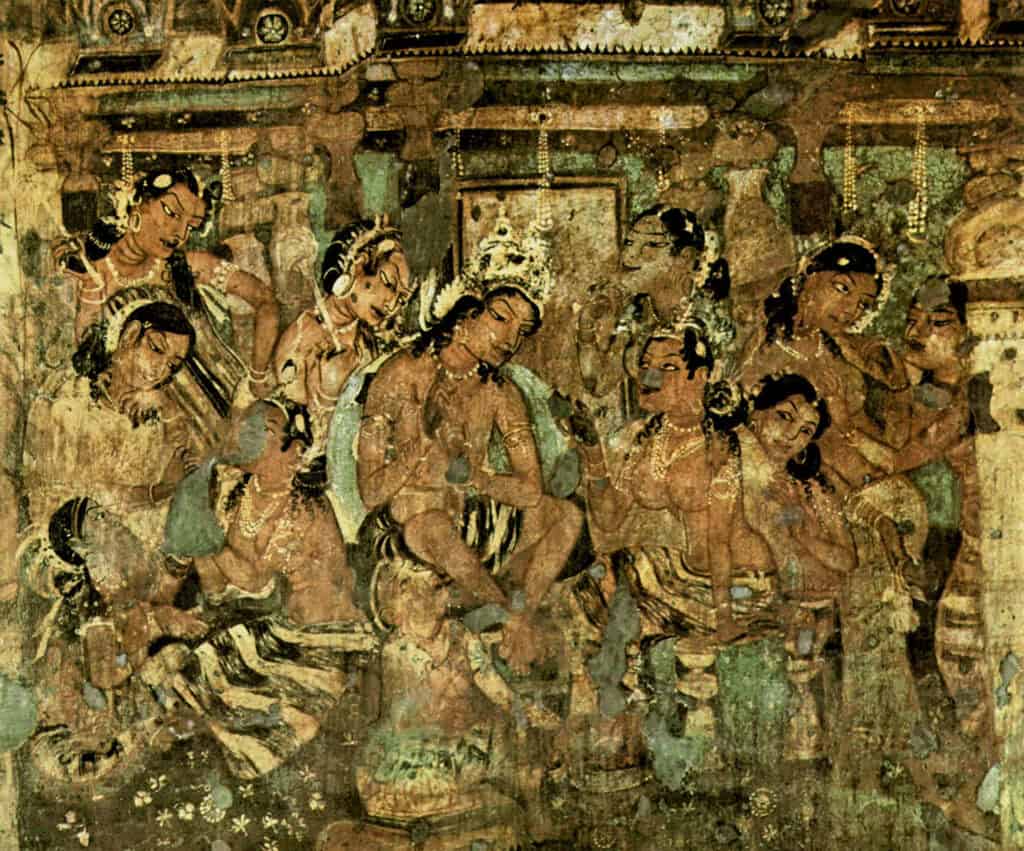

Painting was another important form of art in ancient India. The paintings were made on a variety of surfaces, including walls and cloth. The most famous examples of ancient Indian painting are the murals found at the Ajanta Cave.
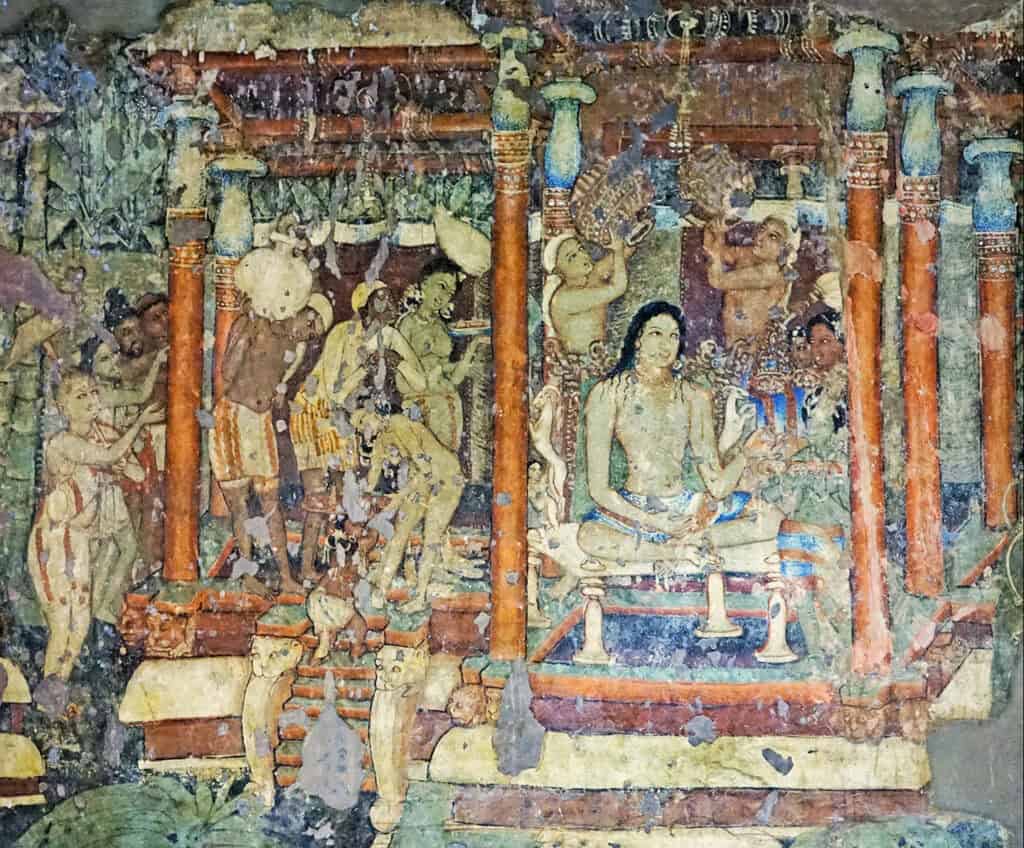

Ancient Indian Art and Architecture






Ancient Indian art and architecture stand as a testament to the country’s rich cultural heritage and diverse history. Through an exploration of the various architectural styles and artistic expressions, we arrived at a deeper understanding of the influences that shaped ancient India.
- Dravidian Architecture: Southern pyramid-shaped towers with intricate carvings.
- Nagara Style: Northern curvilinear towers with detailed sculptures.
- Cave Architecture: Rock-carved temples and monasteries like Ajanta and Ellora.
- Rock Cut Architecture: Solid rock structures, with early examples like the Barabar caves.
- Walled and Moated Cities: Cities like Kushinagar protected by walls and moats.
- Temple Style and Iconography: Evolving from simple wood to ornate stone temples.
Art forms such as sculpture, pottery, and painting also showcase the creativity and skill of ancient Indian artisans, from the Indus Valley’s Dancing Girl to Ajanta’s murals. These contributions reflect the ingenuity and cultural richness of ancient India.