What makes ancient Viking architecture so captivating and enduring? As an enthusiast of history or a student of architecture, you deserve to explore structures that evoke the spirit and ingenuity of the Viking Age. The journey to understanding Viking architecture can be complex, but you’re not alone.
At Landmarks Architect, we understand the intrigue of exploring historical architecture. With years of experience in presenting detailed historical content, we’re here to guide you through every aspect of Viking architectural mastery.
In this article, we will cover:
- Basics of ancient Viking architecture
- Origins and influences shaping Viking structures
- Traditional materials and construction methods
- Iconic Viking structures and their significance
- Artistic and functional elements unique to Viking architecture
Ready to transform your understanding of ancient Viking architecture? Continue reading to gain comprehensive insight into the design and techniques that define an era.
By following our expert guidance, you’ll appreciate the stunning, practical, and culturally rich structures of the Viking Age.
1. What is Ancient Viking Architecture?
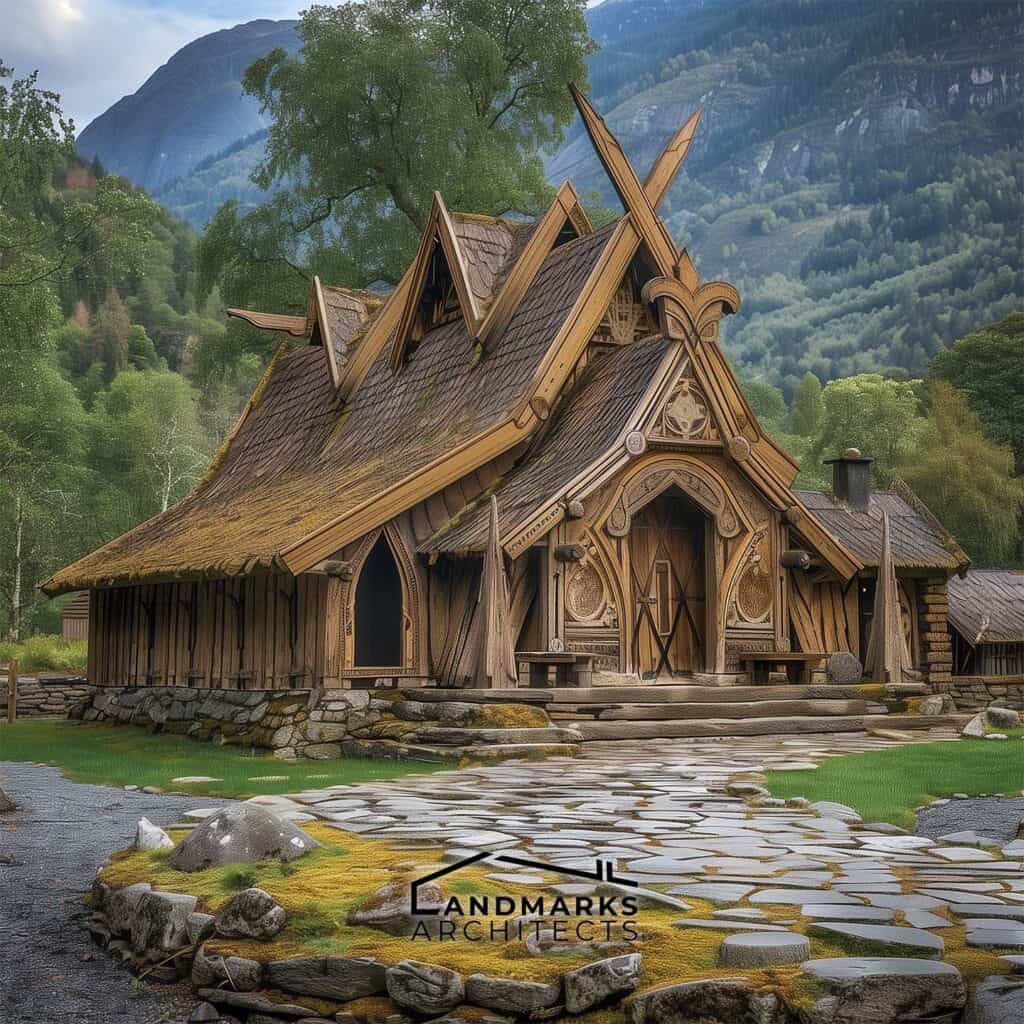
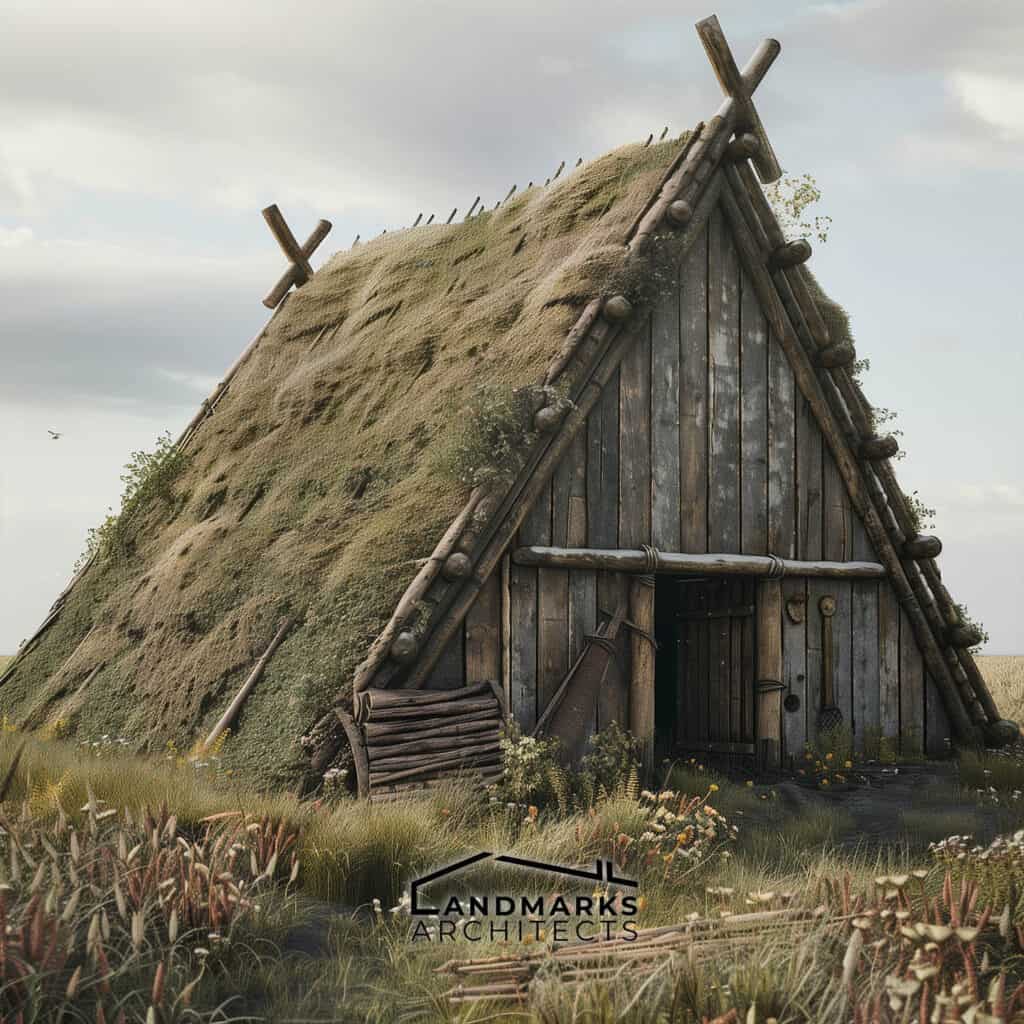



Ancient Viking Architecture refers to the architectural style and techniques developed during the Viking Age (late 8th to 11th century). Key features include:
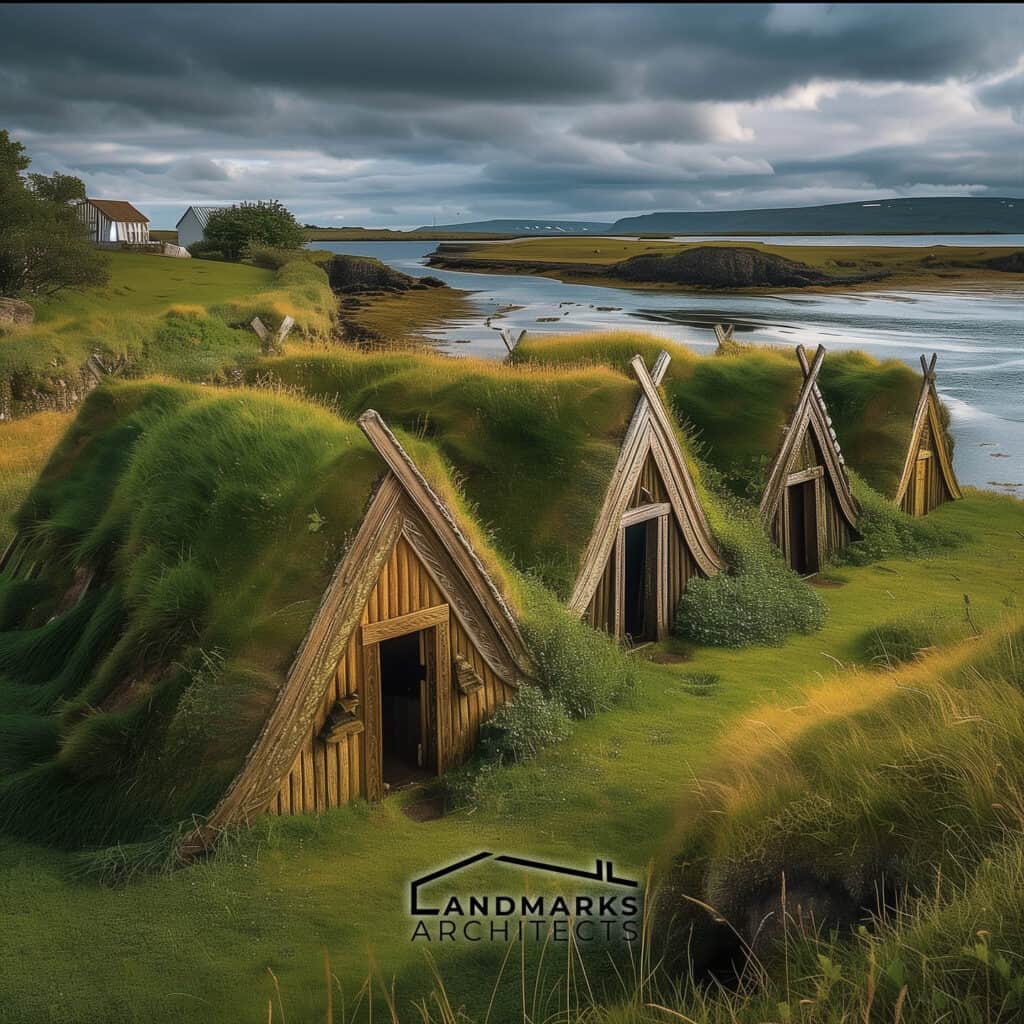
- Viking Longhouse: These were elongated, boat-shaped structures used for communal living. They often had distinctive curved roofs and were constructed to withstand harsh northern climates.
- Building Materials: Vikings primarily used wood, thatch, and sod. These materials were readily available and suited to the local environment.
- Craftsmanship: Skilled artisans crafted intricate carvings and details in their homes, often incorporating Norse mythology and symbolism.
- Central Hearth: Each longhouse featured a central hearth for cooking and heating, underscoring the communal aspect of Viking life.
- Storage Areas: There were designated spaces for storing food and tools, which were essential for survival in the Viking Age.
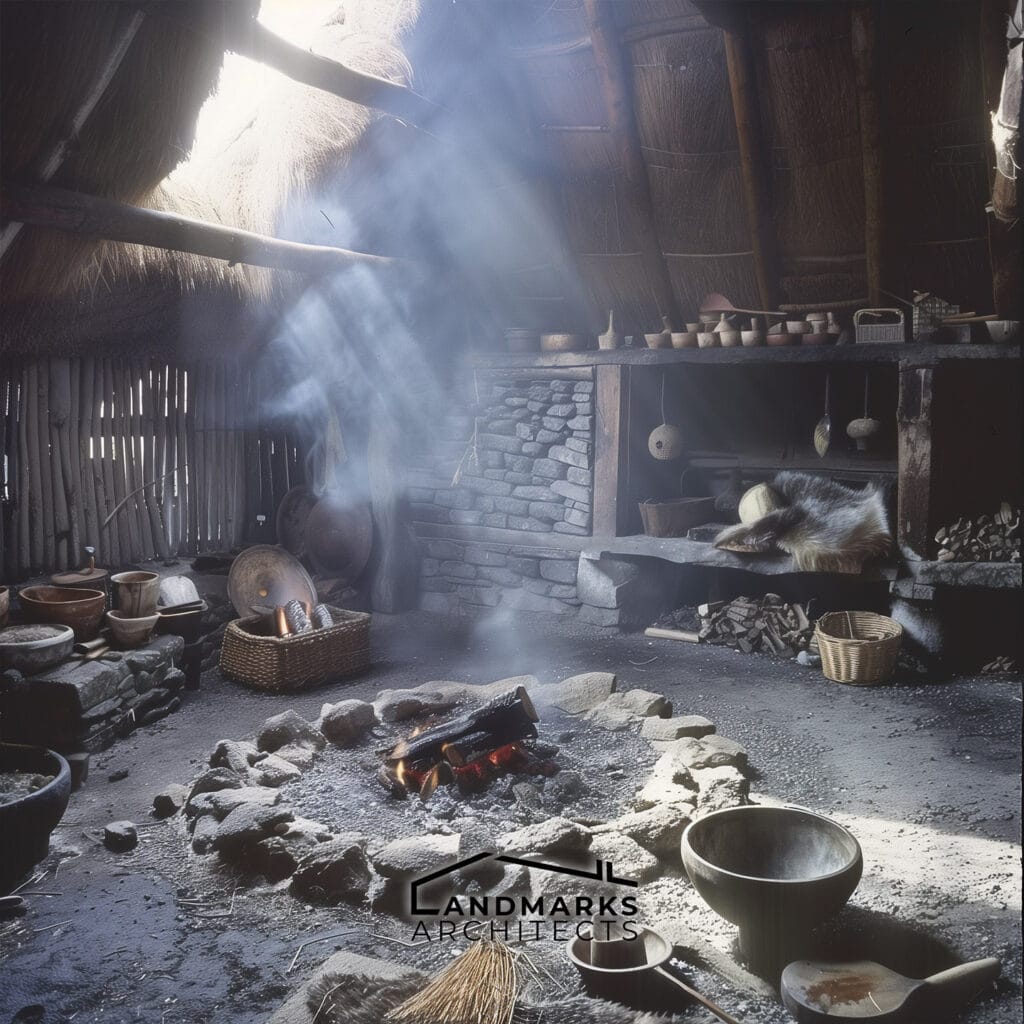
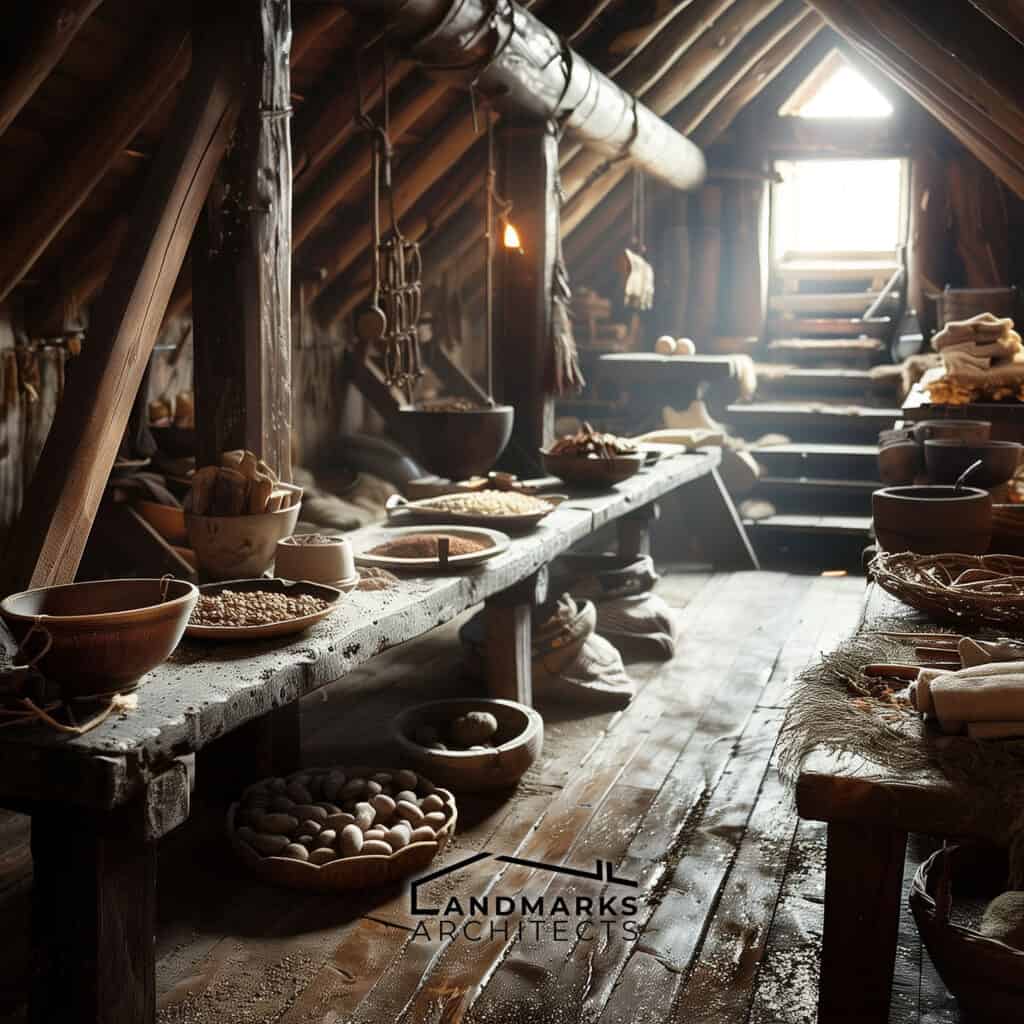



Nordic Viking architecture exemplifies how building techniques were adapted to the geography and climate of Scandinavia. The design of Viking houses accommodated large families and livestock, reflecting the interconnectedness of social and domestic life.
These architectural elements influenced later Norse and medieval structures, impacting the development of architecture in Northern Europe.
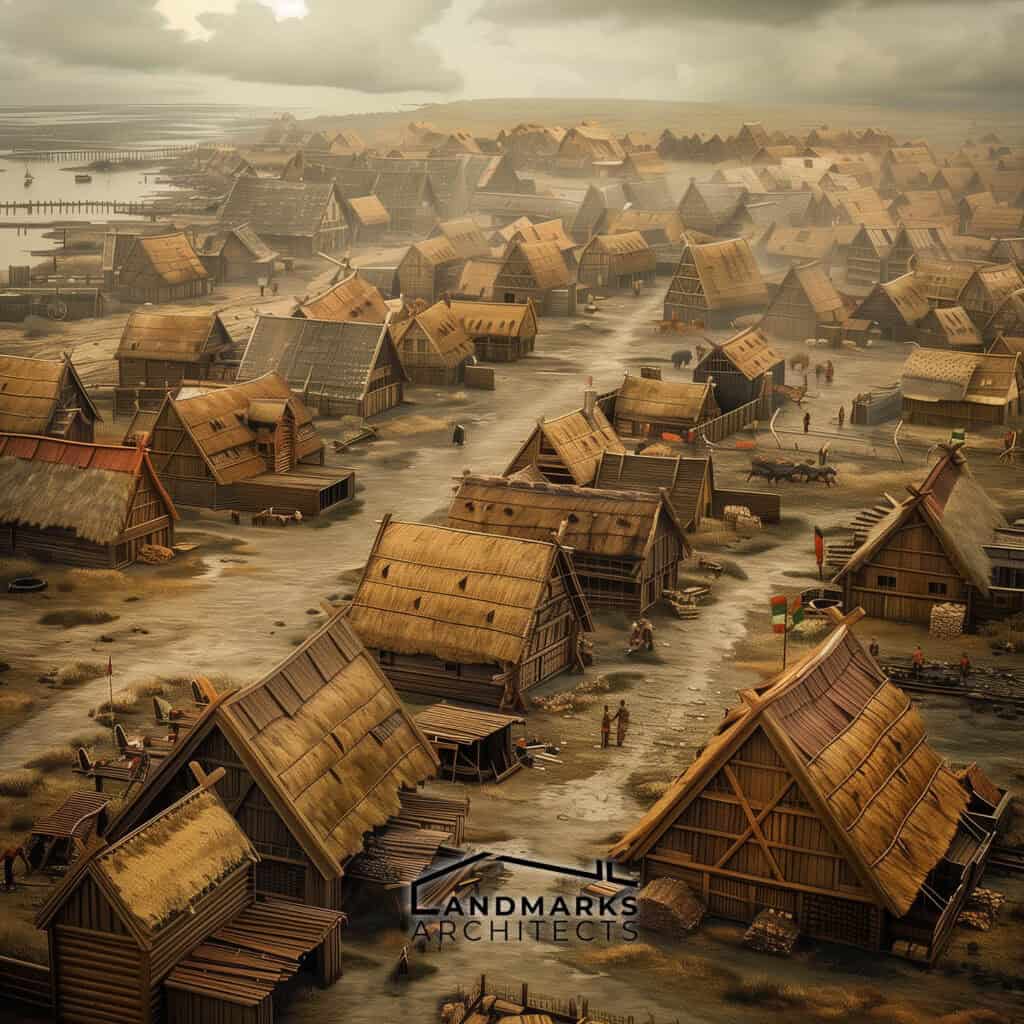

See Also Famous Buildings in Germany
2. Building Materials and Methods
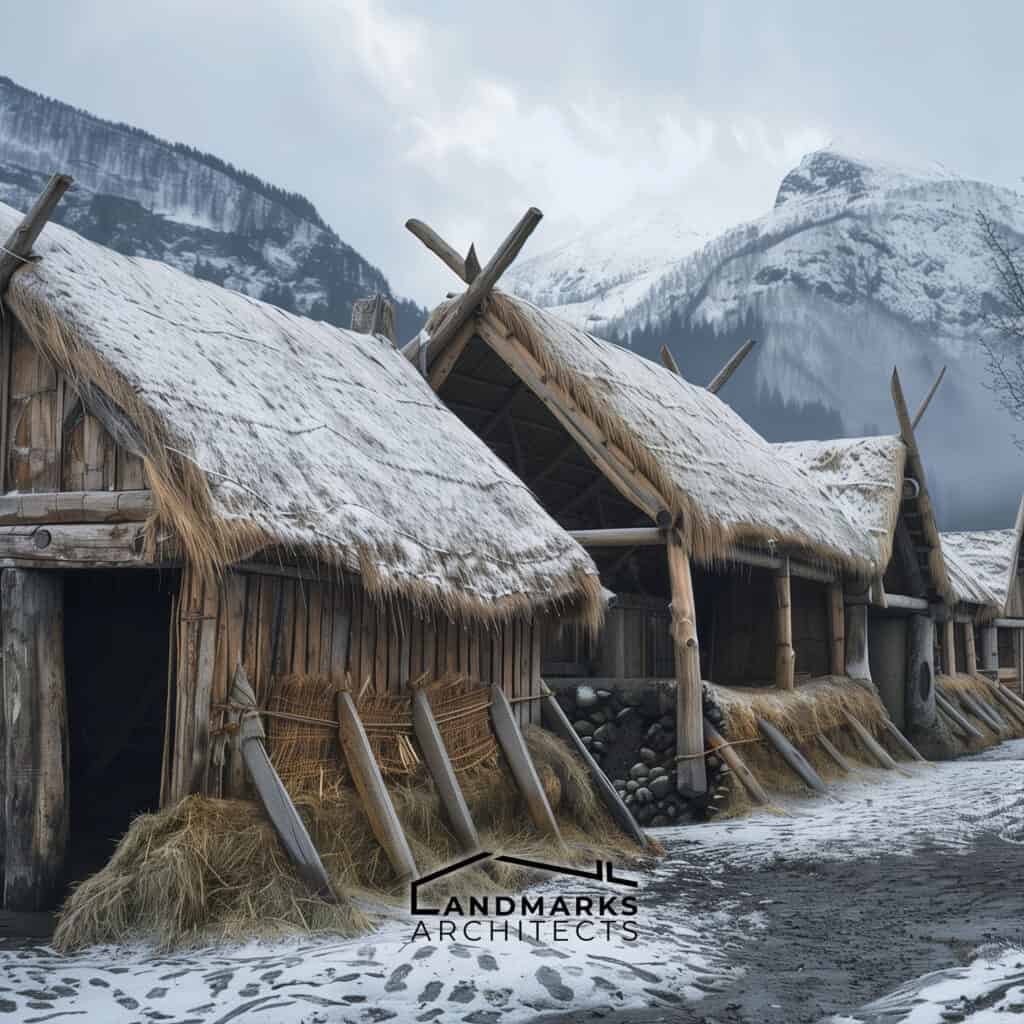
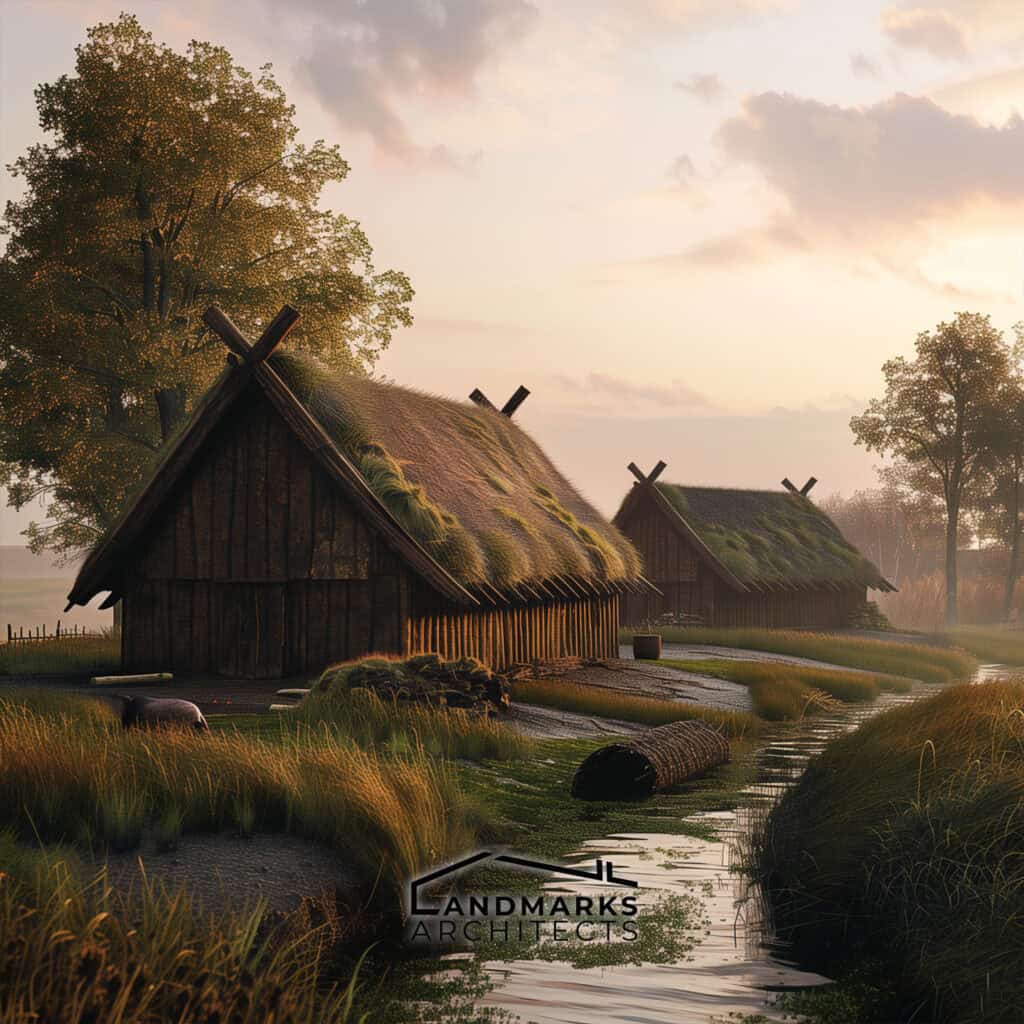



Viking architecture relied on local materials like timber and turf, utilizing innovative techniques to suit Northern Europe’s conditions. They adapted their methods to develop different styles for new environments.
Traditional Materials
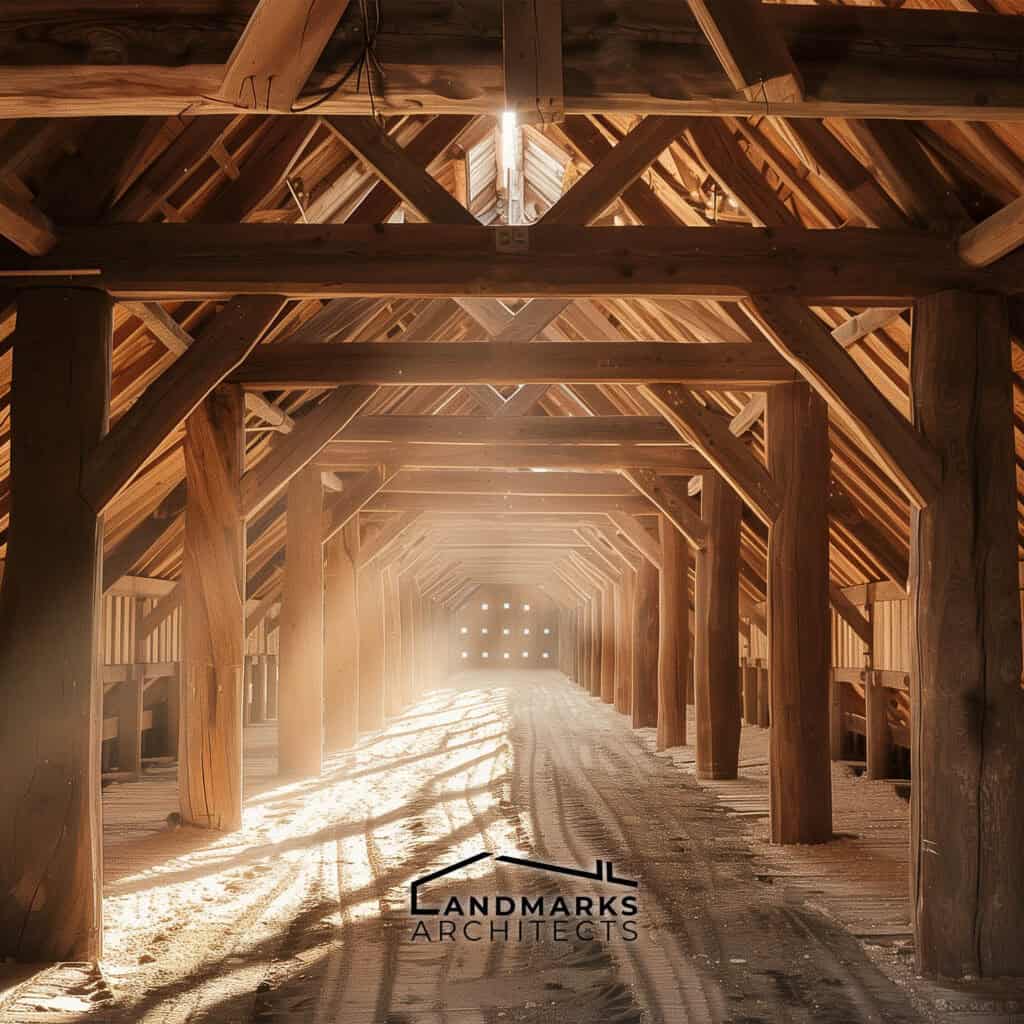
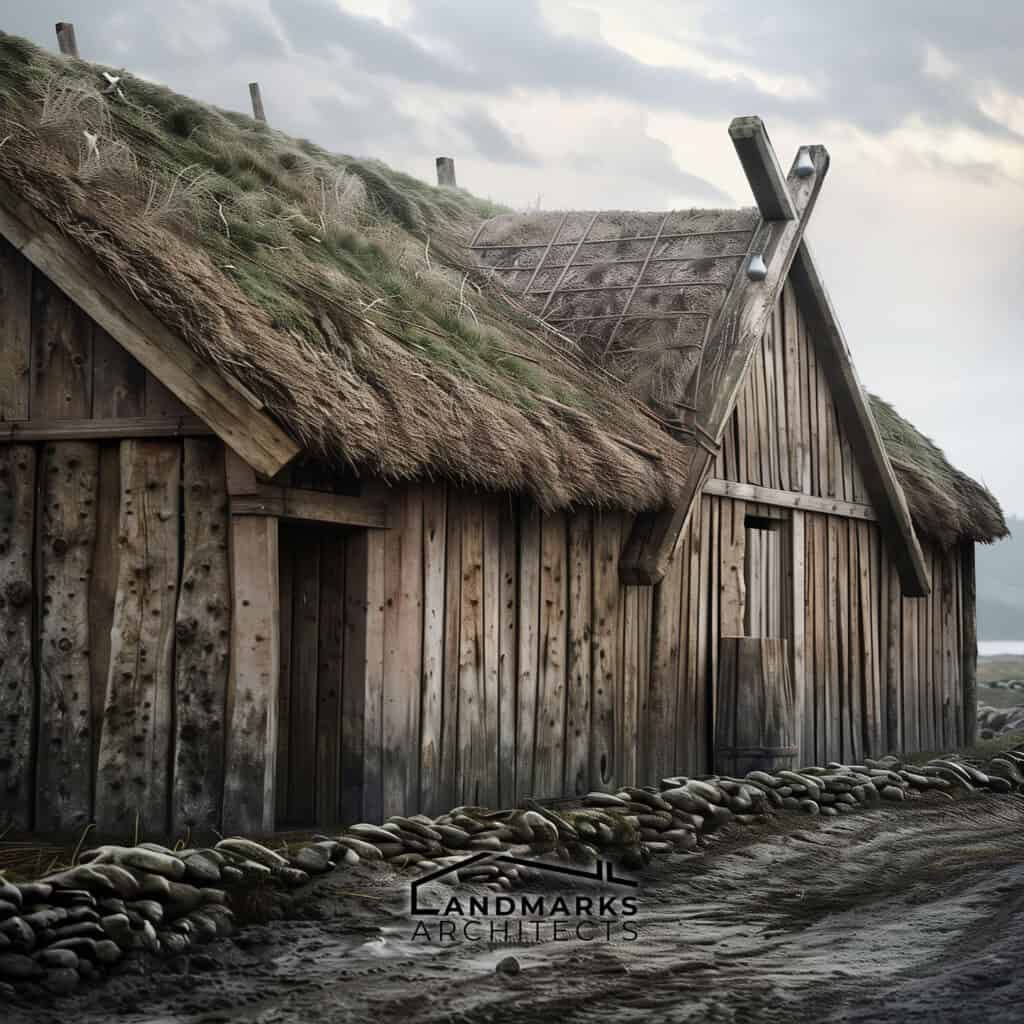



Vikings primarily used locally sourced wood for their homes, utilizing vertical beams and timber frames. The elongated shape of Viking longhouses efficiently housed large families, often featuring turf roofs for insulation against harsh climates.
These buildings typically had stone foundations for stability, with horizontally placed wooden planks providing durability and aesthetic appeal.
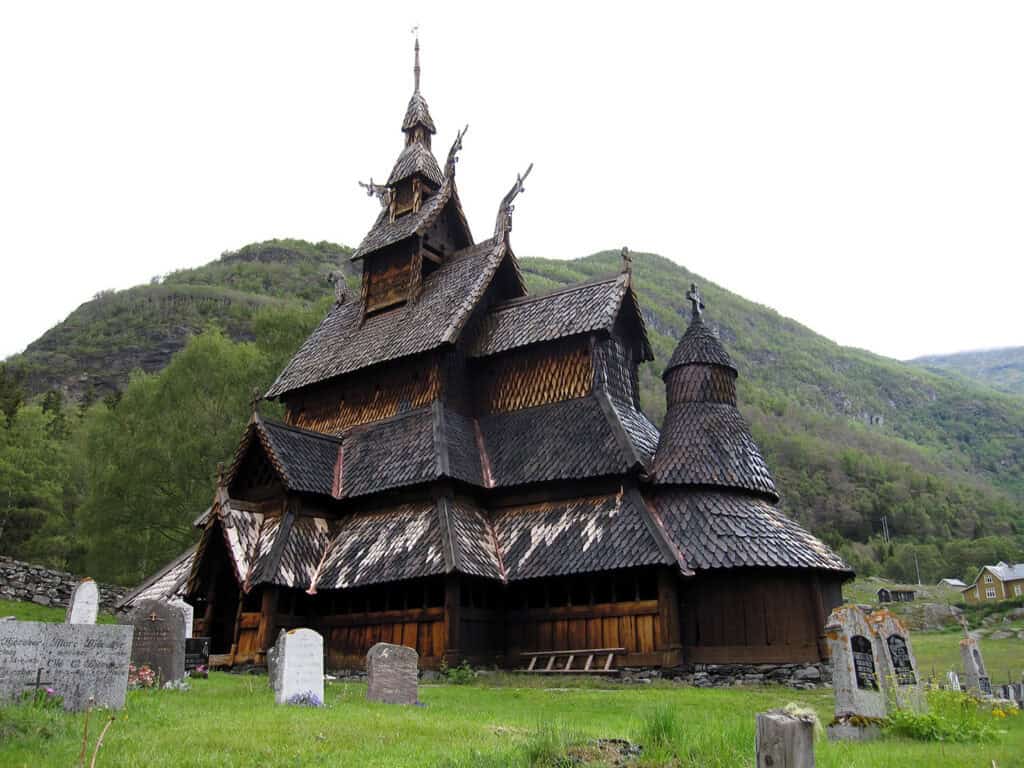

Although the Borgund stave church in Norway, showcasing intricate wood carvings and Norse craftsmanship, was built in the medieval period, it reflects the continuation of the wood-building traditions that began in the Viking Age.
Sustainable Construction
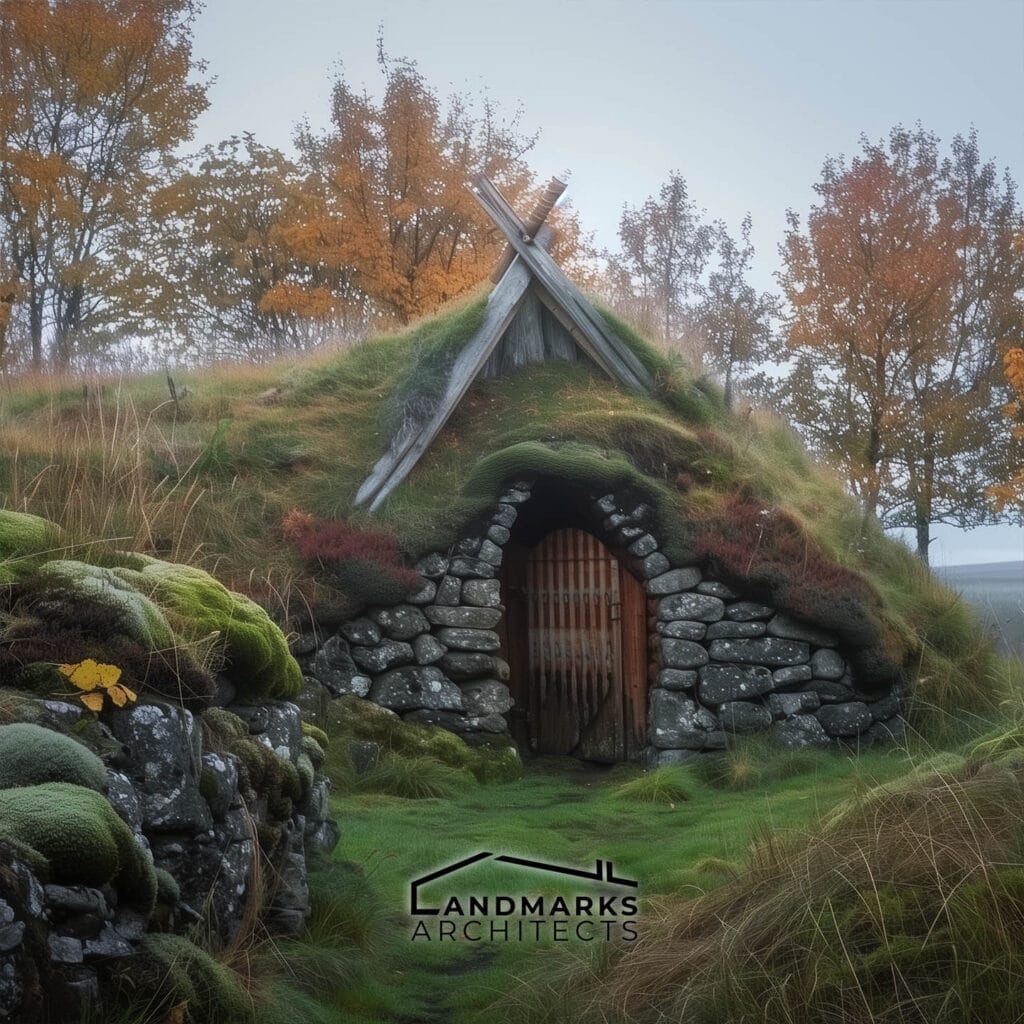


Viking architecture emphasized sustainability by using available resources. Pit houses are built partially underground, regulate temperature naturally, and minimize material use.
Turf roofs and walls provided thermal efficiency and blended with the landscape.
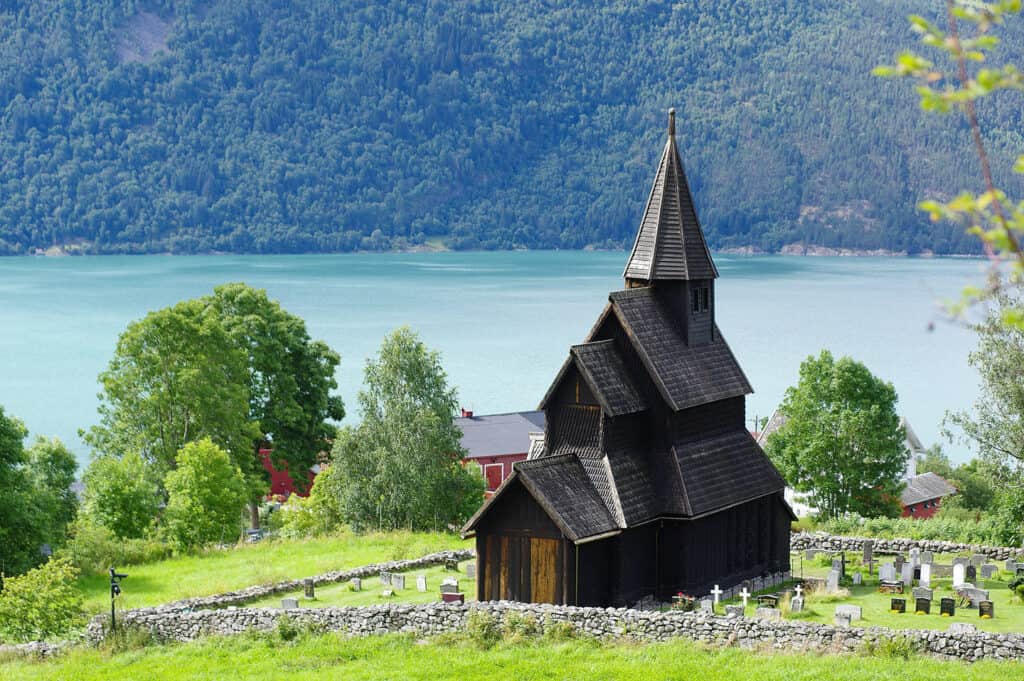

While the Urnes stave church, built in the 12th century, is an example of medieval Norwegian architecture, it reflects the continuation of traditional construction techniques. Its intricate designs incorporate Norse mythology, showcasing a deep respect for nature.
3. Iconic Viking Structures
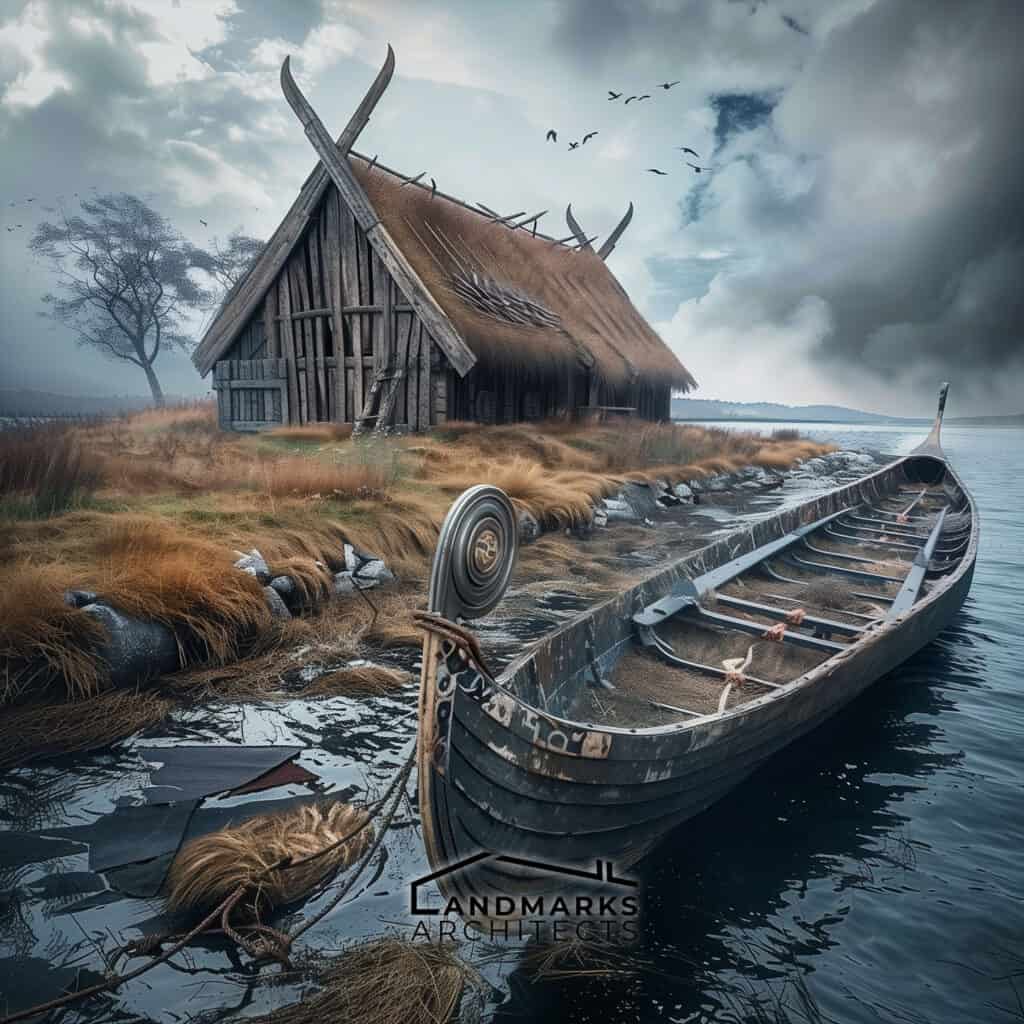
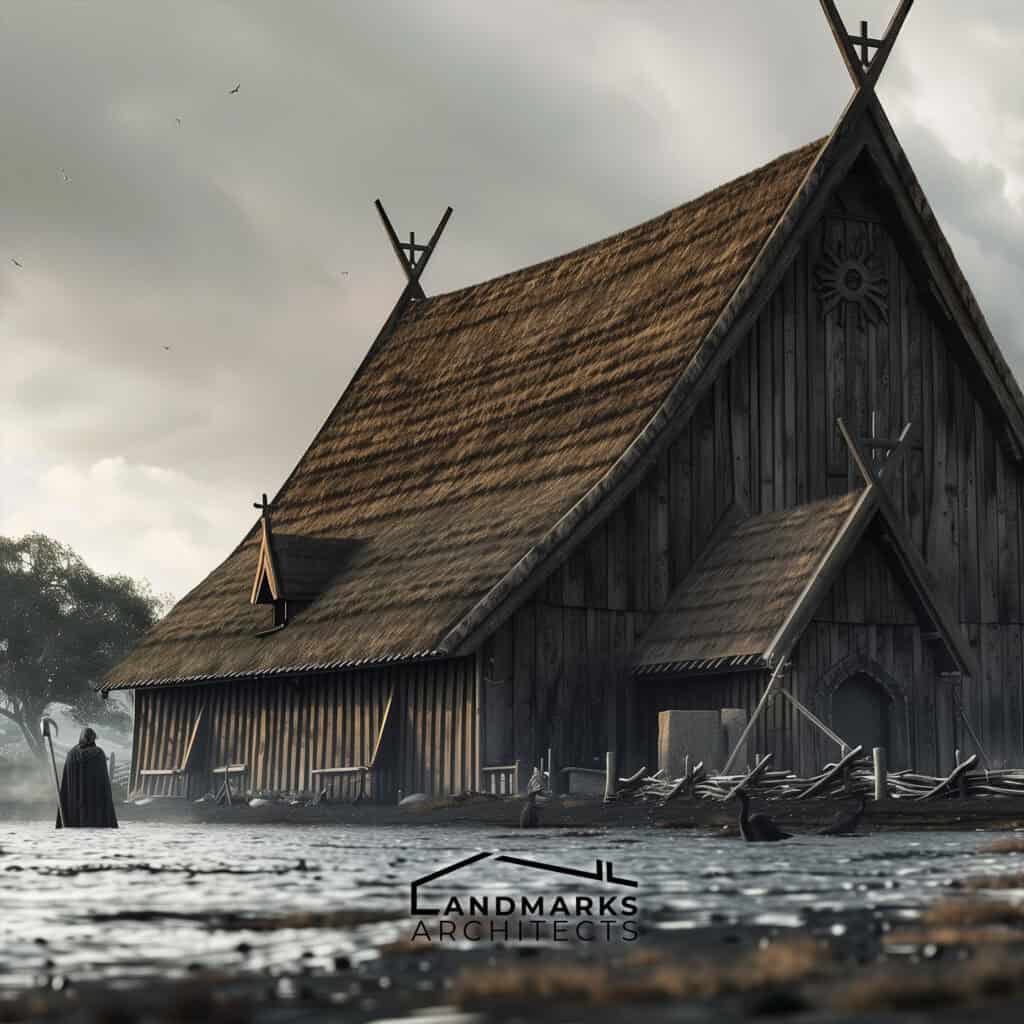


Viking architecture is characterized by its functionality and connection to nature. Key structures such as longhouses, boathouses, fortifications, and stave churches reflect the ingenuity of Viking society and their adaptation to the environment.
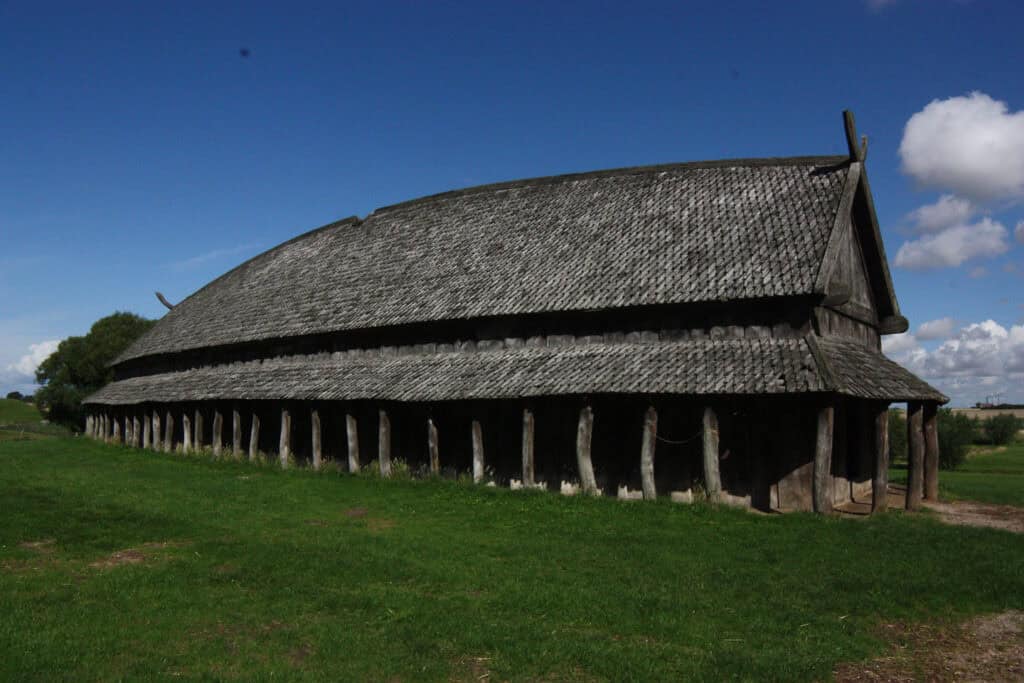
Longhouses


Viking longhouses were the primary dwellings of Viking families, reflecting their communal lifestyle. Constructed using timber frames, these buildings typically had a central hearth for warmth and cooking.
The longhouses featured steeply pitched roofs, often covered with turf, which provided insulation.
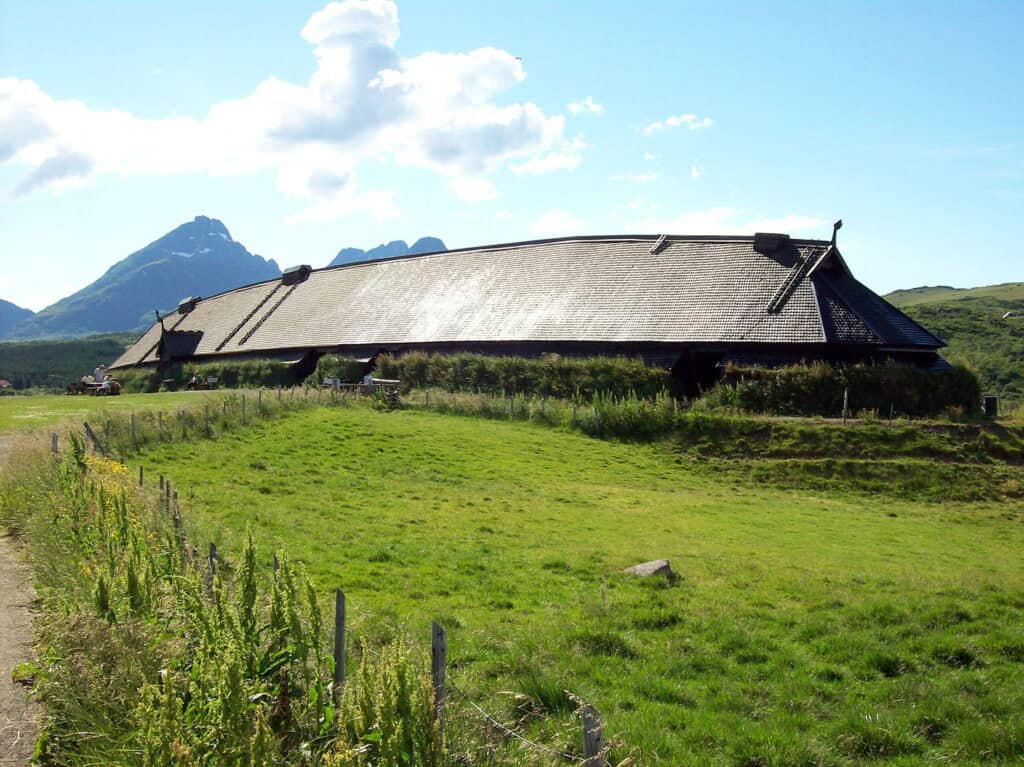

A famous example is the reconstruction at the Lofotr Viking Museum in Norway, showcasing how these elongated structures accommodated extended families and domestic animals.
Inside, the layout included a main room for the whole family, with separate areas for livestock.
Boathouses
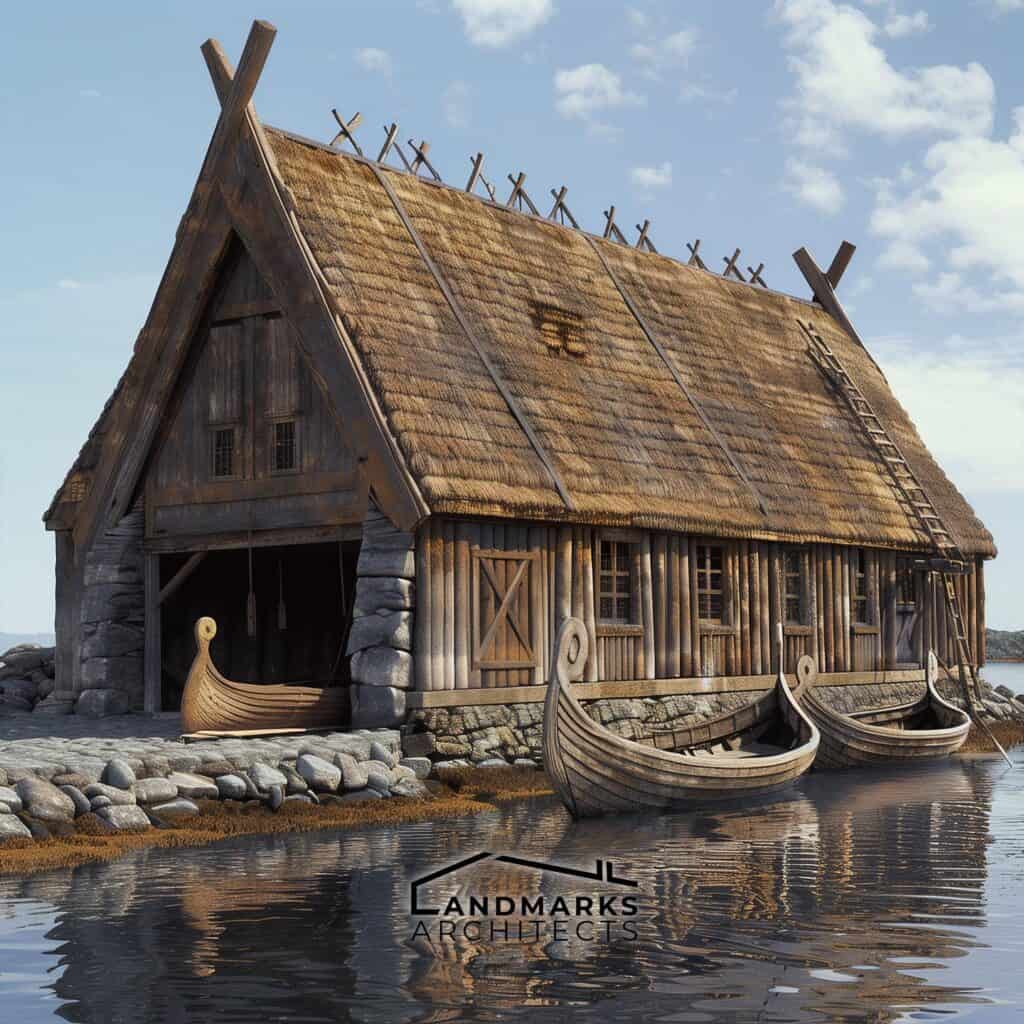

Boathouses, known as nausts, were crucial for protecting Viking ships during harsh weather. Typically built a few meters from the waterline, these wooden structures featured stone foundations, ensuring stability.
Vertical beams supported the roofs, creating a space to store longships, which were essential for trade and exploration.
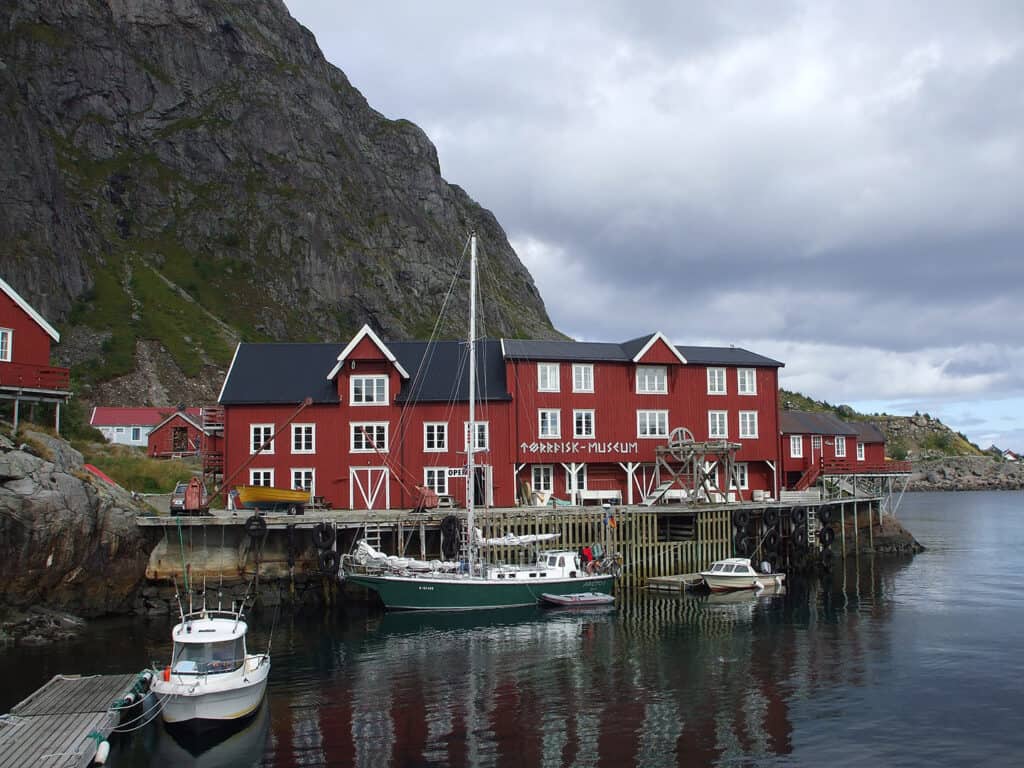

A noteworthy example is the naust found on the Lofoten Islands, illustrating how Vikings balanced functionality with durability. The design allowed easy access to launch ships while safeguarding them from winter elements.
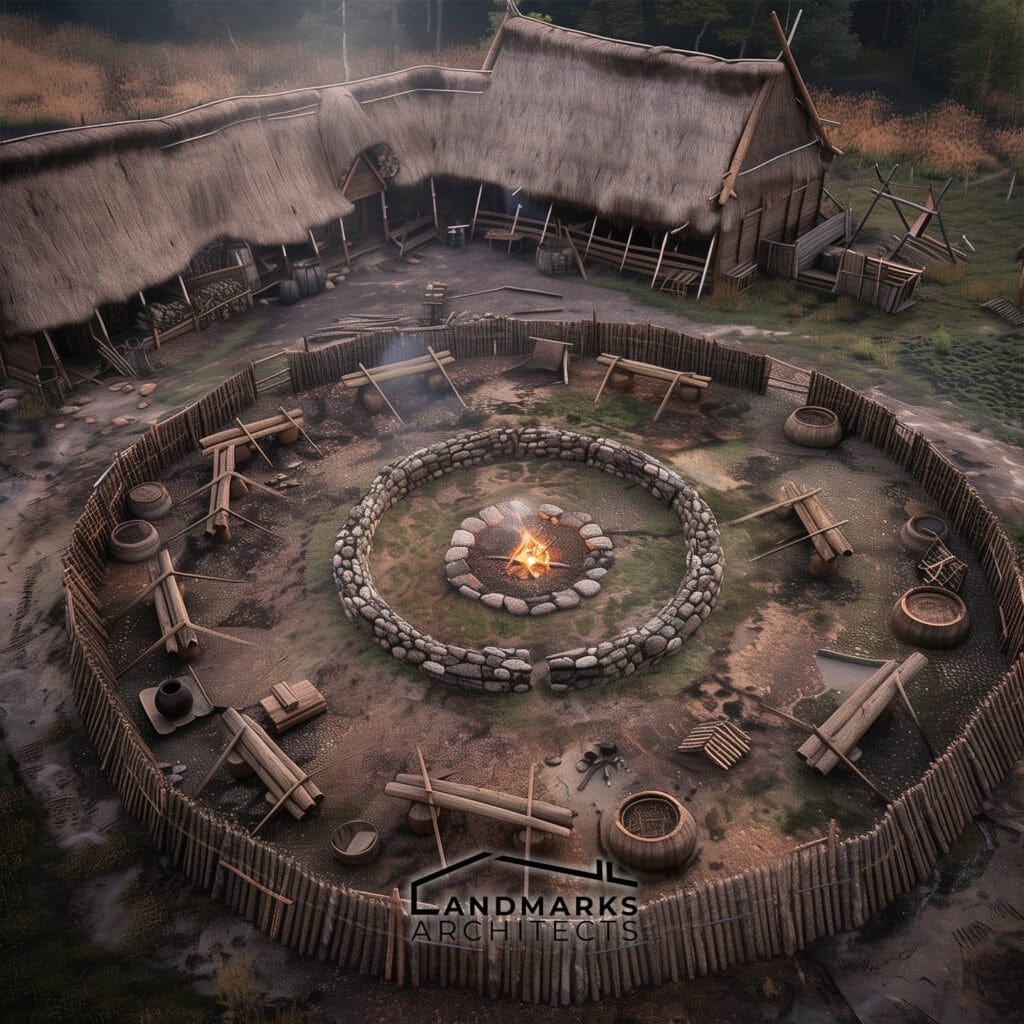
Fortifications and Ring Forts


Viking fortifications, such as ring forts (or ringborgs), were crucial for defense and served as centers for both military and communal activities. These structures typically featured circular earthworks reinforced with wooden walls, creating a strong defensive perimeter.
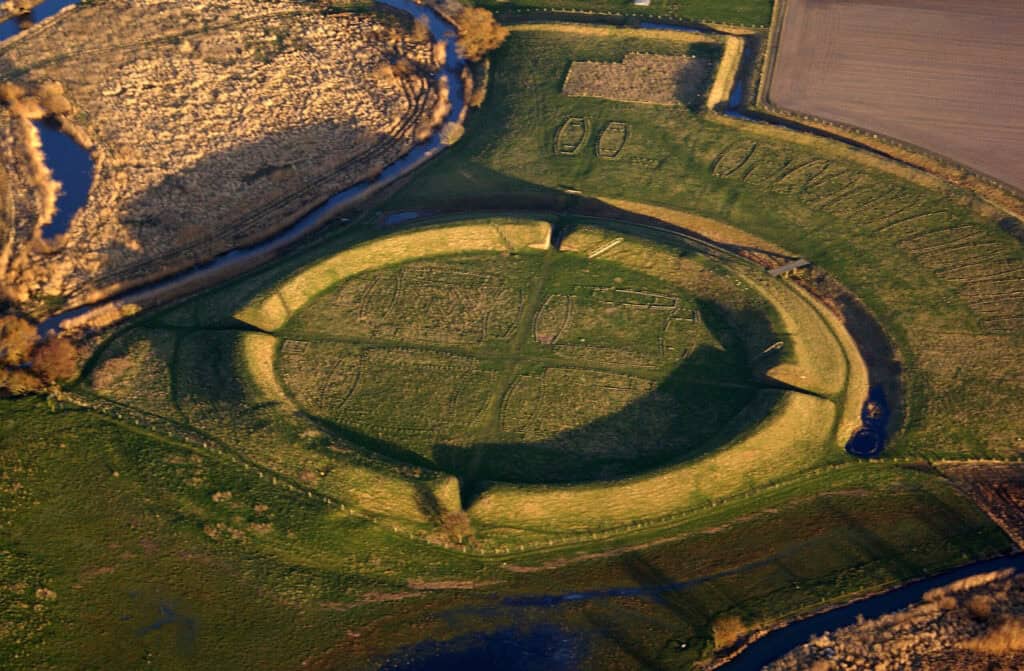


Trelleborg in Denmark is a prime example of a Viking ring fort, known for its well-preserved, symmetrical layout. It features a central area surrounded by a defensive ring and radially arranged interior buildings.
Built from local timber and clay, these forts were essential for defense and communal living, helping to protect Viking communities and preserve Norse culture.
Stave Churches
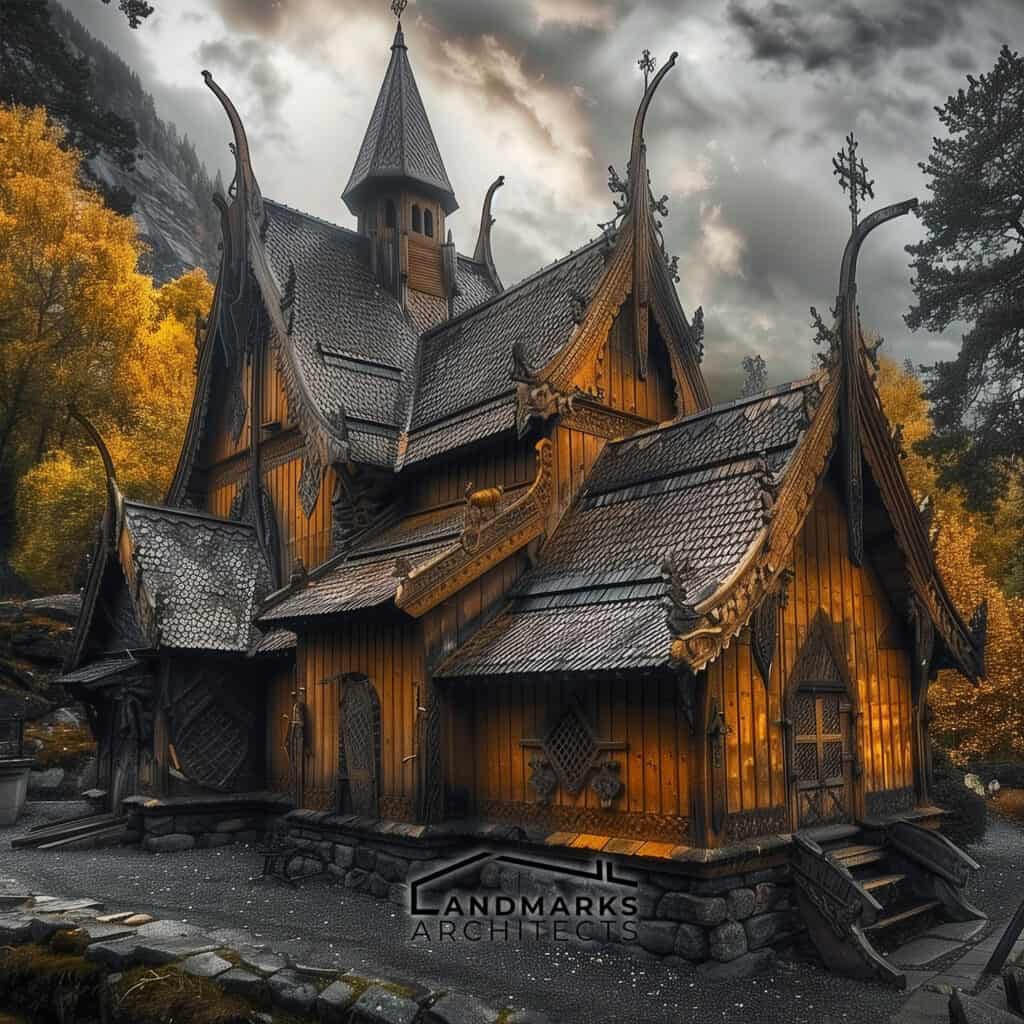



Stave churches represent a unique architectural style developed in the Viking Age, blending pagan and Christian influences. Constructed predominantly of wood, these churches featured intricate carvings that reflected Norse mythology.
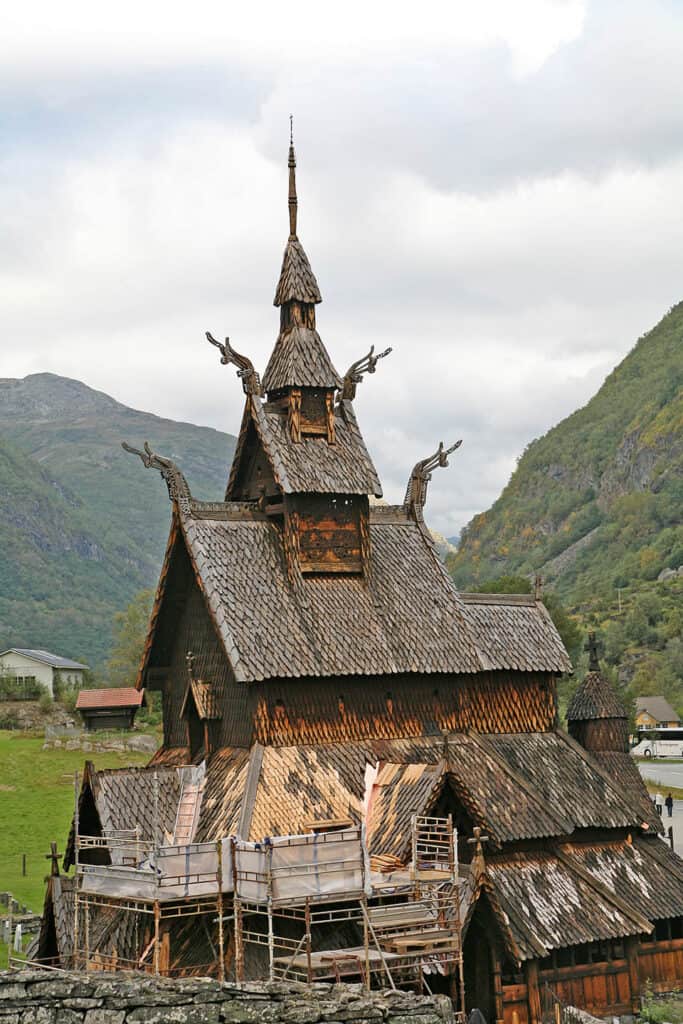
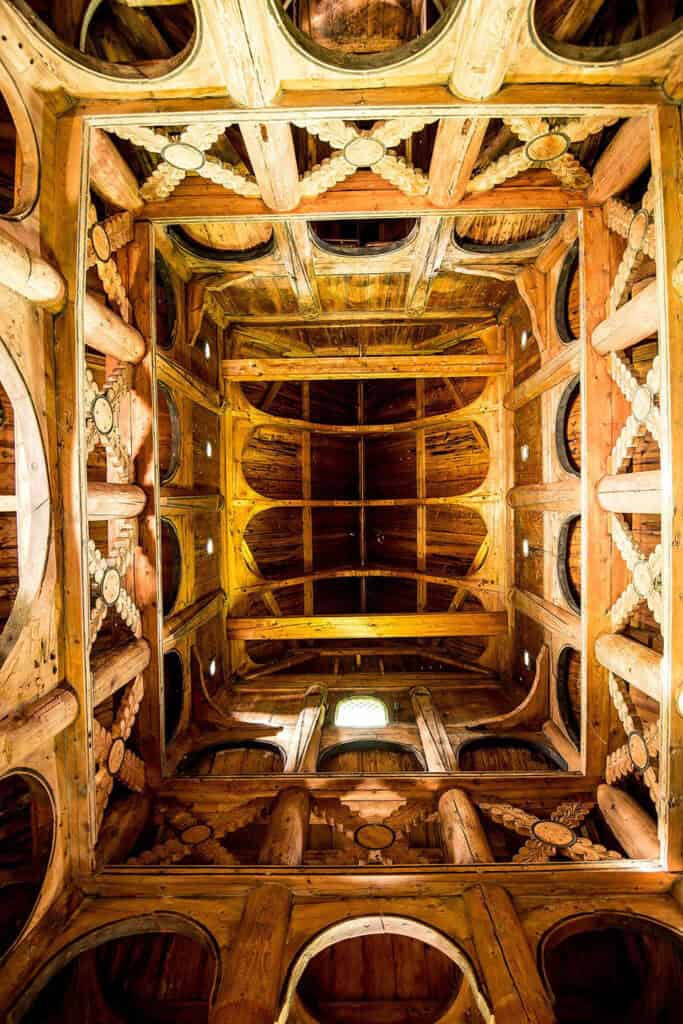


The Borgund stave church in Norway is an iconic example, with its steeply pitched roof and elaborate dragon motifs. Stave churches typically had a stone foundation and used vertical posts for support, allowing them to endure the harsh Scandinavian climate.
They served as important religious buildings, illustrating the transition from paganism to Christianity in Viking society.
See Also Traditional German Architecture
4. Artistic and Functional Elements
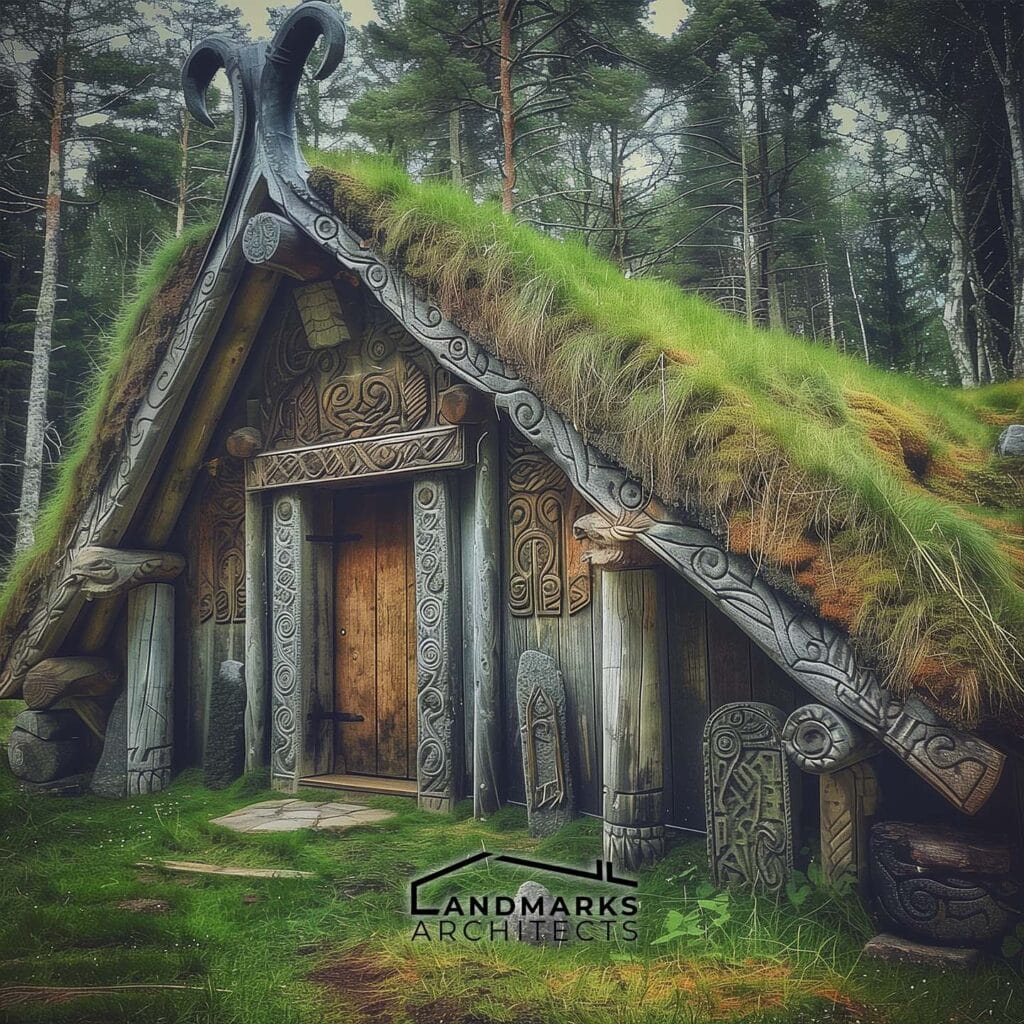

The artistic and functional elements of ancient Viking architecture showcase their unique cultural identity and practical needs. From intricate carvings on wooden structures to the innovative use of turf for roofing, these features served both aesthetic and utilitarian purposes.
Additionally, runestones and decorative elements reveal insights into their beliefs and societal values.
Intricate Carvings
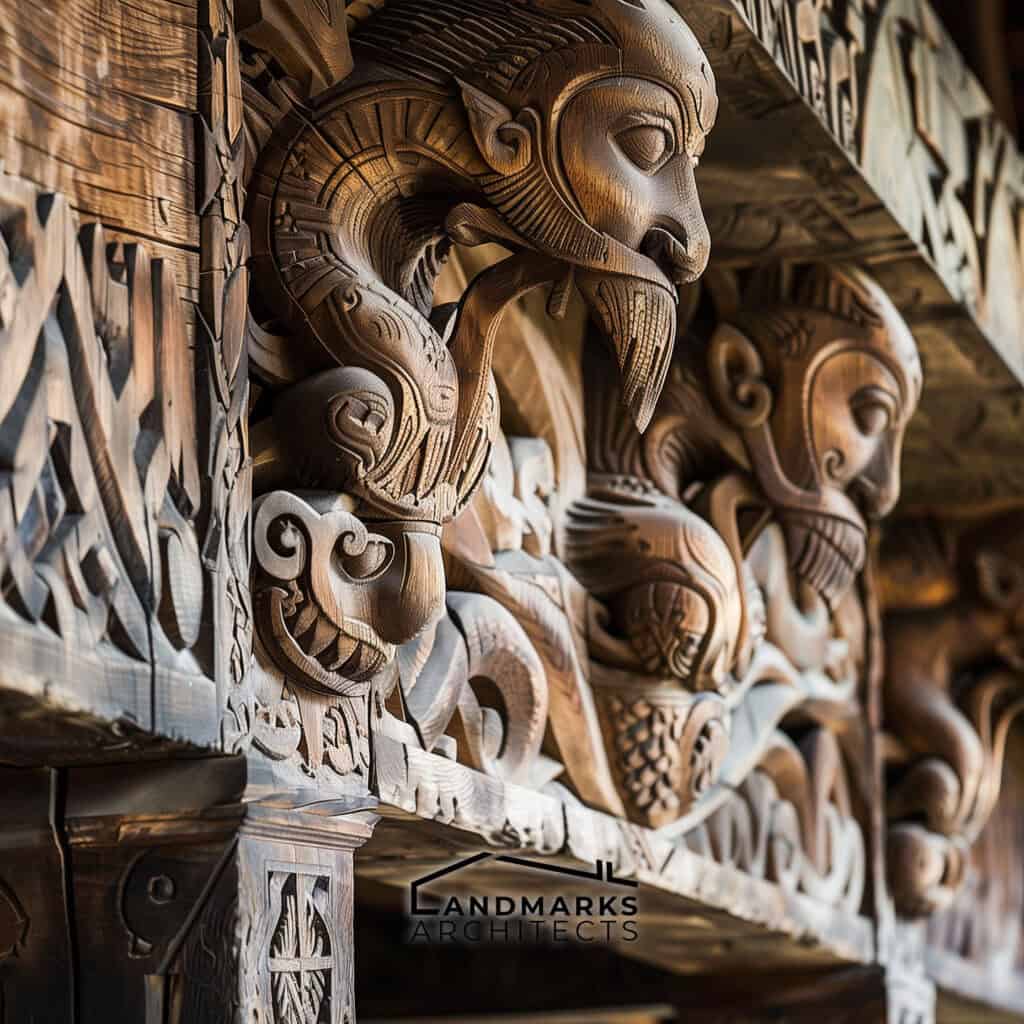
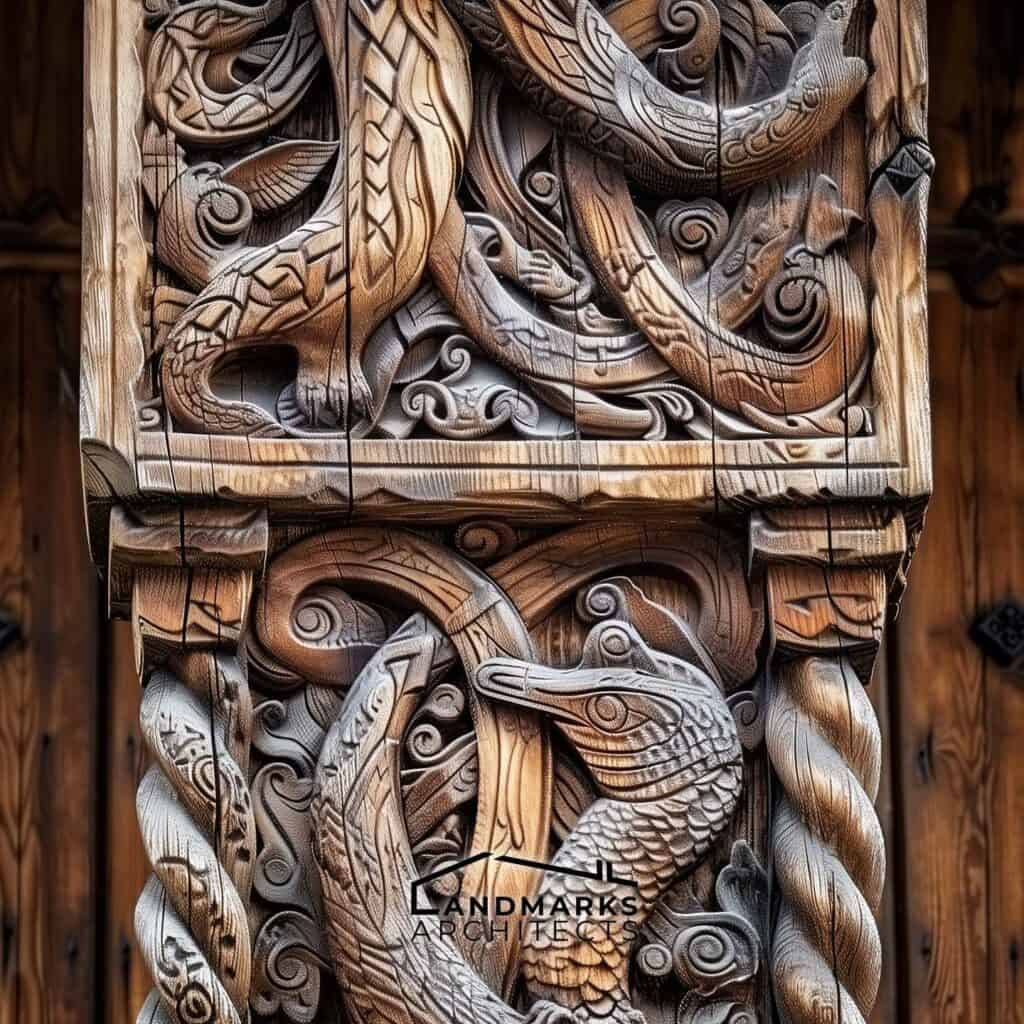


Intricate wood carvings were a hallmark of Viking architecture, adorning wooden structures and longhouses with scenes from Norse mythology and abstract patterns. These carvings demonstrated the Vikings’ advanced craftsmanship.
Turf Roofing
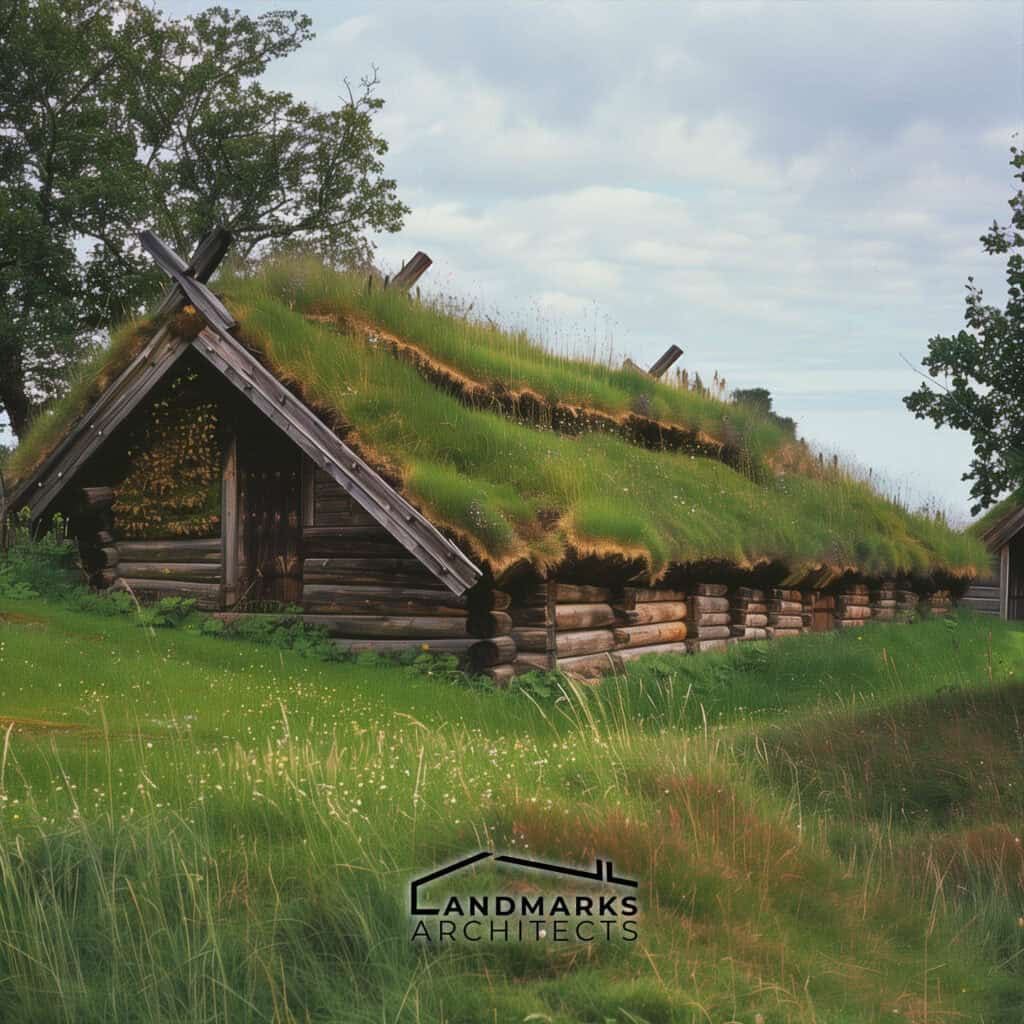


Turf roofing was a practical solution for Viking buildings, particularly in timber-scarce northern Europe. This European-Style Architecture technique involved layering grass and soil on top of a wooden frame, providing excellent insulation and protection against harsh weather conditions.
Runestones and Decor
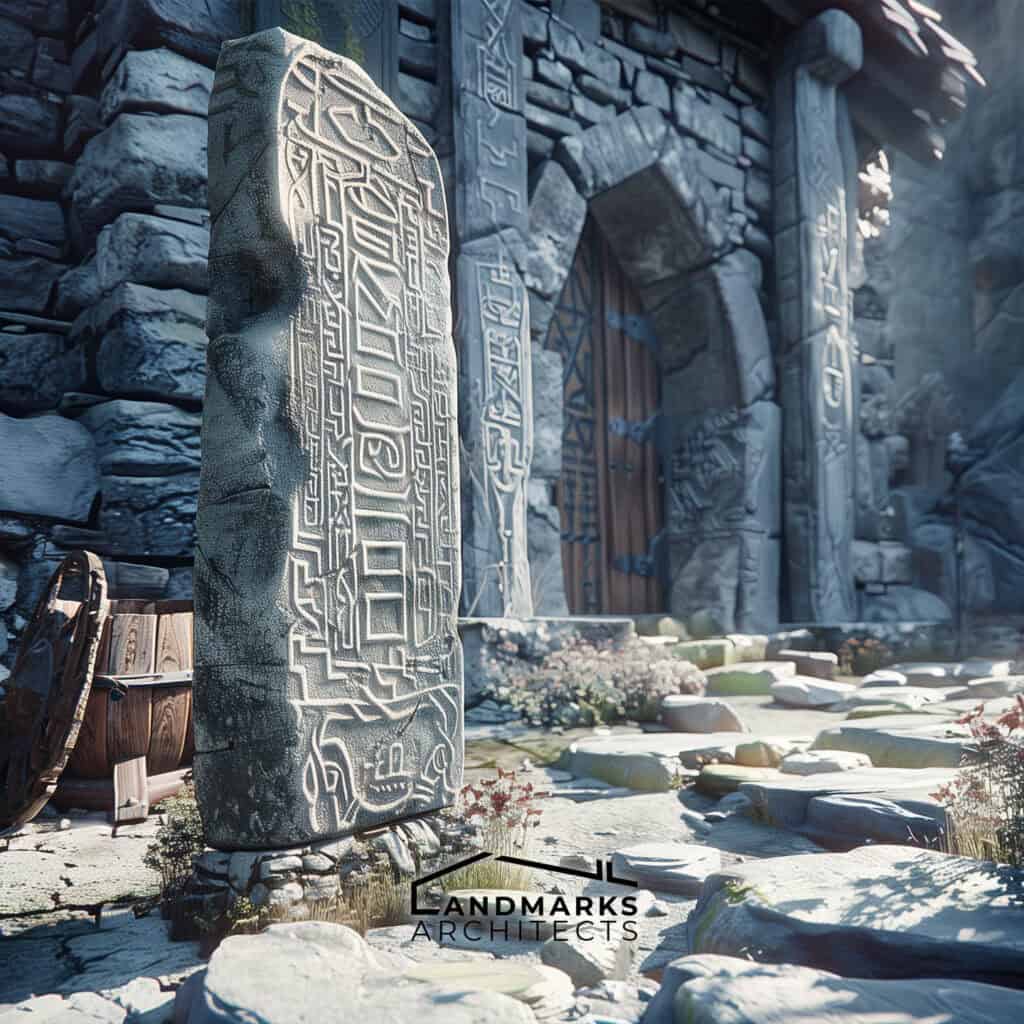
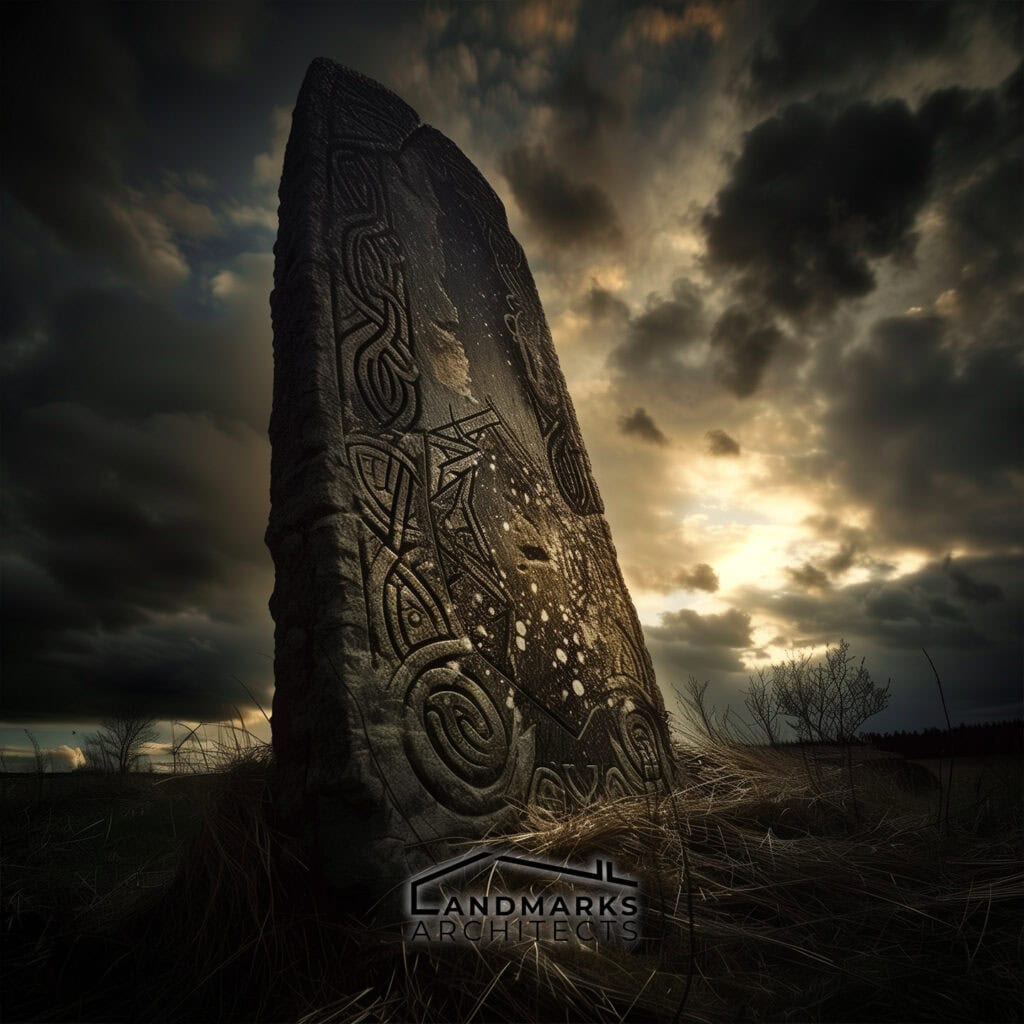


Runestones played a significant role in Viking culture, serving as monumental markers and decorative elements. Inscribed with runes, these stones commemorated notable achievements, and significant events, and were often erected to honor deceased individuals.
They highlight the Vikings’ emphasis on storytelling, remembrance, and social status.
See Also Famous Buildings in Sweden
Ancient Viking Architecture: A Recap
Ancient Viking architecture is a testament to the Vikings’ ingenuity, blending practicality with artistic expression. Through the construction of longhouses, stave churches and fortified structures, they utilized local materials and sustainable practices.
Intricate carvings and turf roofing illustrate their cultural values and environmental adaptability. This Architectural Building Types offers profound insights into Viking society, reflecting their communal lifestyle and reverence for nature.