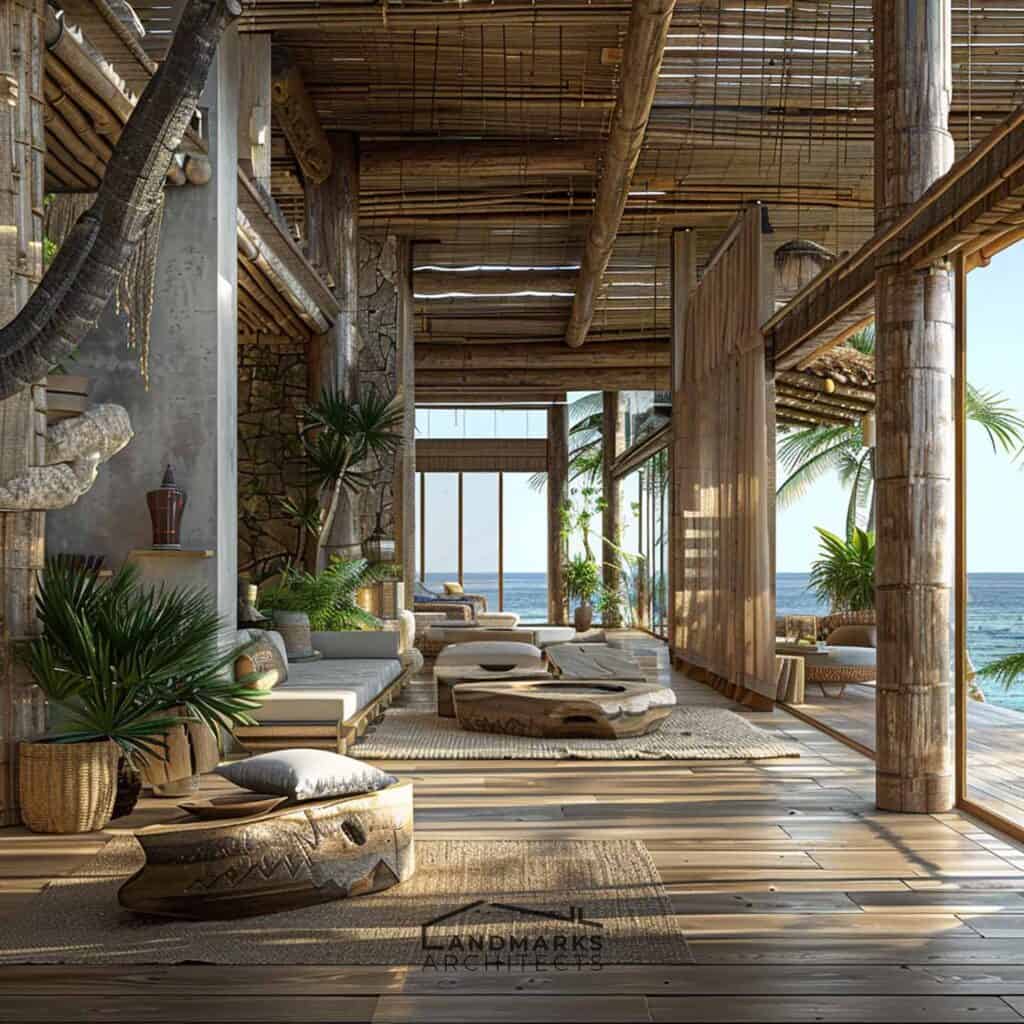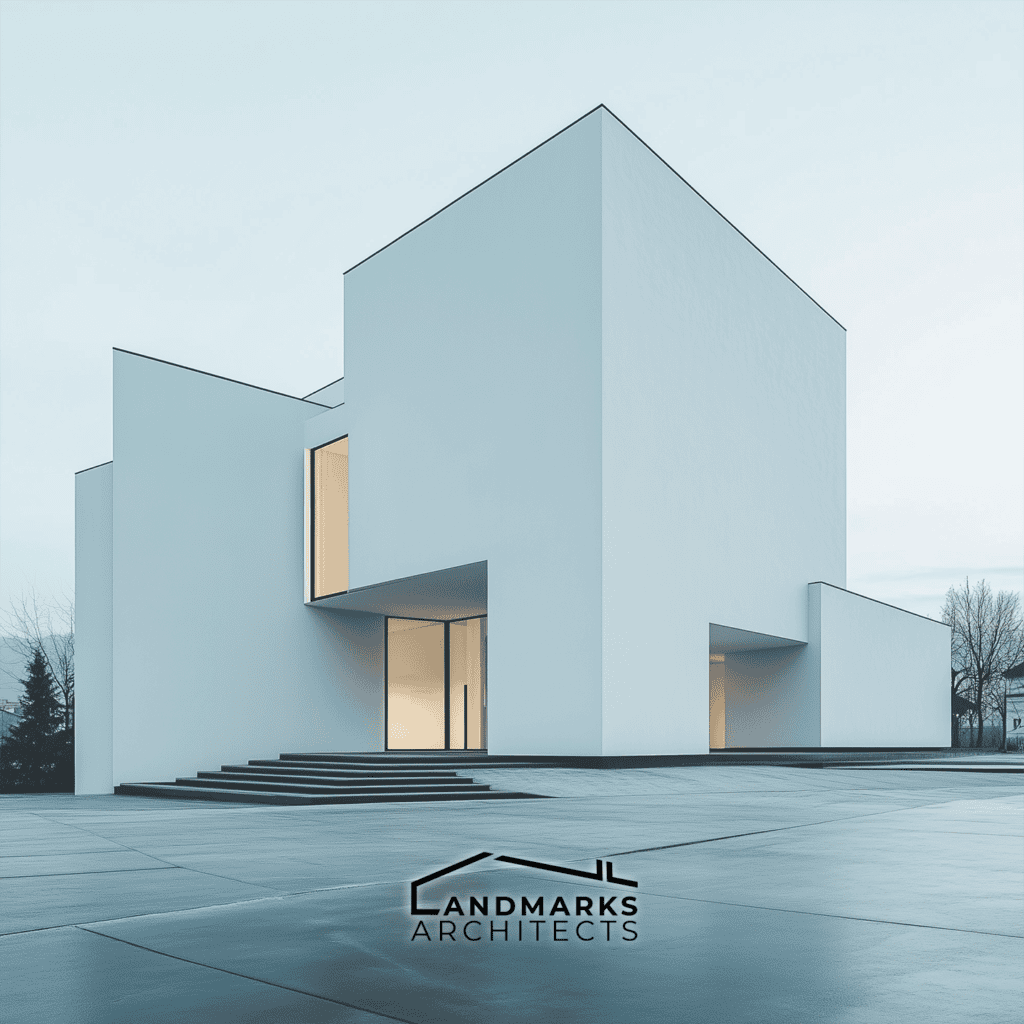
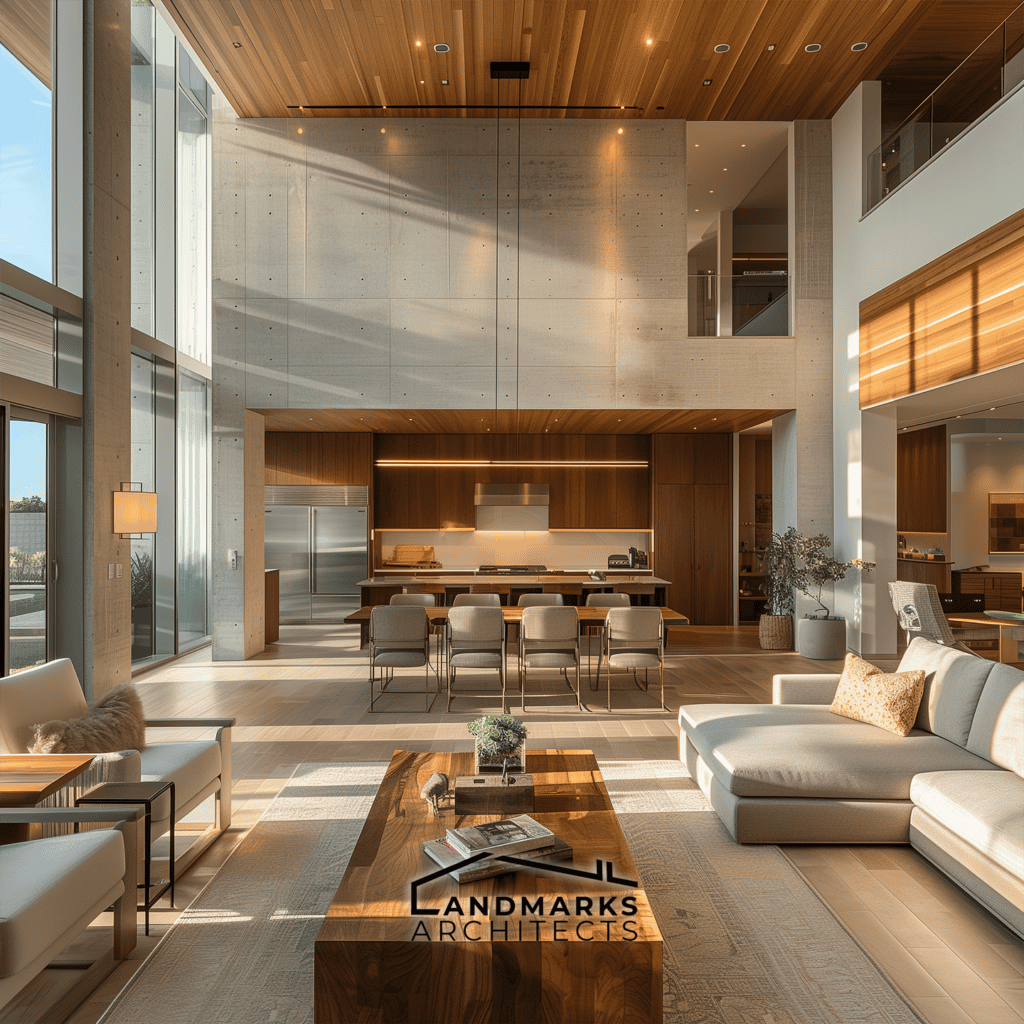
Are you searching for an innovative architectural style that balances form and function? Cubic architecture has clean lines, cubic structures, and geometric forms. It still influences modern design. Discover how to incorporate elements that define this distinctive style.
At Landmarks Architects, we love cubic design. It redefines modern living. We’re here to help you explore the potential of cubic design and its transformative impact on your space.
In this article, we will cover:
- The key features of cubic architecture and why they matter
- Notable examples that showcase the beauty of this style
- The historical context that shaped this architectural movement
Ready to redefine your understanding of modern architecture?
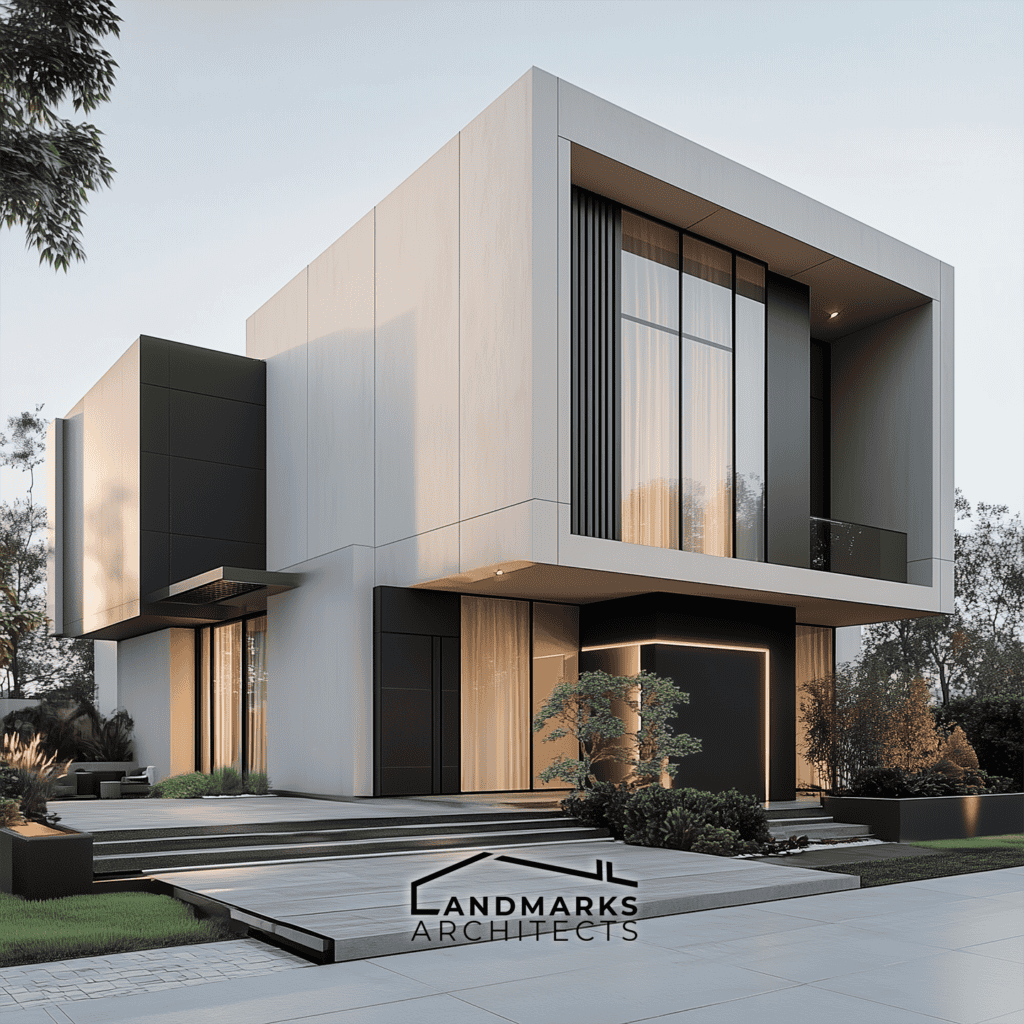

Key Features of Cubic Architecture
1. Geometric Simplicity
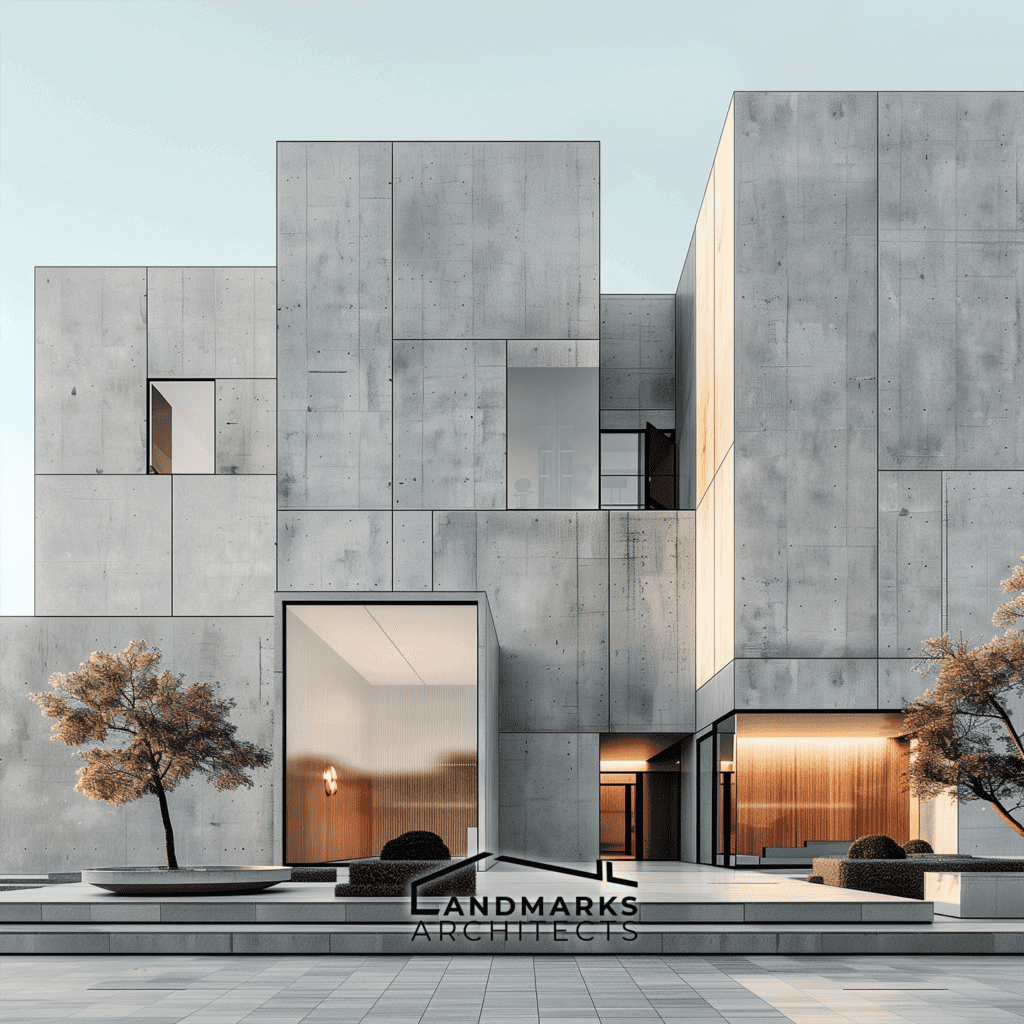
Cubic architecture relies heavily on geometric simplicity. This is showcased through the use of sharp lines, angles, and cubic forms. Buildings often have a simple structure. It minimizes complex shapes and helps us understand their form better.
2. Minimalism
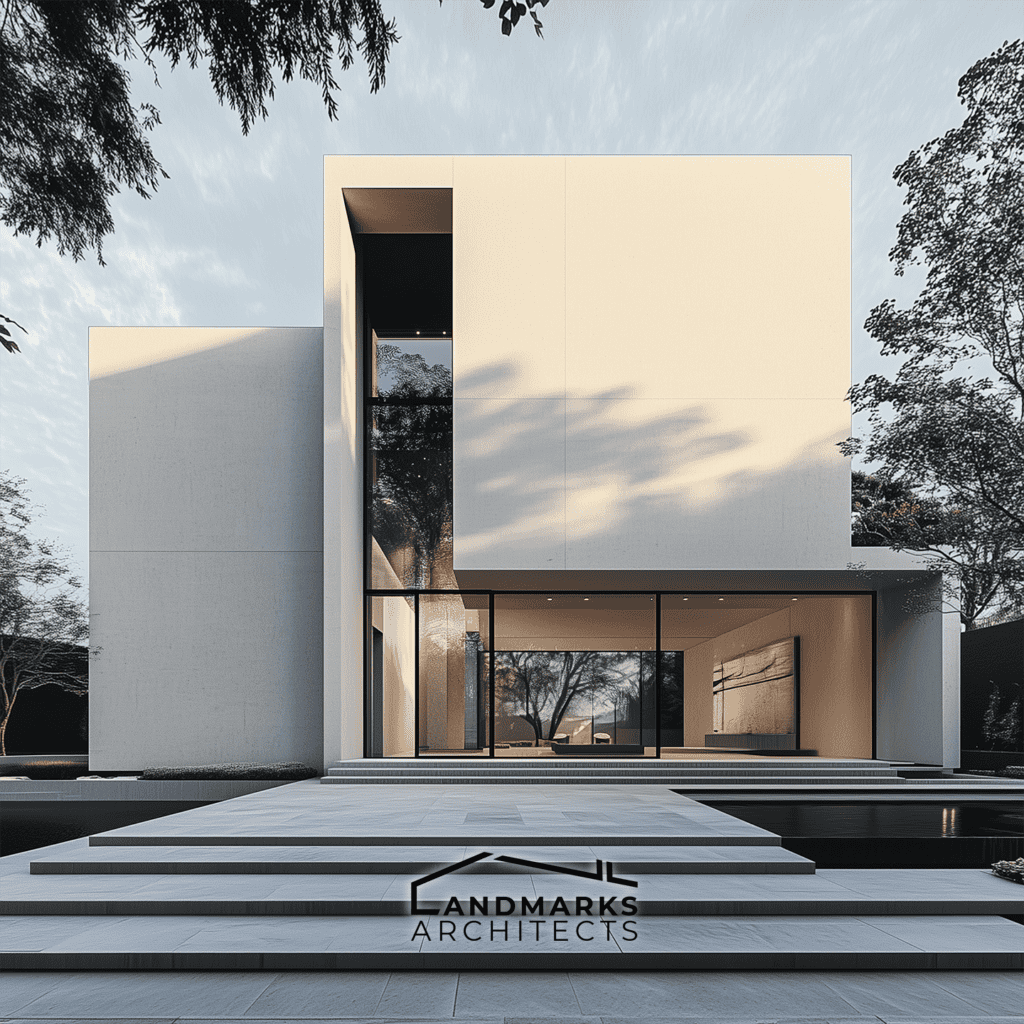
A hallmark of cubic style architecture is minimalism. Clean, unadorned facades are common. They let the form take center stage. The lack of decoration creates calm and order. It highlights the purity of the geometric shapes.
3. Functional Design
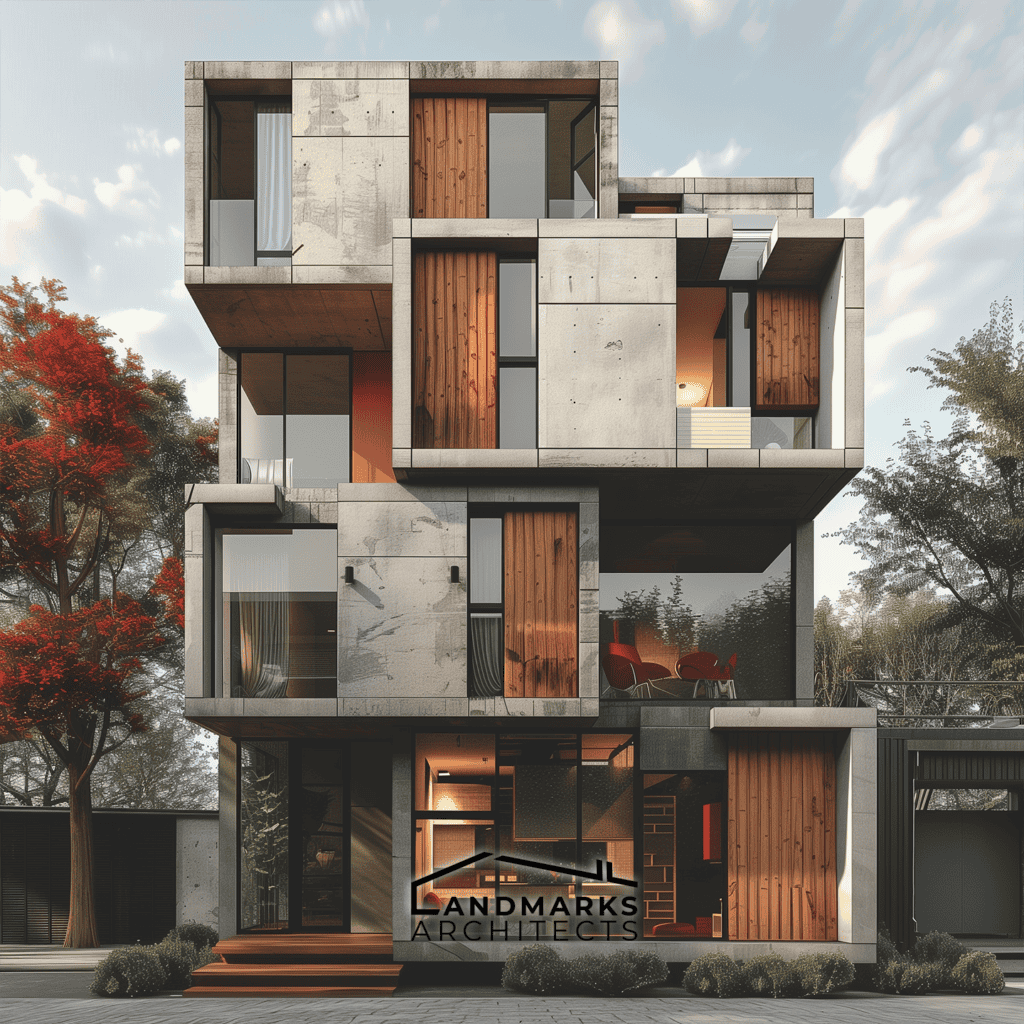

Cubic architecture prioritizes functional design. Every aspect of the structure is carefully considered. It aims to enhance utility and maximize space efficiency. Compact designs use functional spaces that can adapt to various needs.
This is especially beneficial in urban areas where space is limited.
4. Use of Modern Materials

The use of modern materials such as glass, wood, and steel is essential in cubic architecture. They help create the clean lines and sharp angles of this style. The mix of materials adds texture to the façade. It creates interest while keeping the design simple.
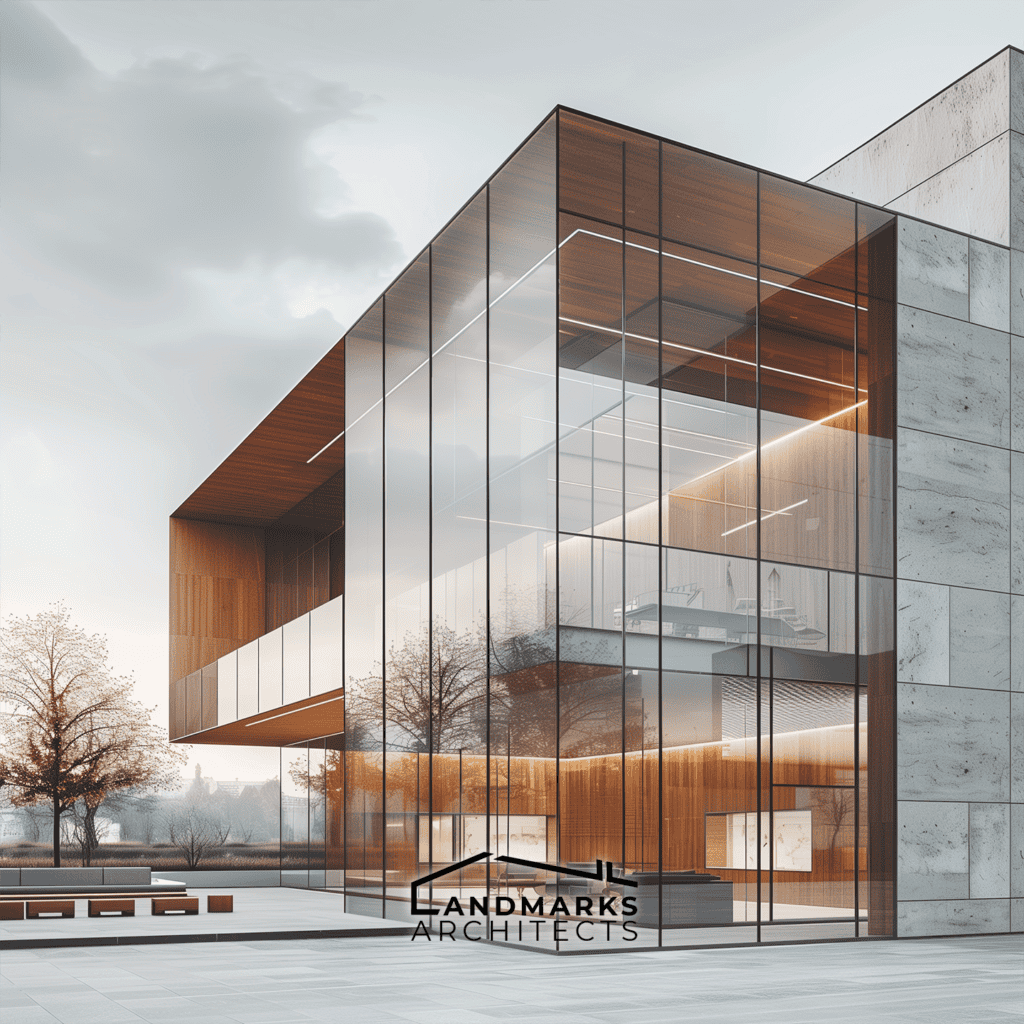
5. Flat Roofs and Boxy Structures
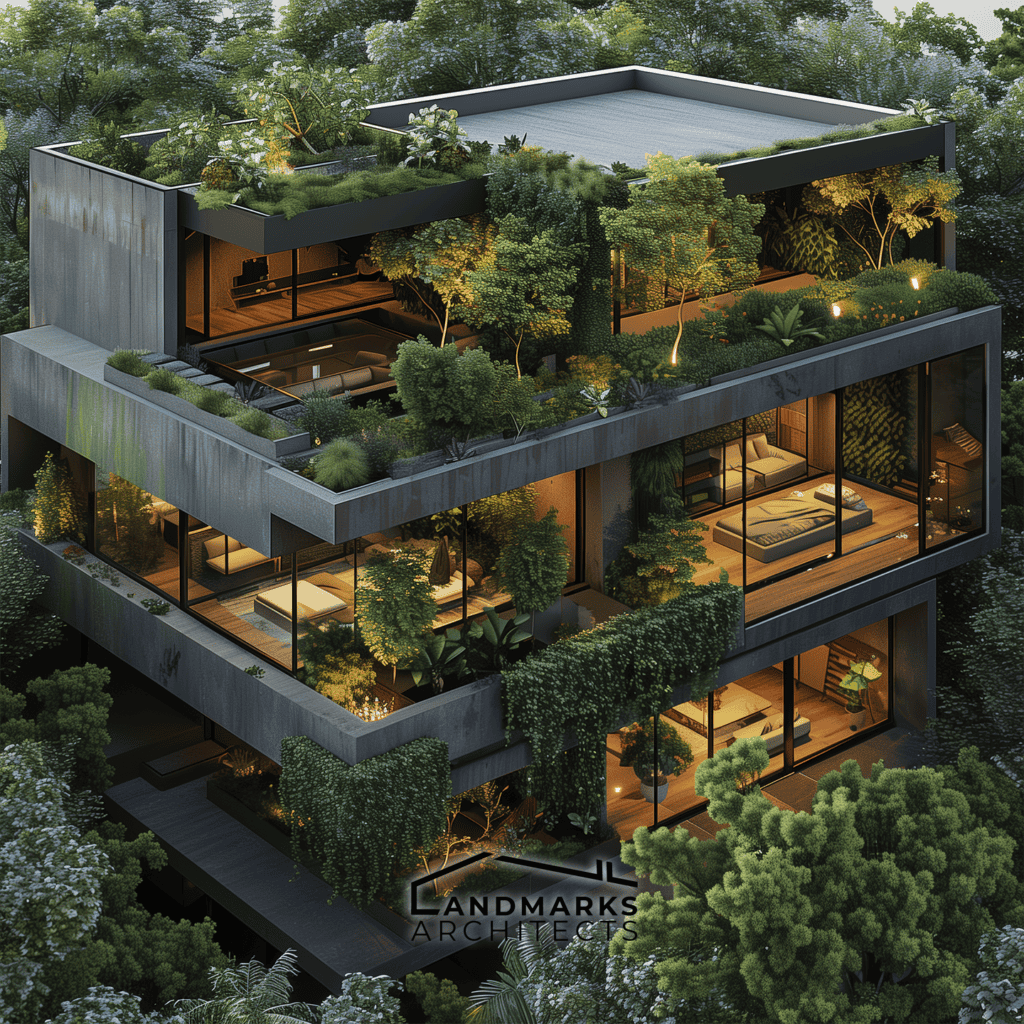
Flat roofs and boxy structures are common features of cubic architecture. Flat roofs enhance the cubic shape. They provide a modern look and add space for rooftop gardens or terraces. Also, boxy forms let large windows in. They flood the interiors with natural light.
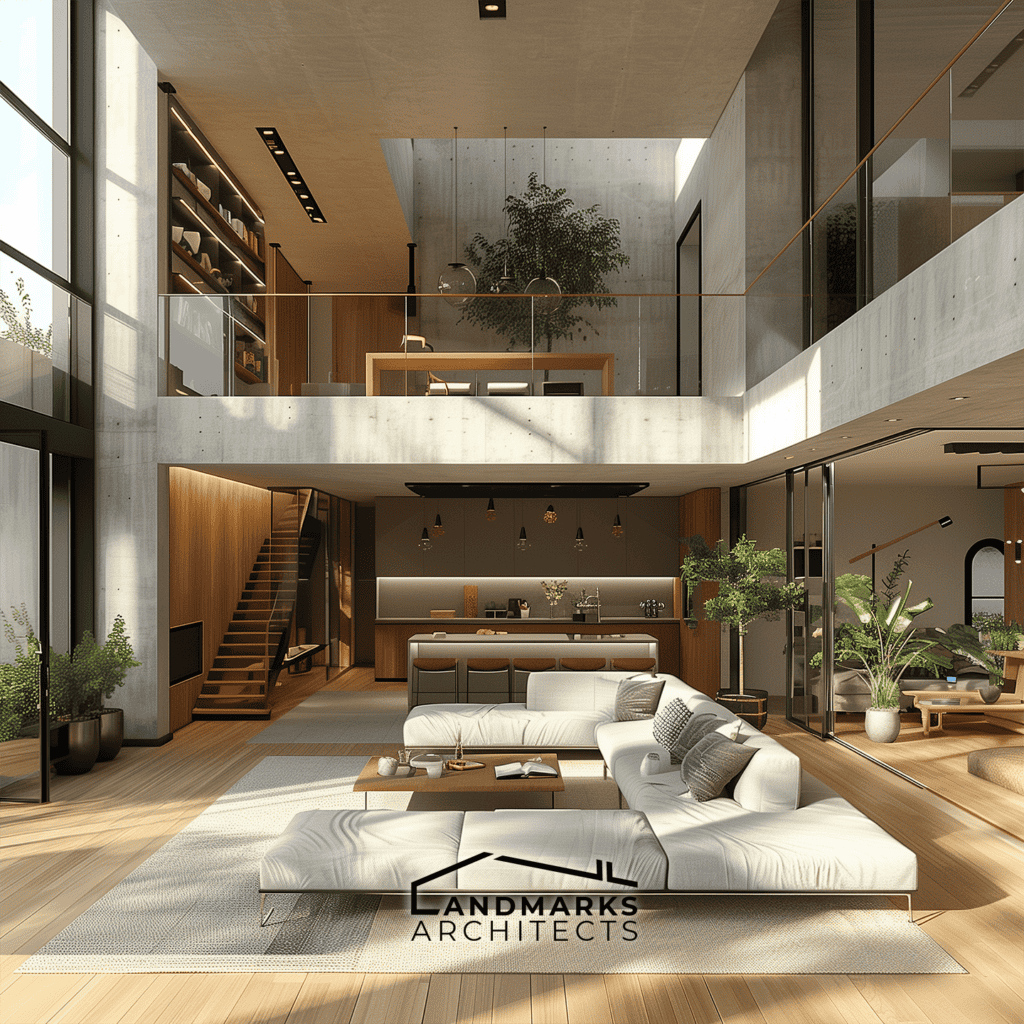
6. Open and Flexible Interiors

Cubic designs often stand out with open and flexible interiors. Architects use open floor plans to create adaptable spaces. They can serve different functions as needs change. The design uses natural light to create a sense of space. It makes small areas feel more open and inviting.
Notable Examples of Cubic Architecture
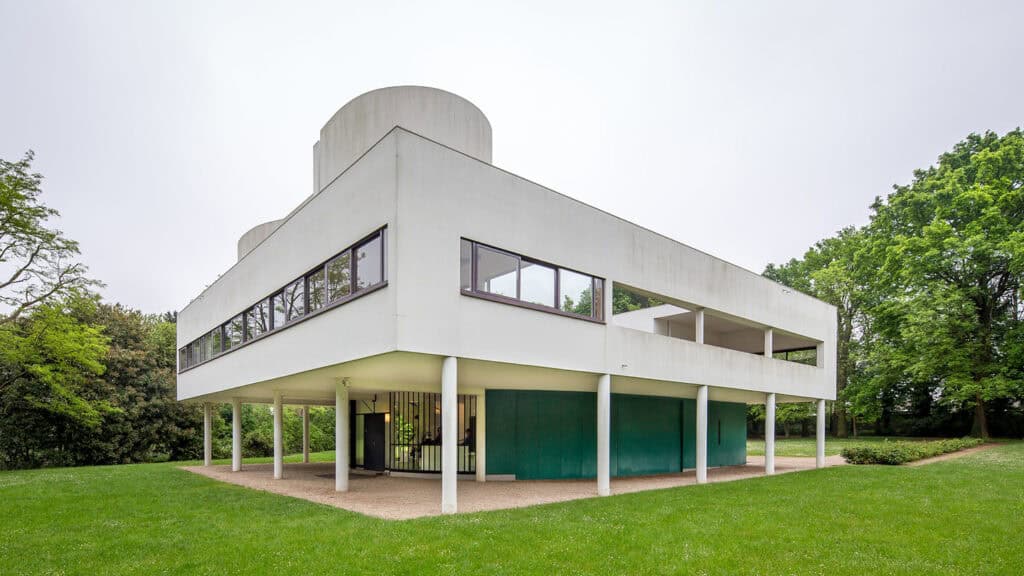
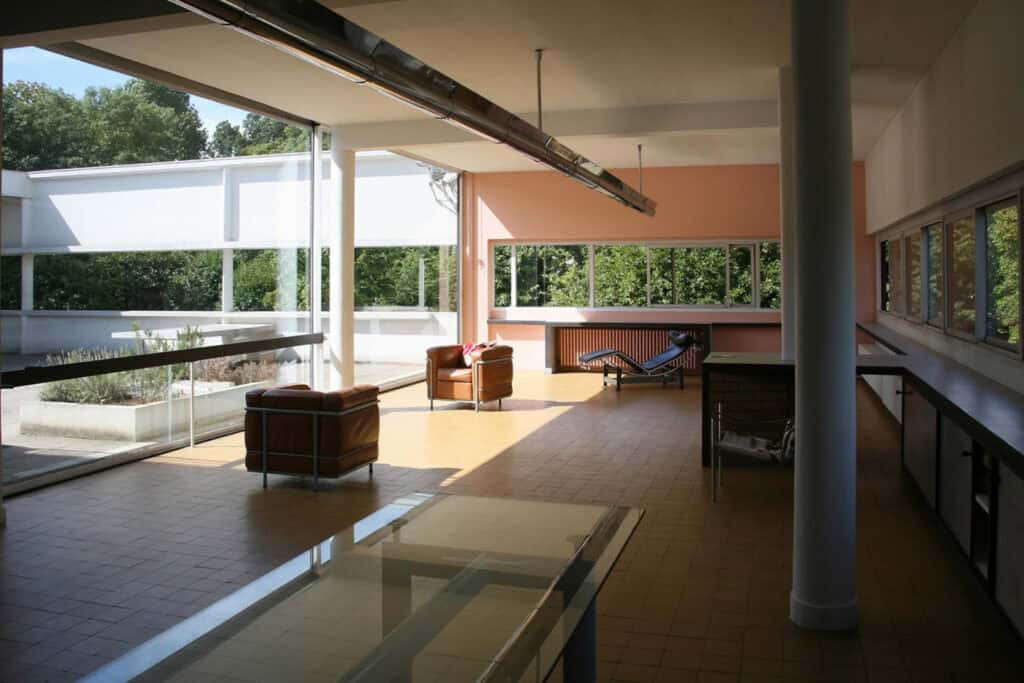
- Villa Savoye (France): Designed by Le Corbusier, this modernist masterpiece has clean lines and a focus on function. Its floating cube design continues to influence architectural practices.


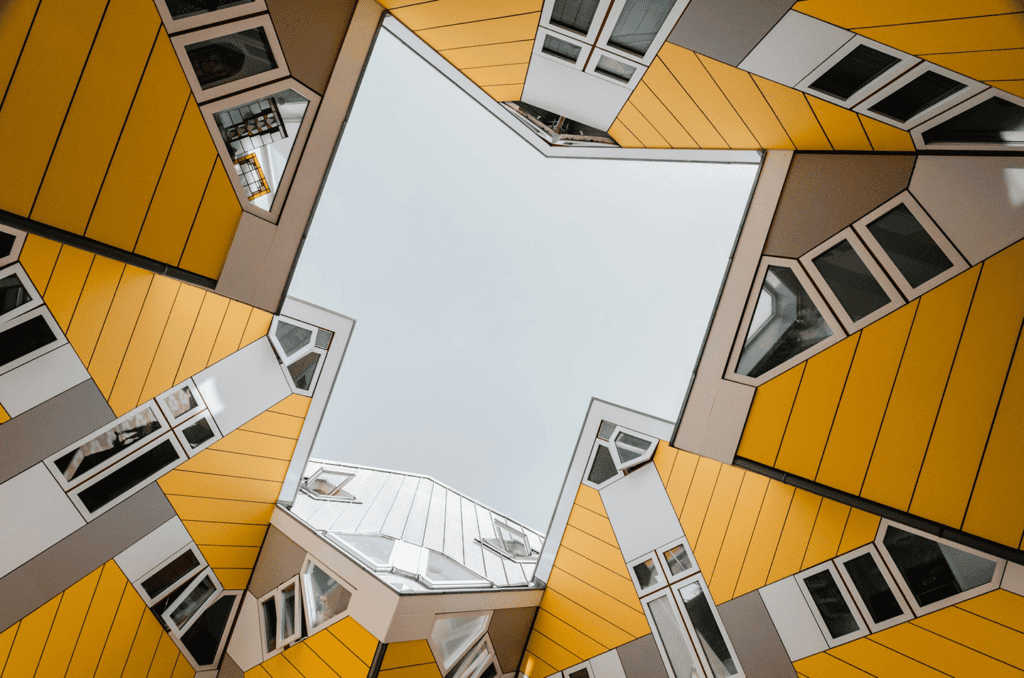
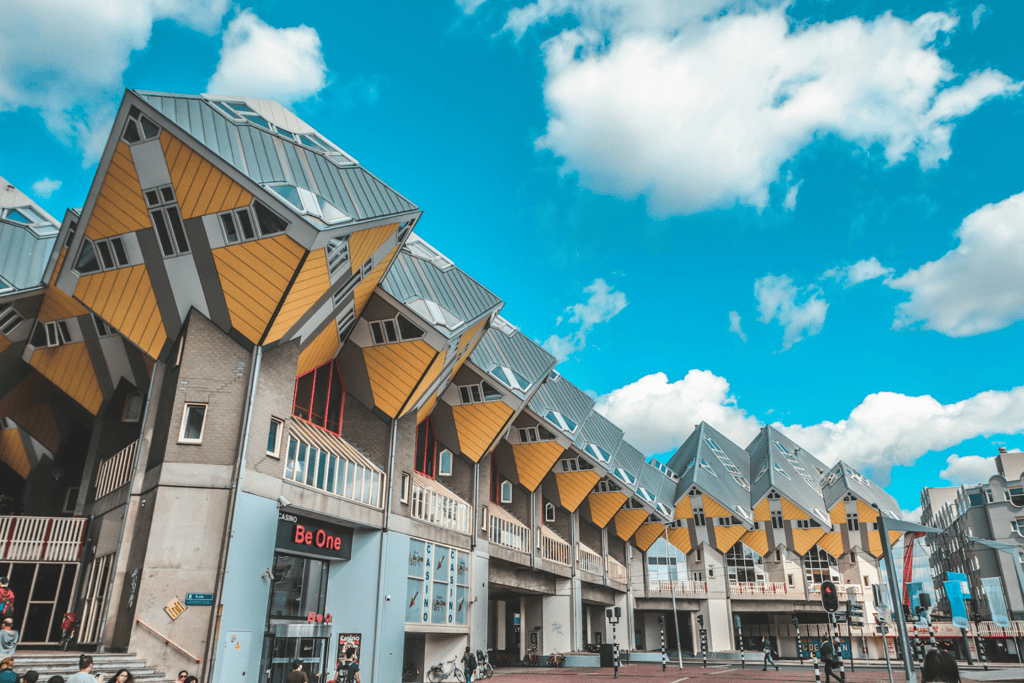
- Cube Houses (Kubuswoningen) by Piet Blom (Rotterdam, Netherlands): These striking structures are designed as stacked cubes, representing a unique approach to urban living. The tilted cube form maximizes interior space while providing an uncommon visual experience.


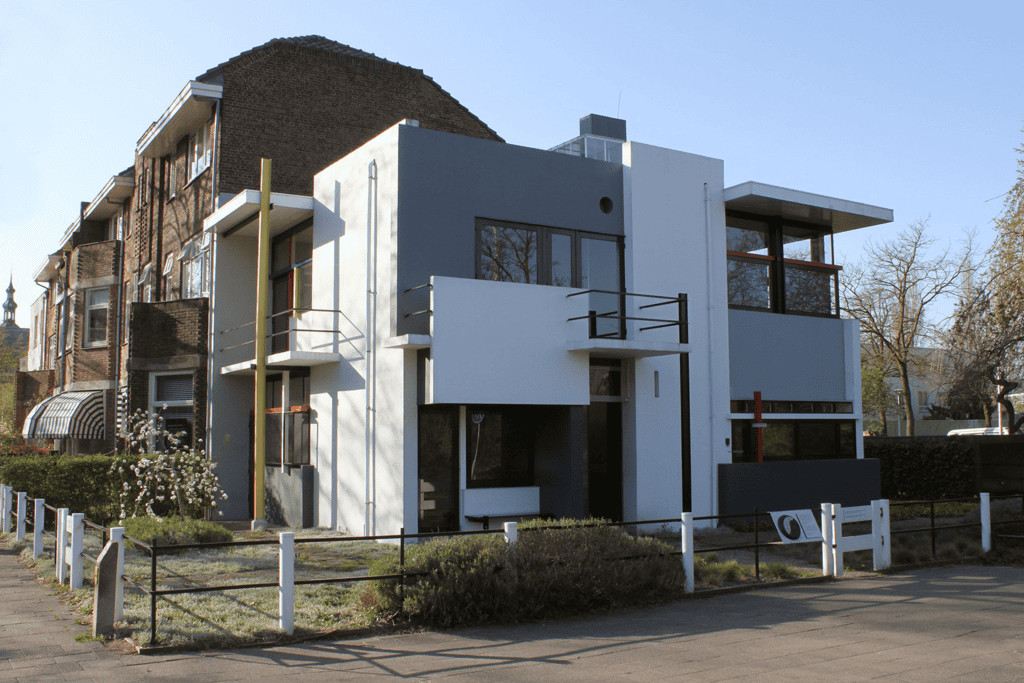
- The Rietveld Schröder House (Netherlands): This iconic building exemplifies the De Stijl movement. It features geometric shapes and an open layout. The use of bold colors enhances its cubic aesthetic.

Architectural Heritage

Cubic architecture is an architectural style. It traces its roots to modernism, which emerged in the early 20th century. This architectural movement favored simple, functional designs. It rejected the ornate styles of the past.
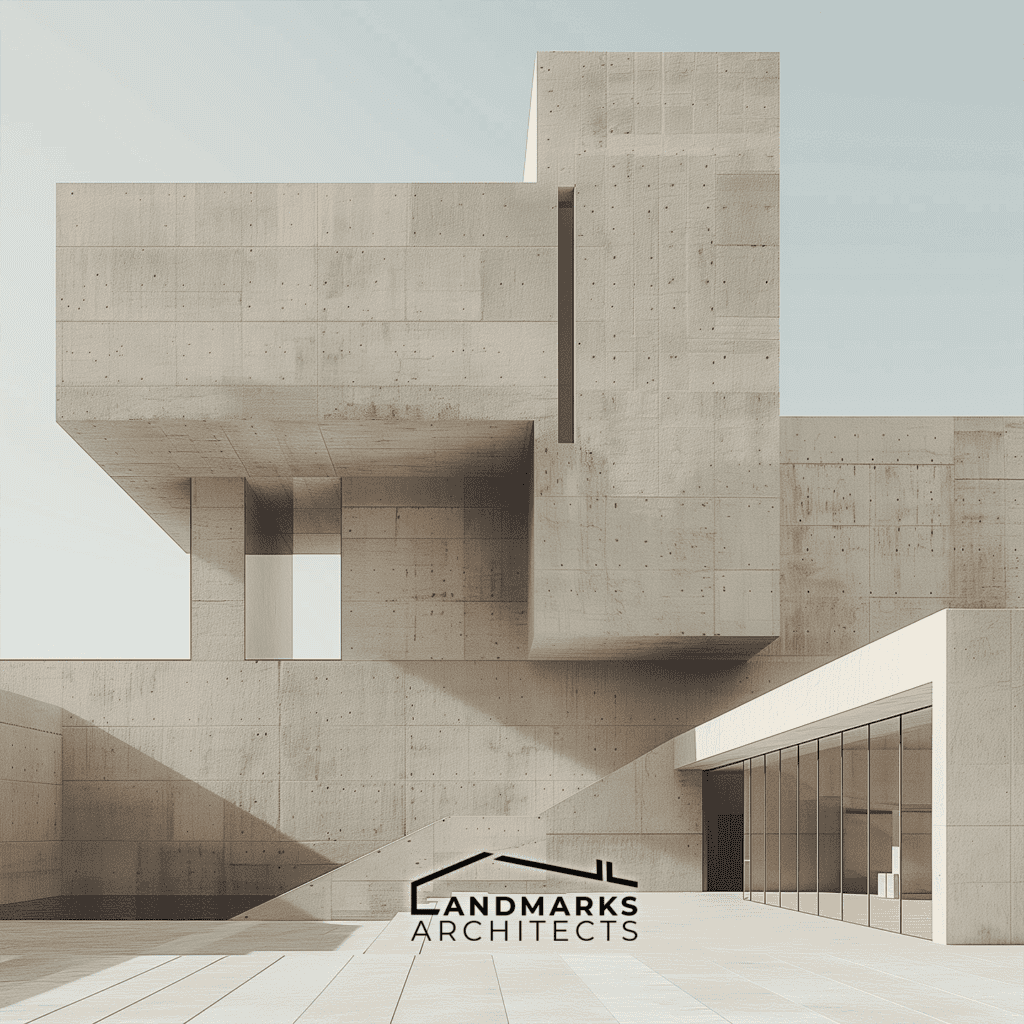
As cubic architecture evolved, it incorporated elements such as asymmetrical balance. This trait let structures be both dynamic and orderly.
See also: What is modernist style in architecture? 10 key features
Cubic Architecture Style: A Recap
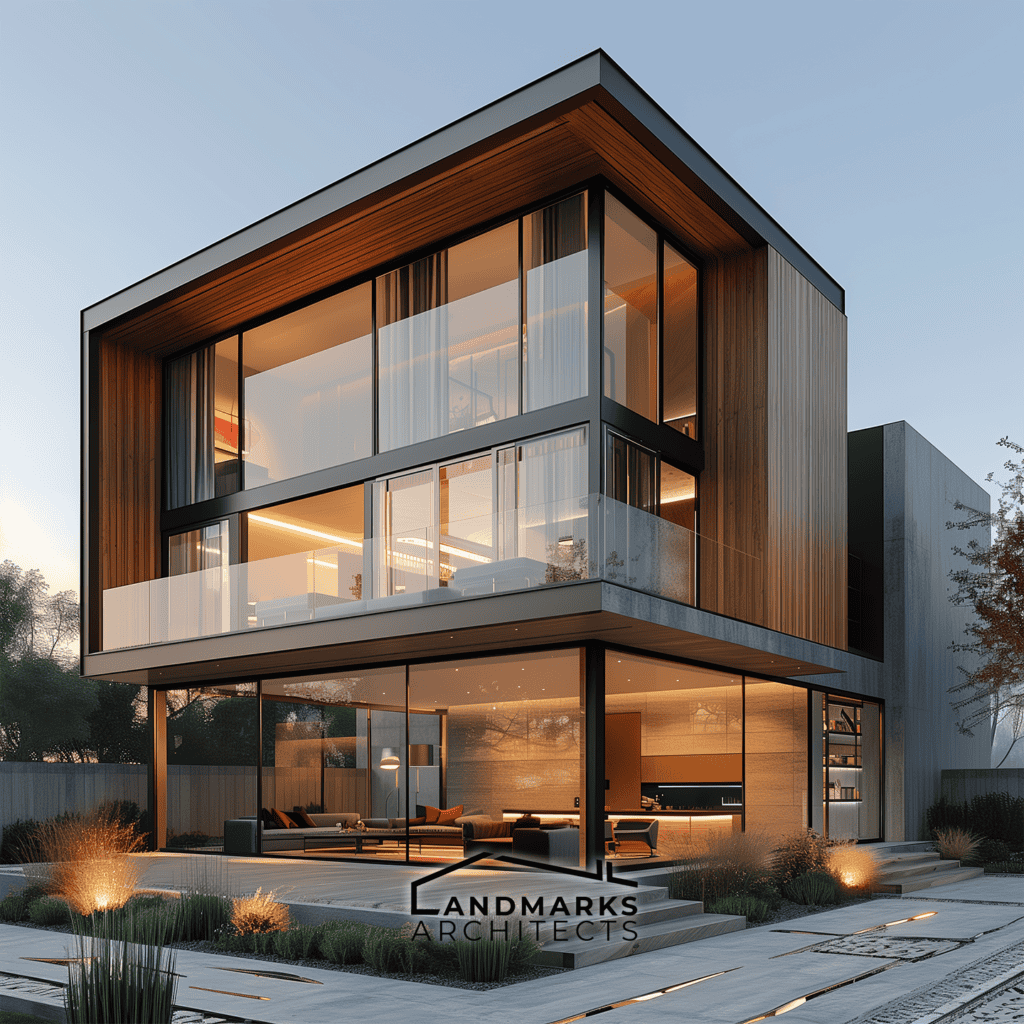
Cubic structures stand out for their focus on form and function. This style prioritizes functional spaces, emphasizing how these structures and the surrounding space interact harmoniously.
Why should you care about cubic architecture? As urban spaces become more compact, cubic homes offer a smart, functional, and aesthetically appealing solution. While maintaining a compact footprint, cubic forms contribute to efficient land usage at ground level.