Are you fascinated by the idea of living amidst architectural masterpieces that tell a story of heritage and innovation?
At Landmarks Architects, we recognize the challenge of navigating the sea of architectural styles and designs. We are here to serve as your trusted guide through this exhilarating adventure.
In this article, we will explore the rich fabric of Traditional German Architecture, from its historic roots to its enduring influence on modern design. We’ll explore key architectural styles such as Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, and more, offering insights into their unique characteristics and cultural significance.
- Historical evolution of German architecture across major periods.
- Distinctive German styles like Brick Gothic and timber-framed houses.
- Influence of modern and contemporary movements, including Bauhaus and post-war reconstruction.
- Iconic monuments and UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Are you ready to begin an exploration of the timeless allure of Traditional German Architecture?
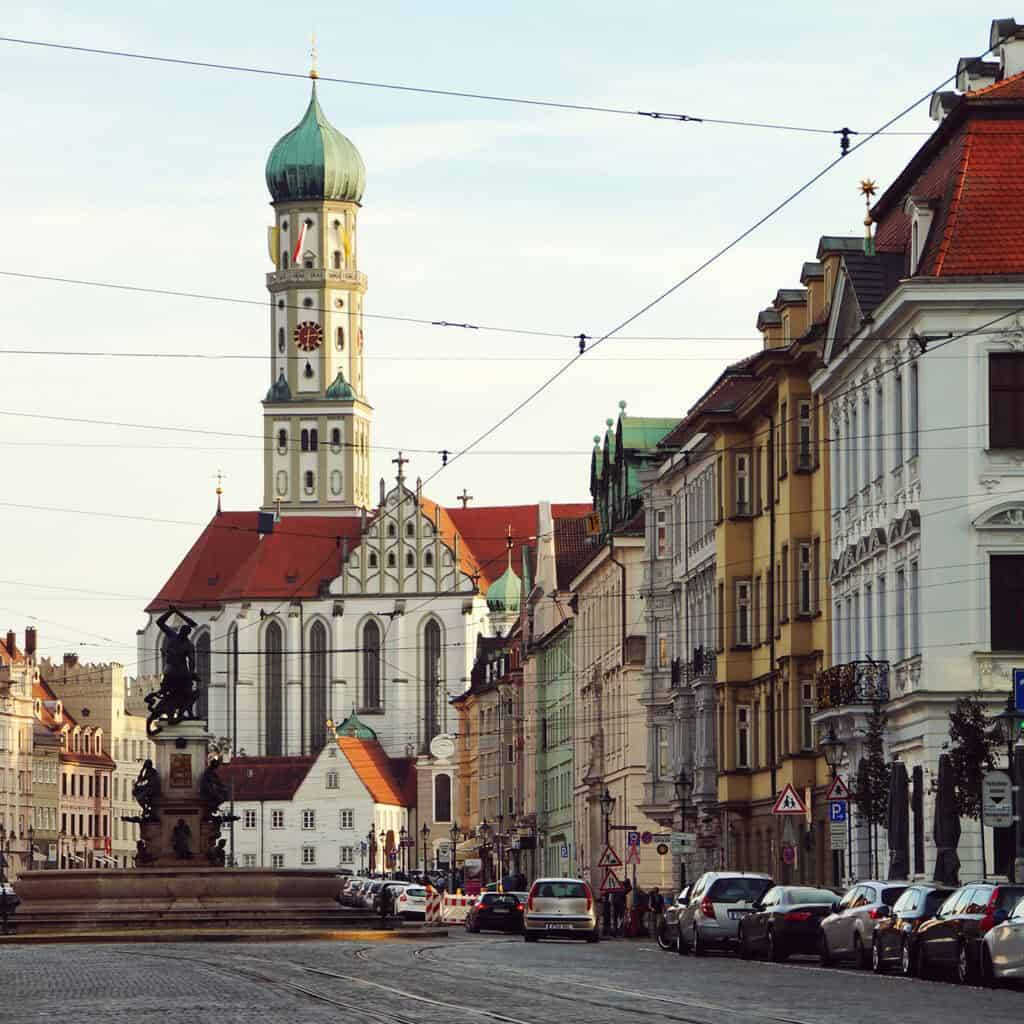

Historical Evolution of German Architecture
German architecture has a long and diverse history, influenced by various styles from different periods. This section will explore the historical evolution of German architecture, including Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, Classicism, and Historicism.
1. Romanesque
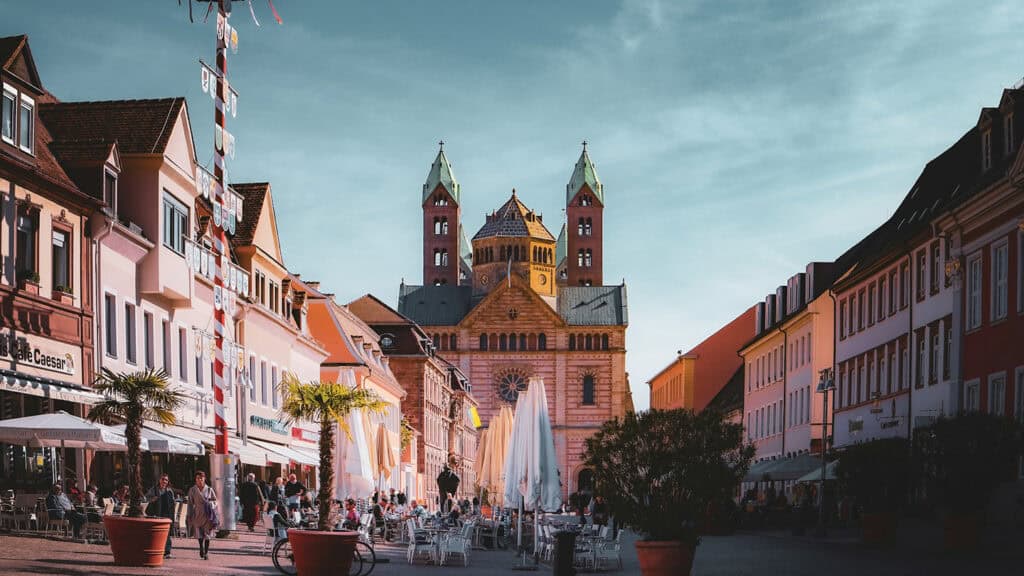

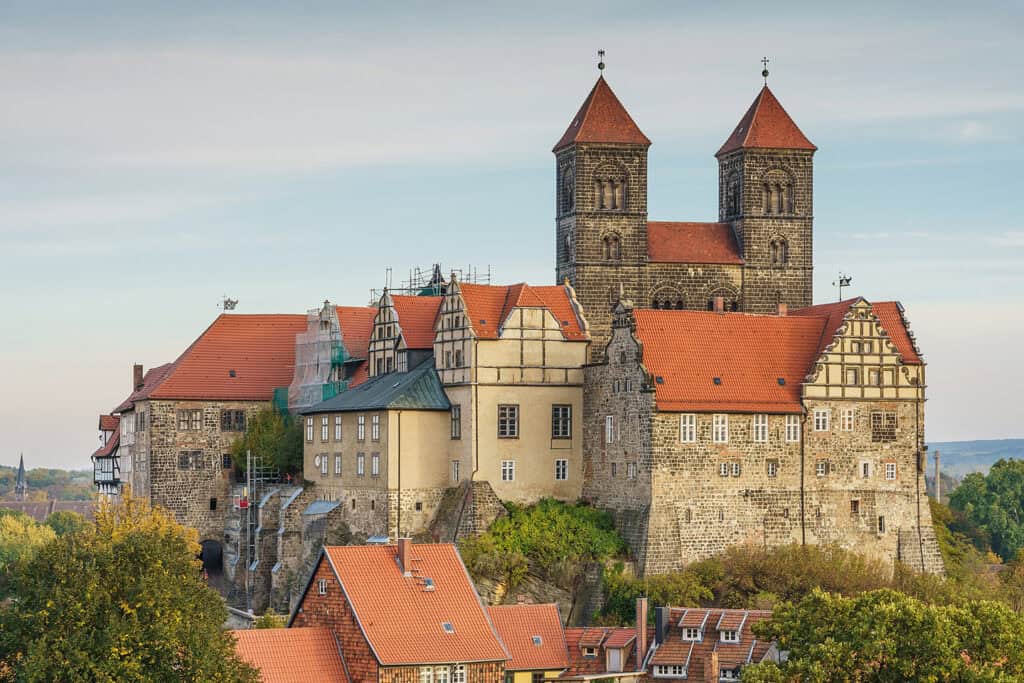
The Romanesque architectural style dominated Germany during the Middle Ages. It was characterized by thick walls, semi-circular arches, and barrel vaults. The style was heavily influenced by the ancient Roman architecture.
Some of the most notable examples of Romanesque architecture in Germany are the Speyer Cathedral and the Quedlinburg Abbey.

2. Gothic Architecture
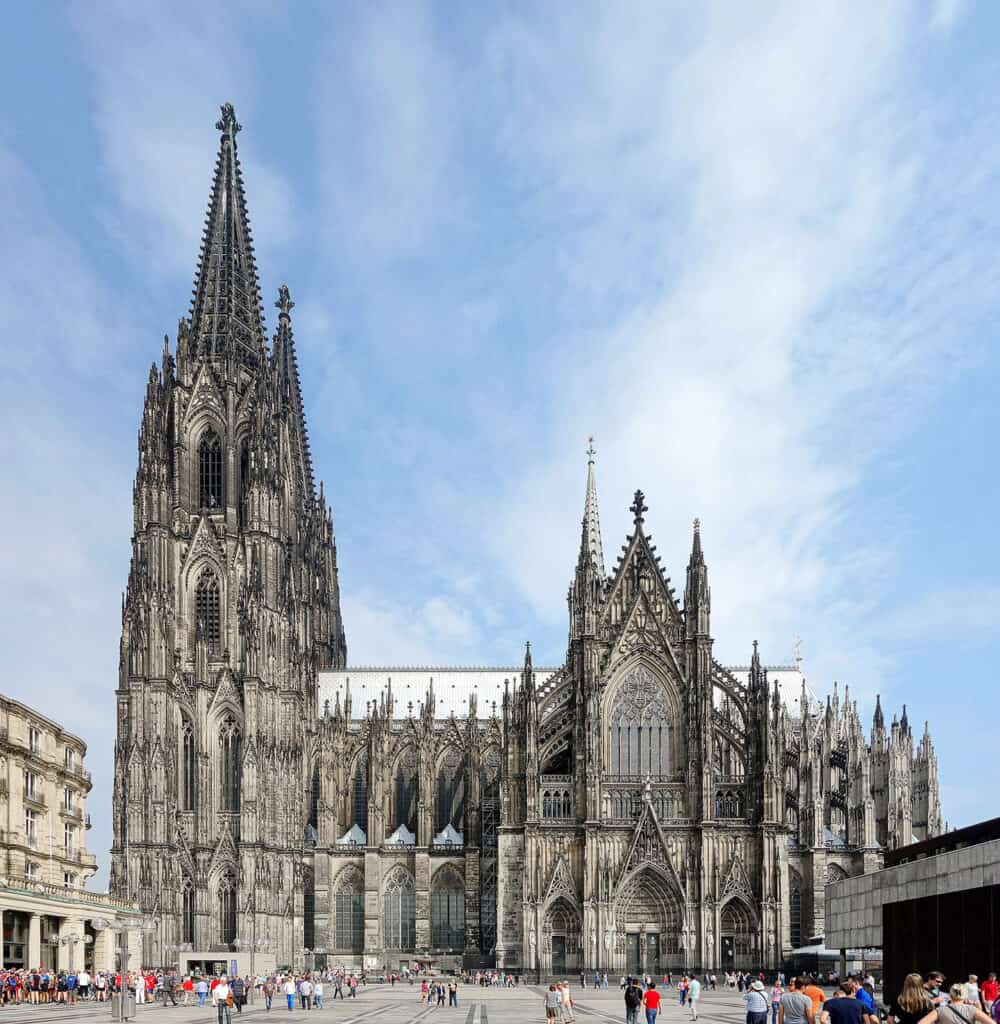

The Gothic style originated in France and spread throughout Europe, including Germany. Gothic architecture was characterized by its emphasis on height, light, and intricate details. It was a significant departure from the heavy, solid forms of the Romanesque style.
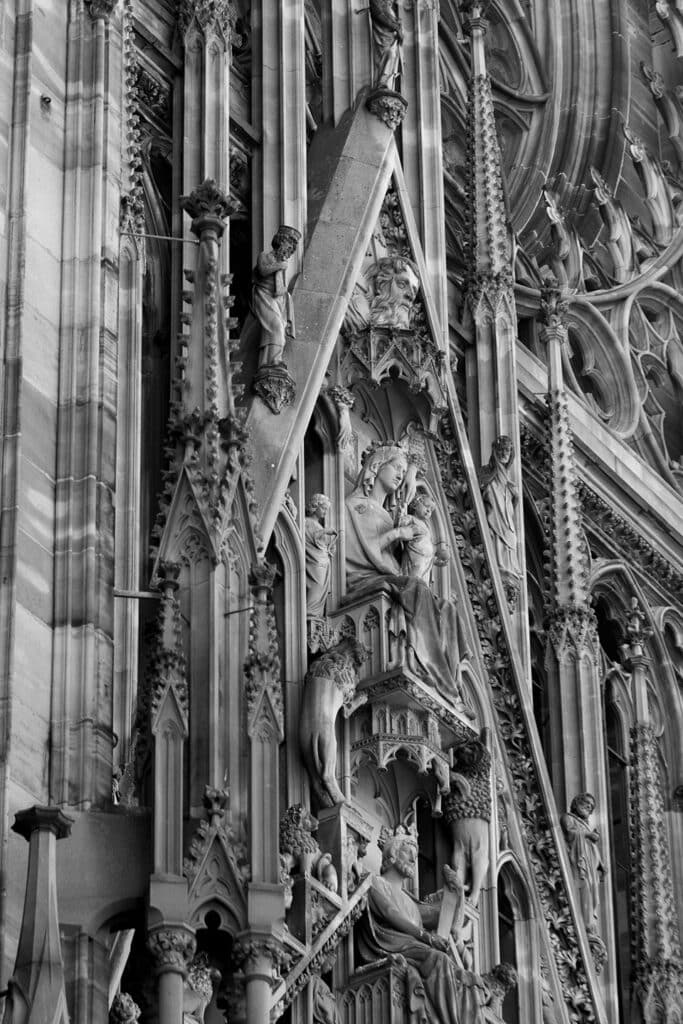
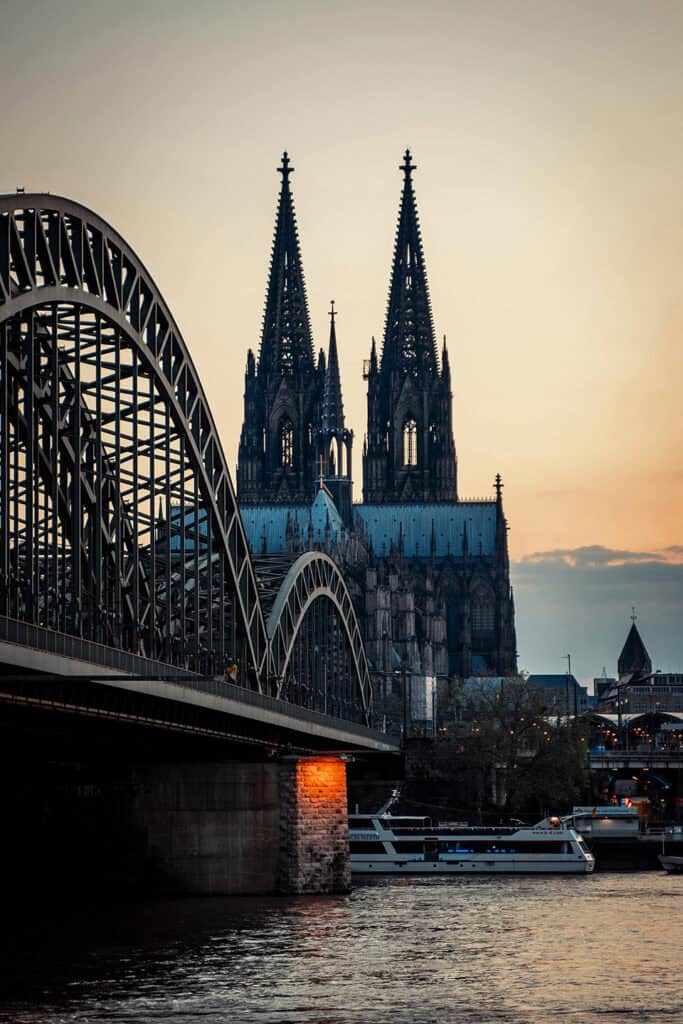


Some of the most iconic examples of Gothic architecture in Germany include the Cologne Cathedral and the Ulm Minster.

3. Renaissance Architecture
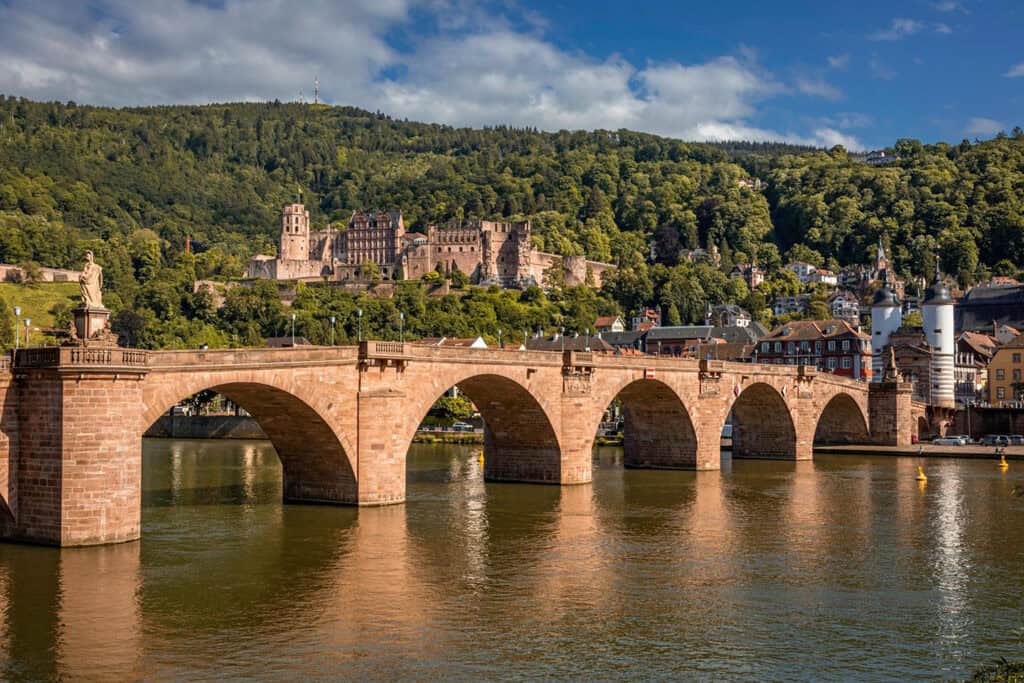

The Renaissance style emerged in Italy during the 14th century and spread throughout Europe, including Germany. It was characterized by a return to classical forms and a focus on symmetry and proportion. The Fugger chapel in St. Anne’s Church, Augsburg, represents Germany’s earliest instance of Renaissance architecture.
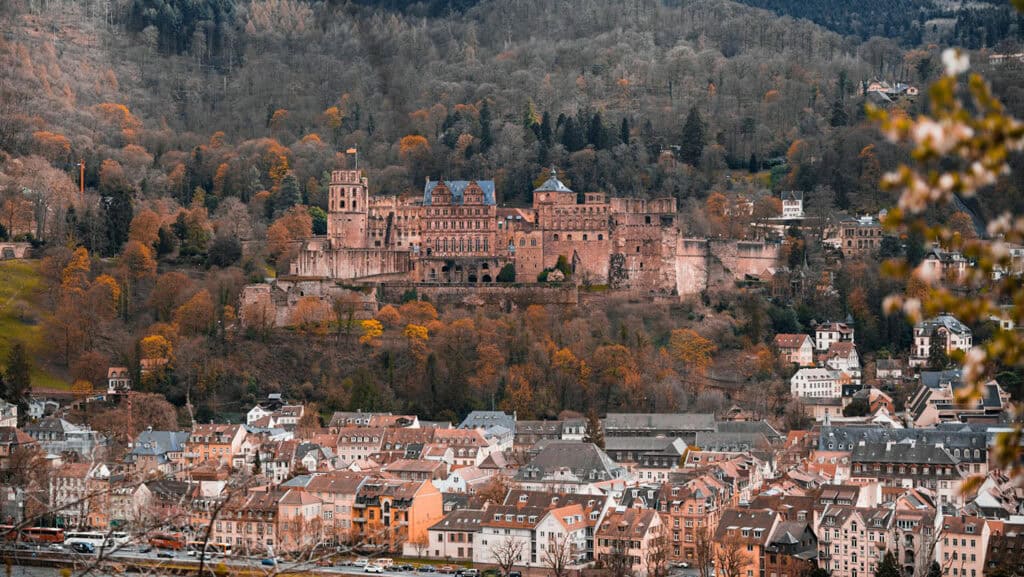

One of the most notable examples of Renaissance architecture in Germany is the Heidelberg Castle.
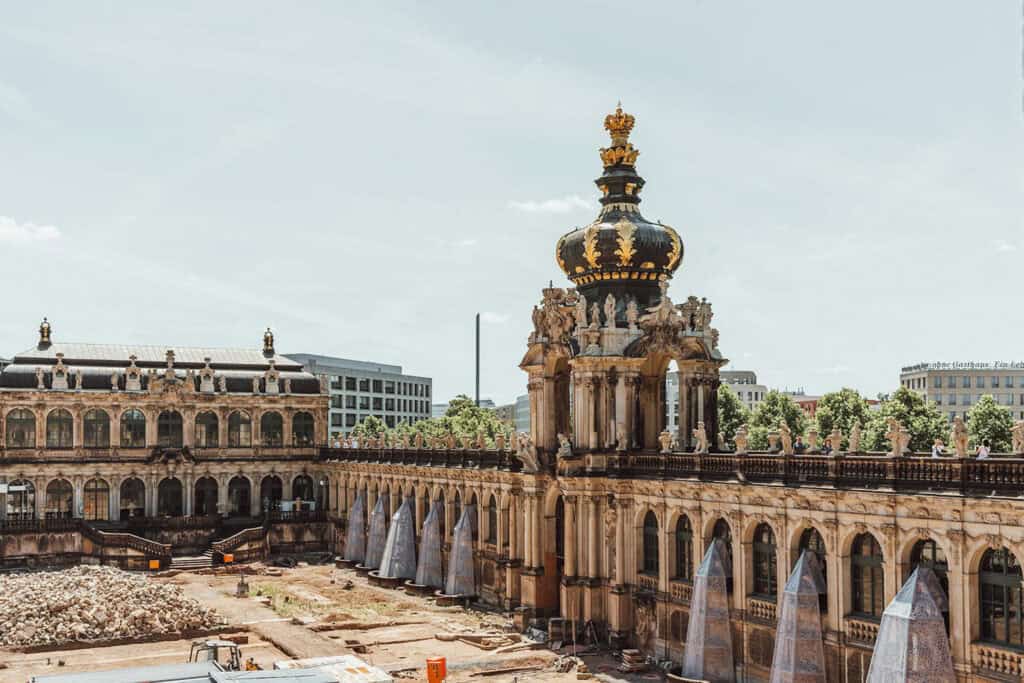
4. Baroque Styles

The Baroque style emerged in Italy during the 17th century and spread throughout Europe, including Germany. It was characterized by its ornate decorations.
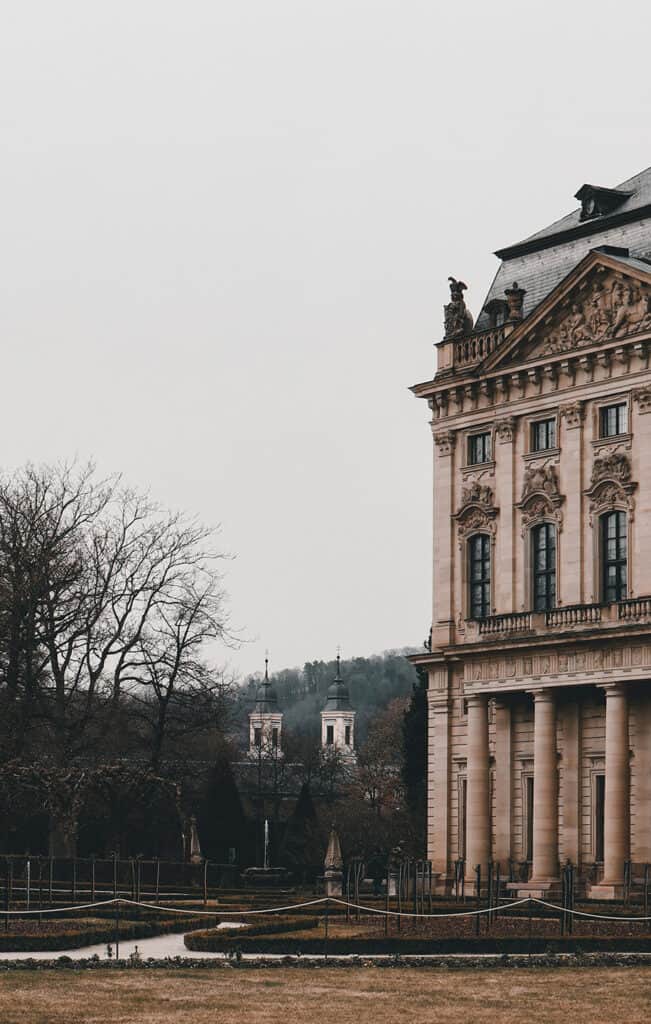
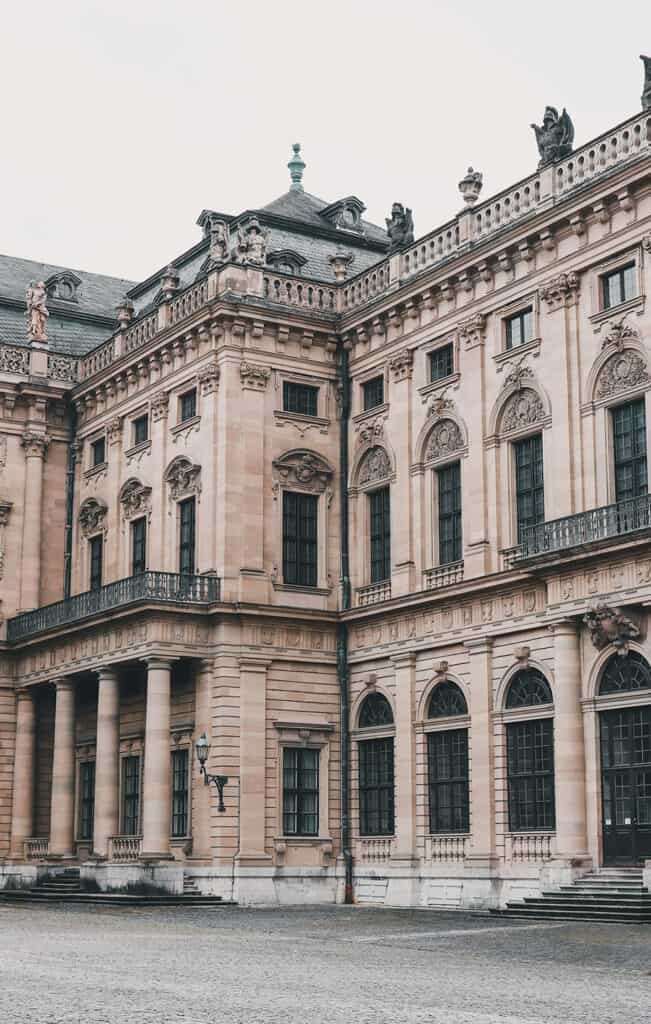


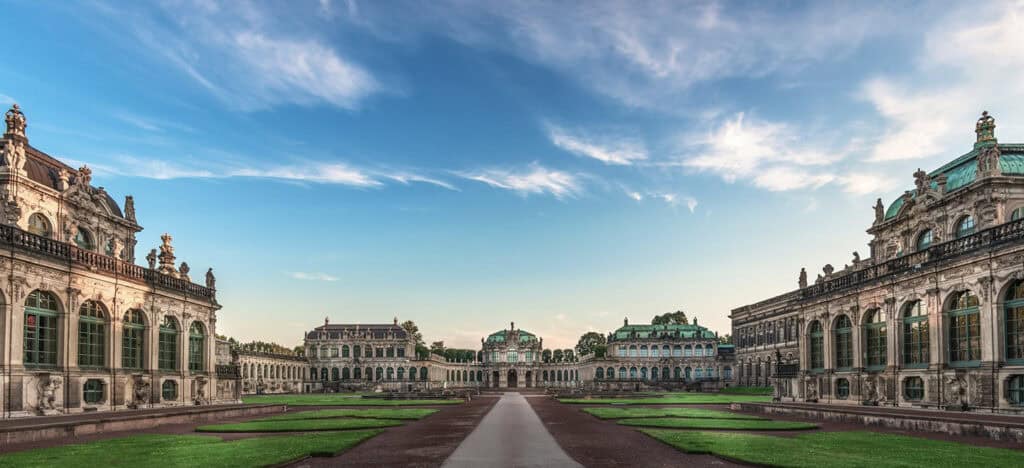
Some of the most notable examples of Baroque architecture in Germany are the Würzburg Residence and the Zwinger Palace in Dresden.


5. Classicism
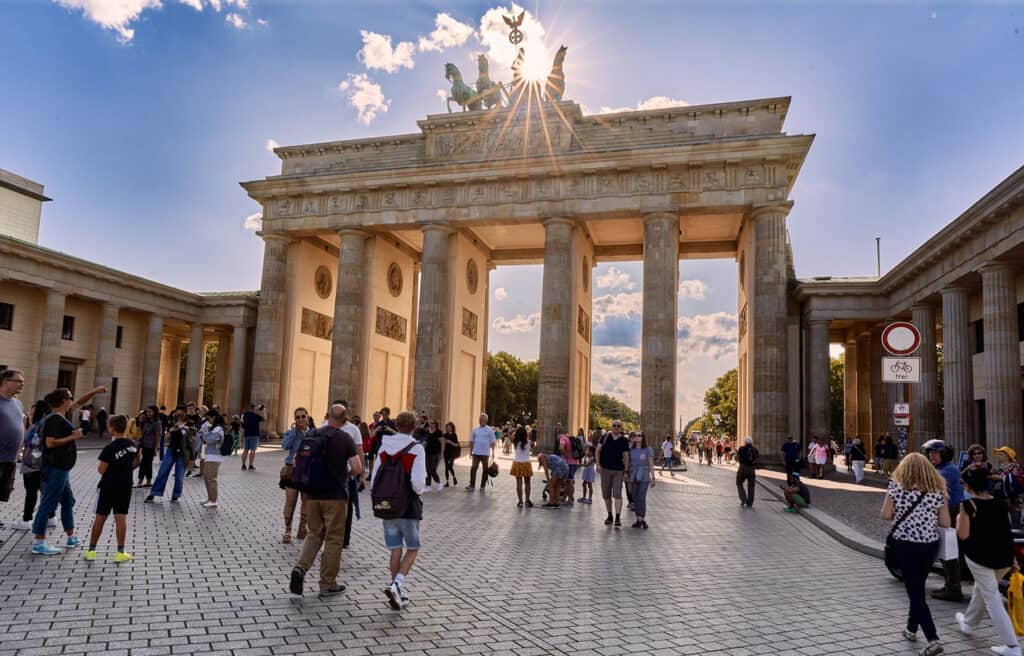

The Classicism style emerged in Germany in the second half of the 18th century and was influenced by ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
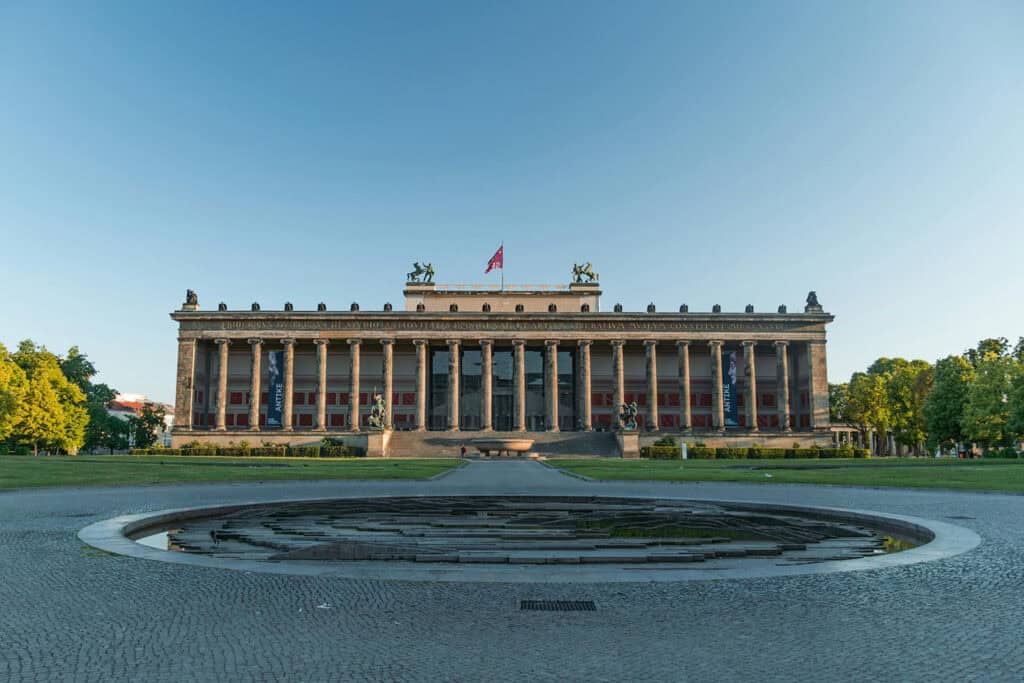

Some of the most notable examples of Classicism architecture in Germany are the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin and the Altes Museum in Berlin.
6. Historicism
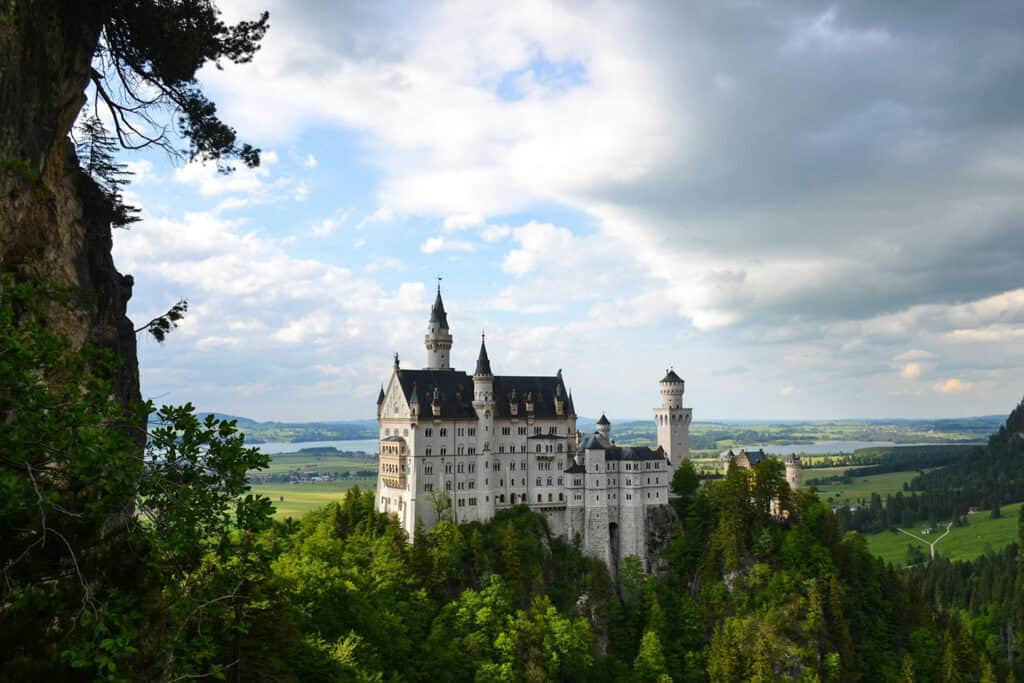

Historicism emerged in Germany during the 19th century and was characterized by its eclectic mix of different architectural styles from different periods. It was a response to the rapid industrialization and urbanization of Germany, which led to a renewed interest in the country’s architectural heritage.
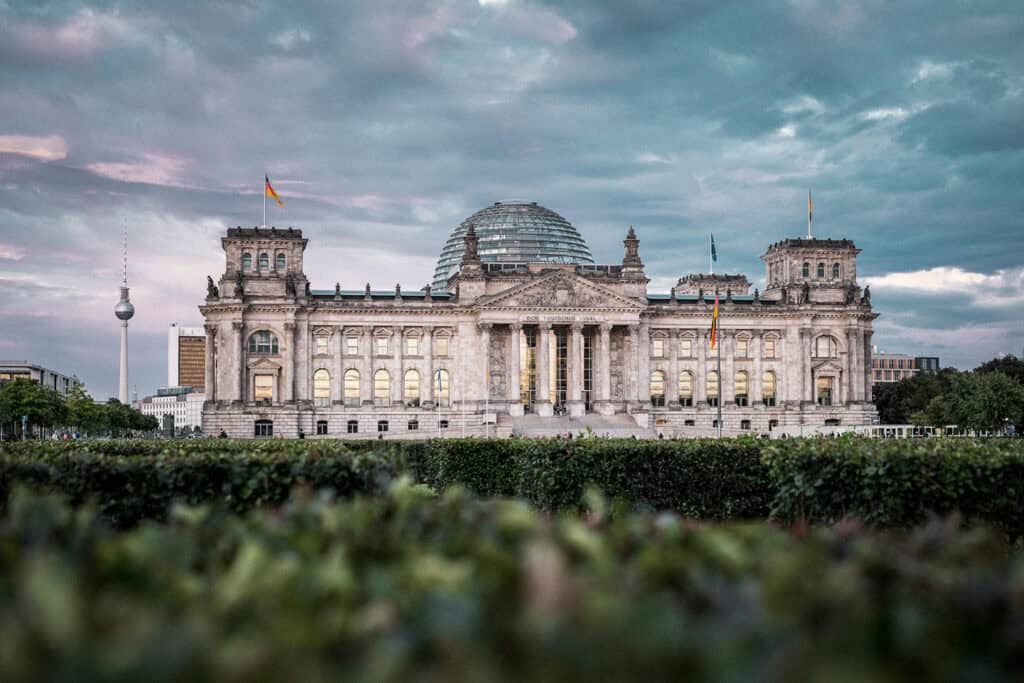

Some of the most notable examples of Historicism architecture in Germany are the Neuschwanstein Castle and the Reichstag building in Berlin.
7. Art Nouveau (Jugendstil)
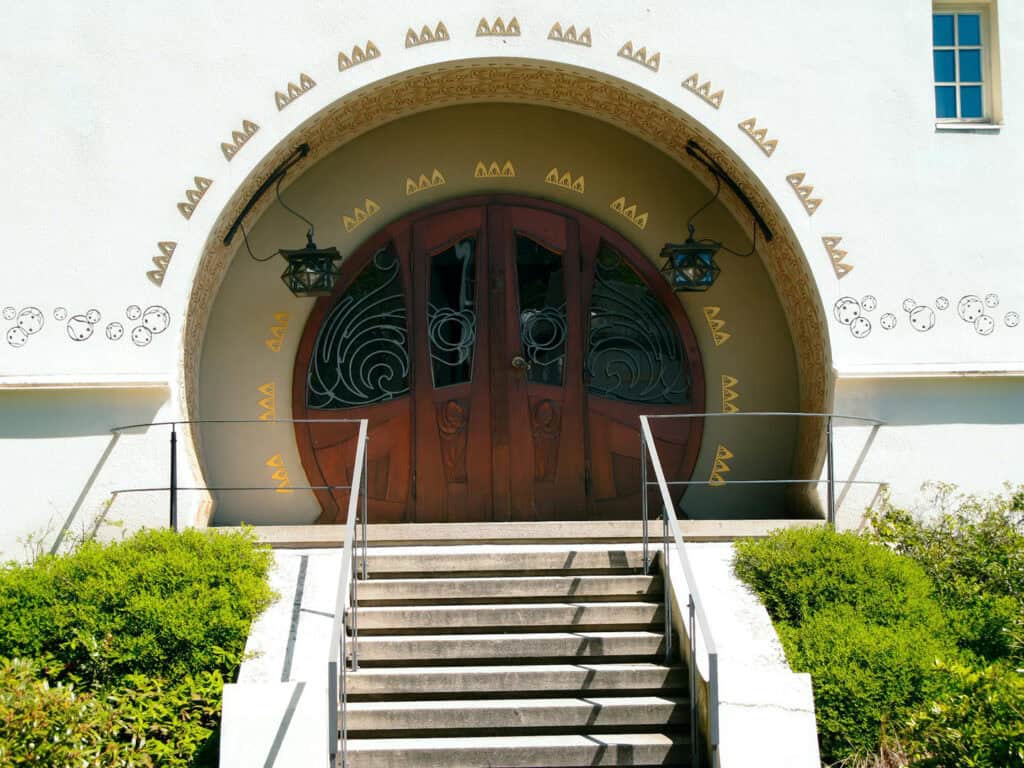

Art Nouveau, known as Jugendstil in Germany, emerged around the turn of the 20th century as a highly decorative and ornamental artistic movement.
One prominent example of Art Nouveau architecture in Germany is the Mathildenhöhe in Darmstadt, a complex of buildings including the Wedding Tower (Hochzeitsturm) designed by Joseph Maria Olbrich.
Distinctive German Architecture Styles
1. Brick Gothic Architecture

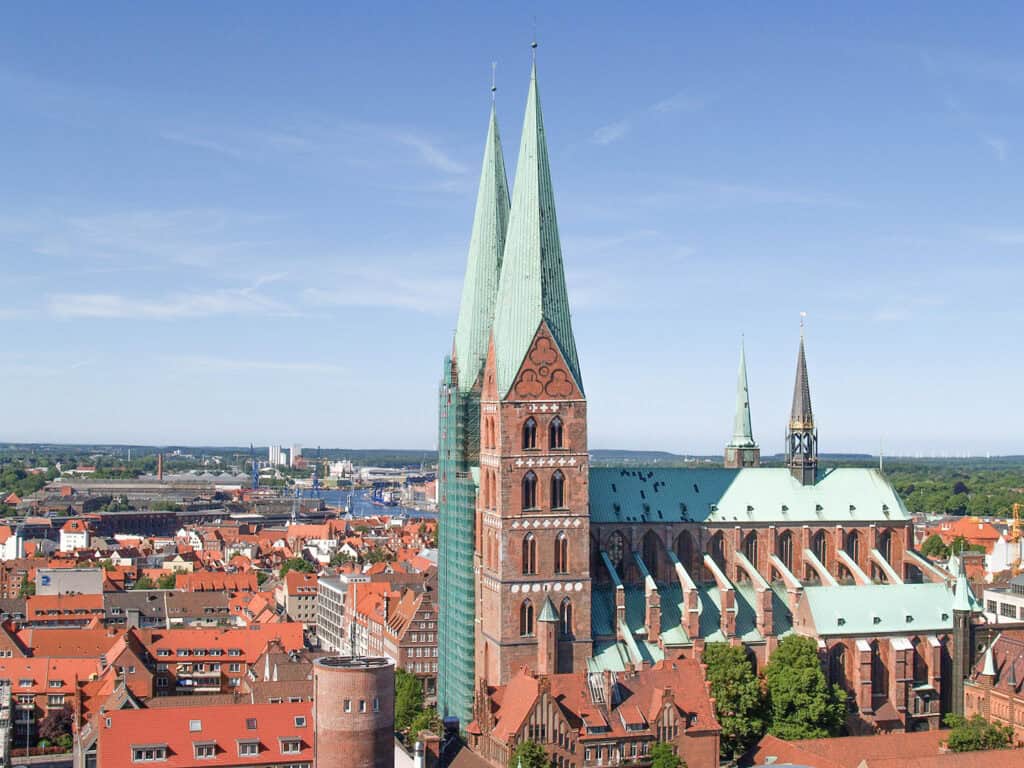
The Brick Gothic style is characterized by its use of red brick, ribbed vaults, and pointed arches. This style was prevalent in Northern Germany during the Middle Ages, and many of the region’s historic city centers still feature stunning examples of Brick Gothic architecture.
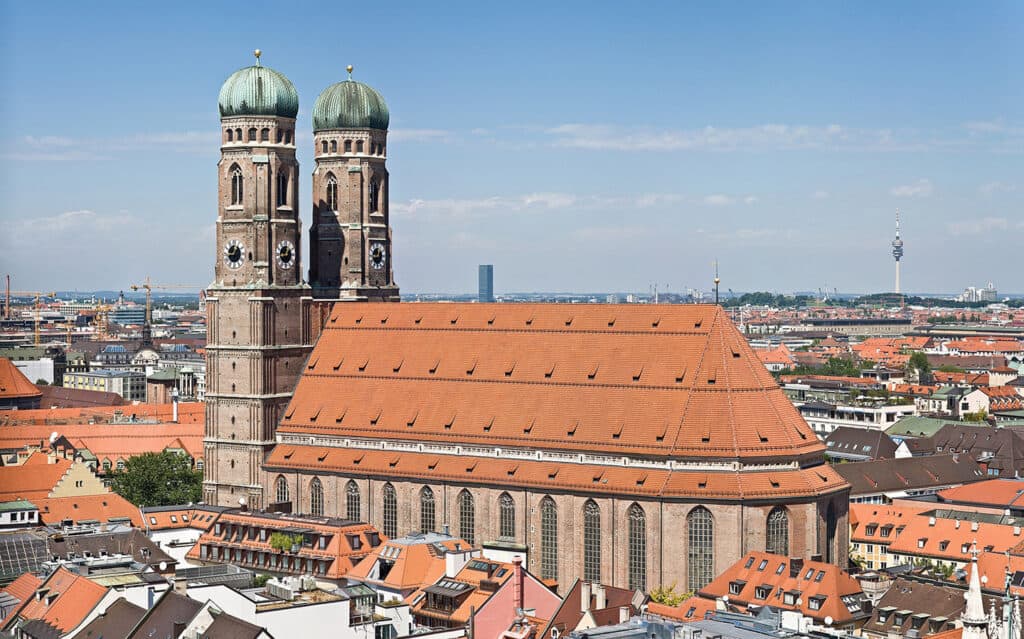

St. Mary’s Church in Lübeck and Frauenkirche in Munich, are excellent examples of Brick Gothic architecture.
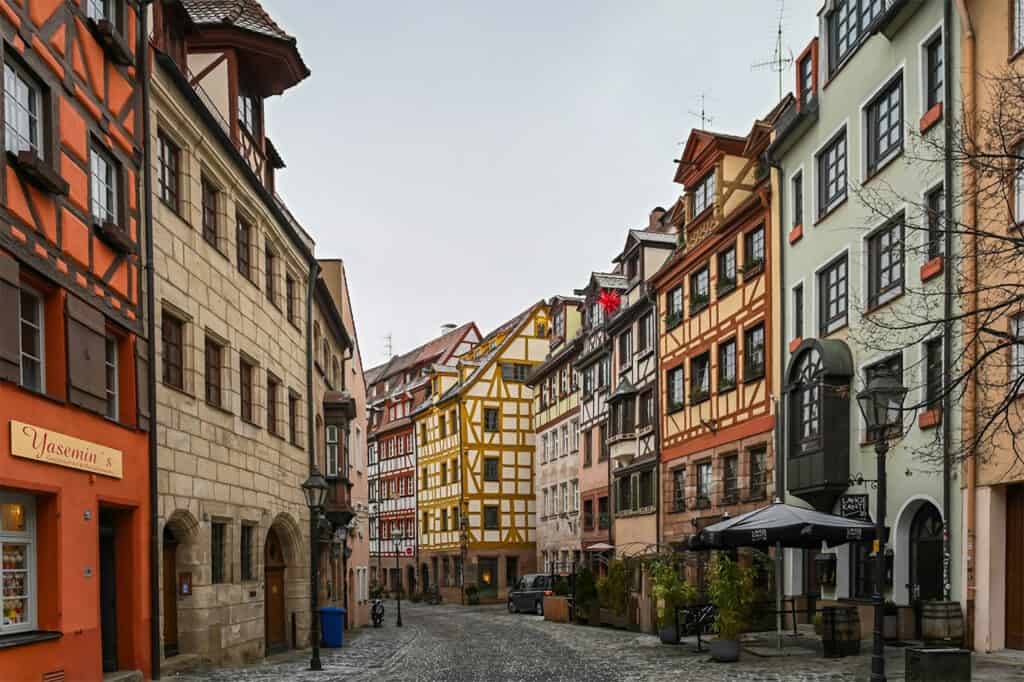
2. Timber-Framed Houses
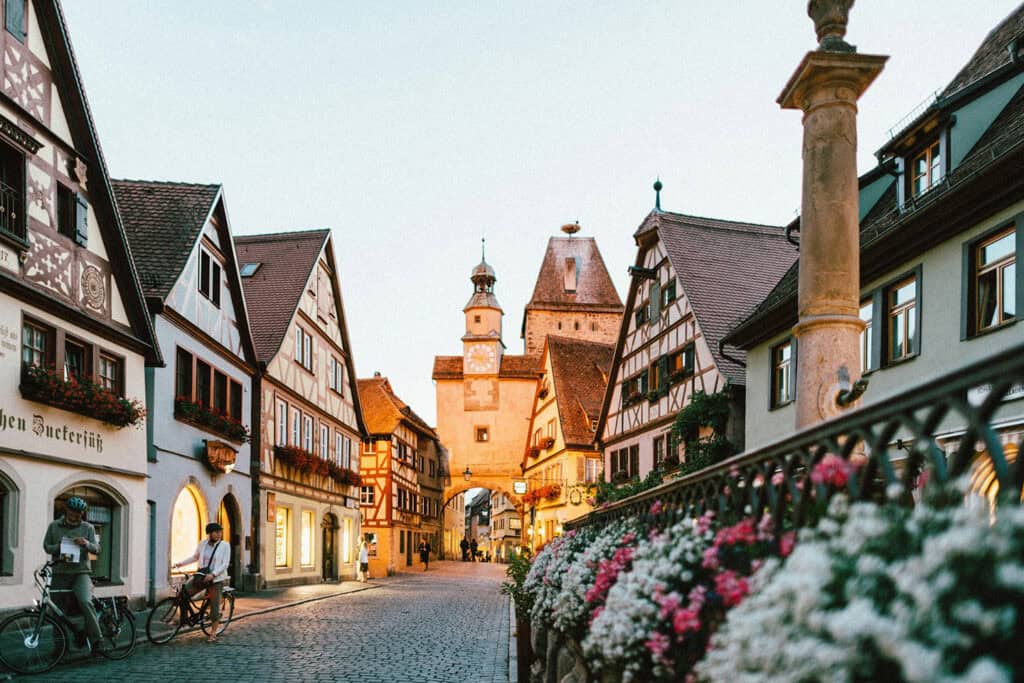

Timber-framed houses, also known as half-timbered houses, are a hallmark of traditional German architecture. These houses are constructed with wooden frames filled with plaster or brick, and their distinctive appearance is characterized by their exposed wooden beams.
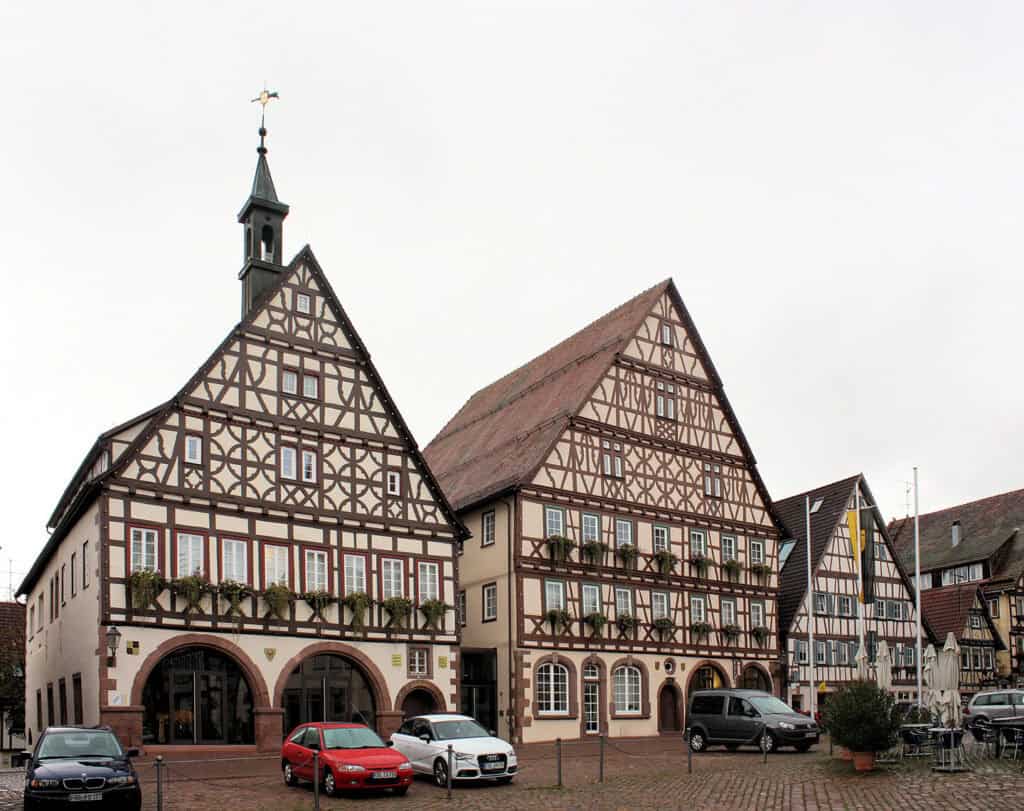

The market square of Dornstetten, Germany, is an ensemble of half-timbered buildings.
Modern and Contemporary Influences
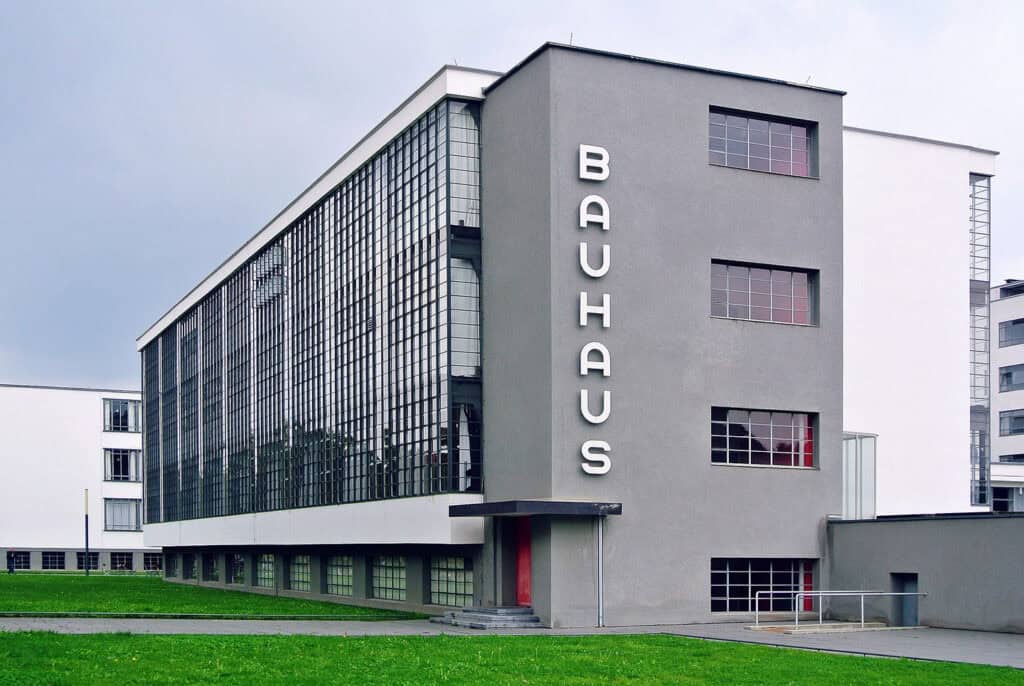

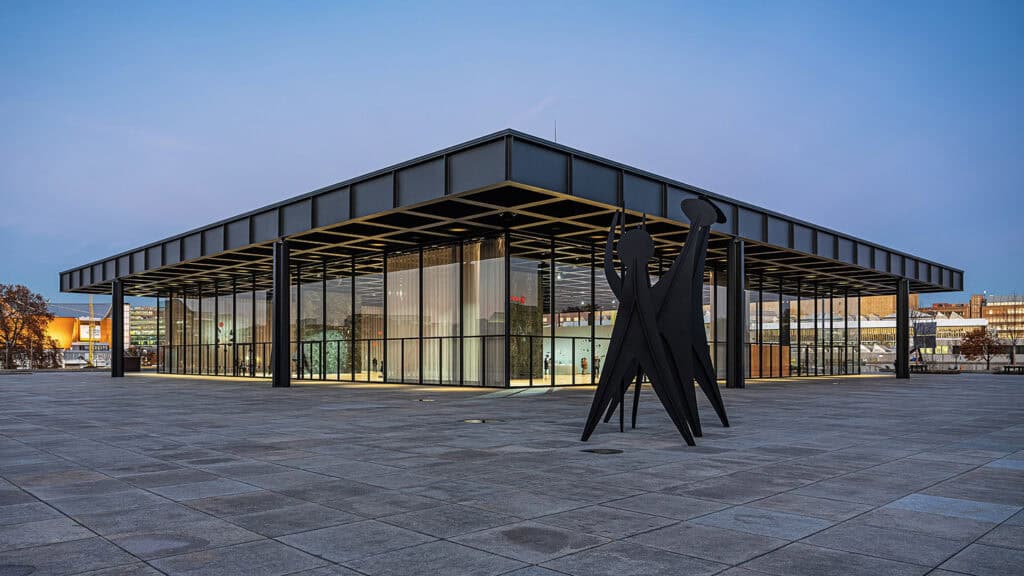
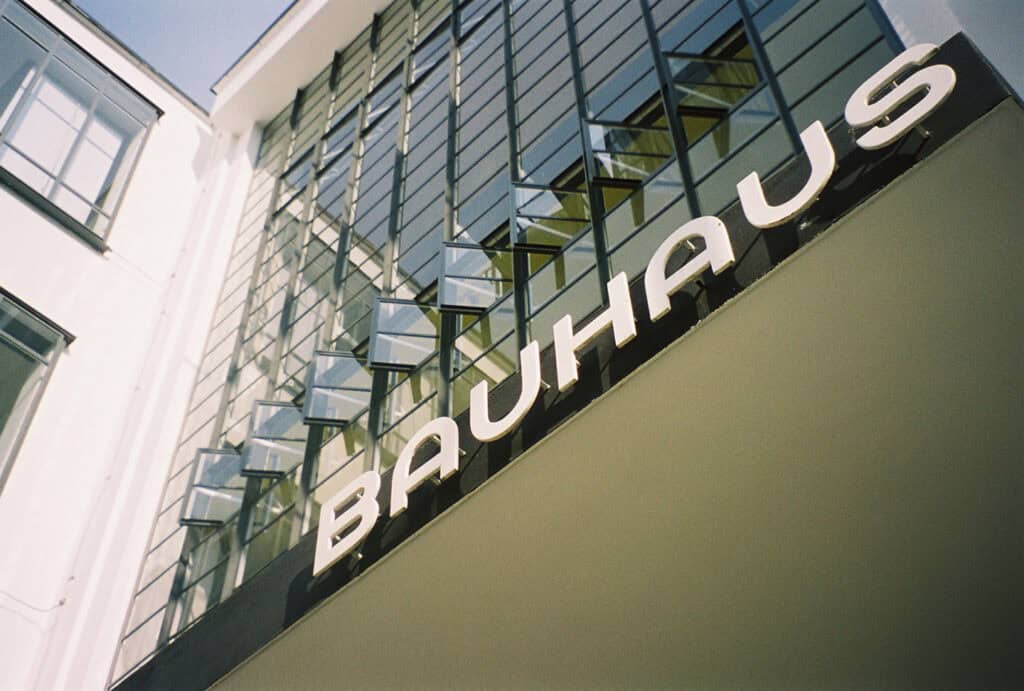
Germany has made significant contributions to modern and contemporary architecture, particularly through the Bauhaus movement and modernist architecture. The Bauhaus building in Dessau, designed by Walter Gropius, is a notable example of the movement’s architectural style. The Neue Nationalgalerie in Berlin, designed by Mies van der Rohe, is another example of modernist architecture.

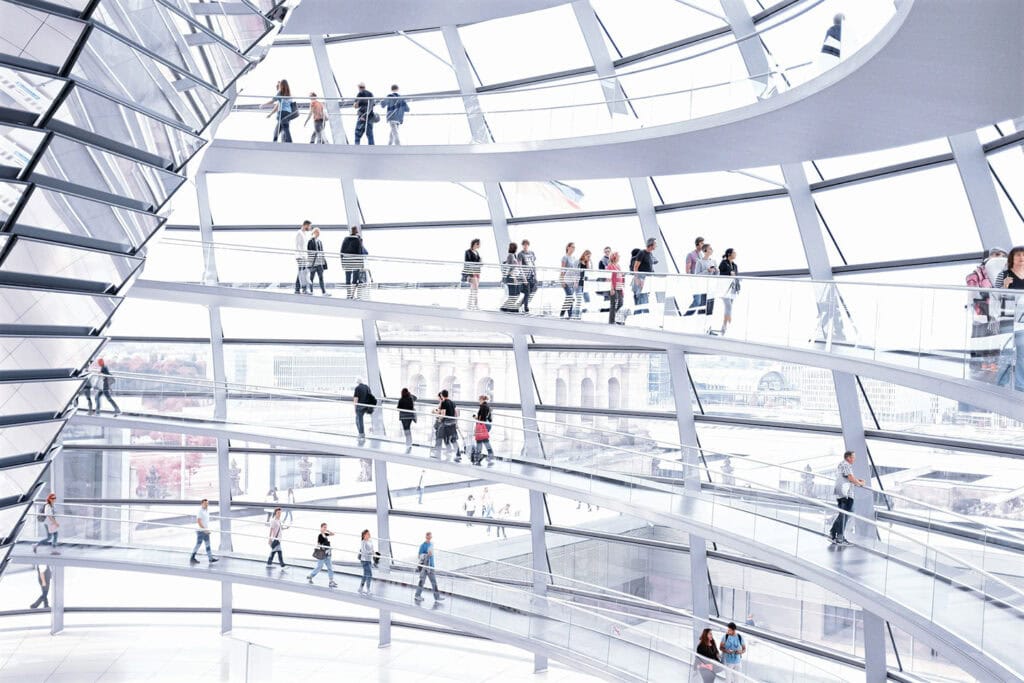
After World War II, Germany underwent a period of post-war reconstruction, which led to the development of modern architecture. Notable examples of modern developments include the renovation of the Berlin Reichstag and the Frankfurt skyline.
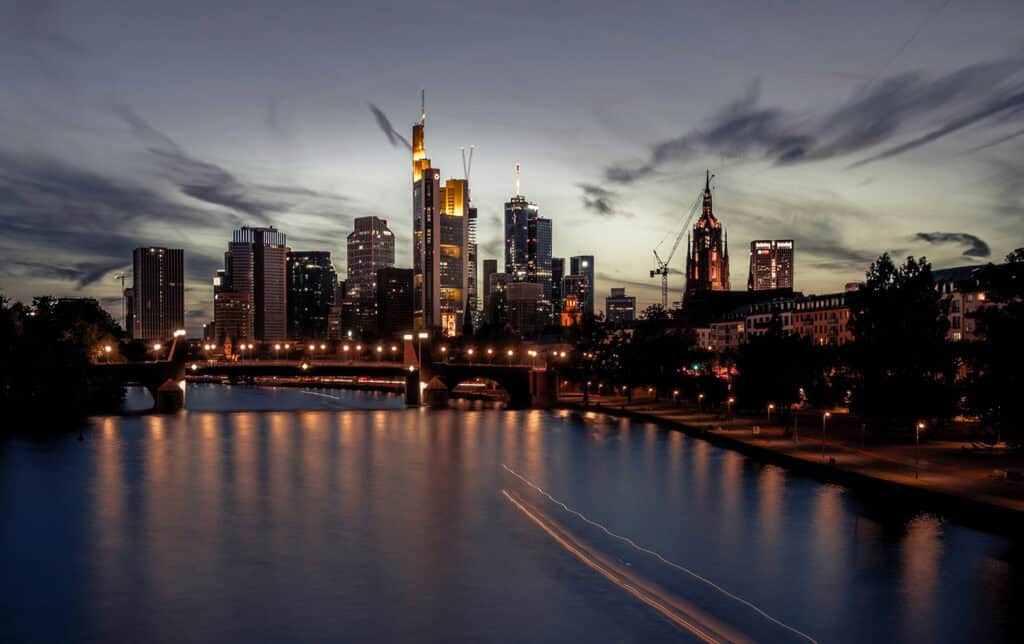


Contemporary architecture in Germany continues to incorporate modern materials and design elements. The use of glass and steel in building construction has become increasingly popular in recent years.

German Architecture
In conclusion, German architecture is a fascinating blend of various styles that have evolved over time. From the medieval Gothic churches to the modernist Bauhaus buildings, Germany has a diverse architectural heritage that reflects its rich history and culture.
Germany’s UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the Bauhaus School and Museum Island, showcase some of the finest German buildings. The country’s architectural diversity is enriched by traditional half-timbered houses, Baroque and Rococo styles, and Art Nouveau structures.
Overall, German architecture is a unique blend of traditional and modern styles, and it continues to evolve with contemporary architecture. The country’s diverse architectural heritage is a testament to its rich history and culture, and it is a major attraction for tourists from around the world.