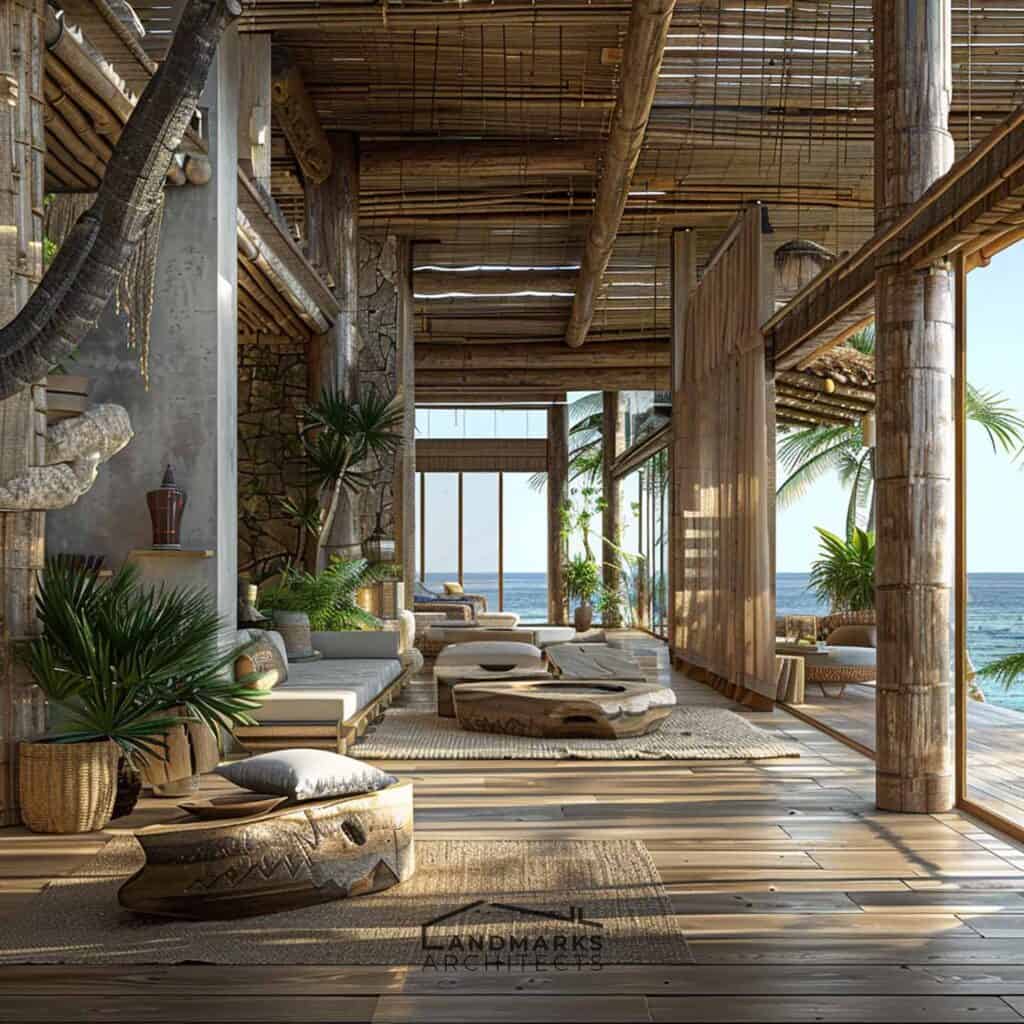
Are you seeking a design approach that combines functionality with aesthetic simplicity?
We will show you how modern architects use modernist principles. They design spaces that combine function with aesthetic appeal.
In this article, we’ll explore the key elements of modernist architecture, including:
- Functionality: Prioritizes practical design over decoration.
- Design: Features clean lines and open layouts.
- Materials: Utilizes modern materials like concrete and glass.
- Integration: Harmonizes with nature and avoids ornamentation.
Ready to see how Modern Architectural Styles can elevate your design projects?
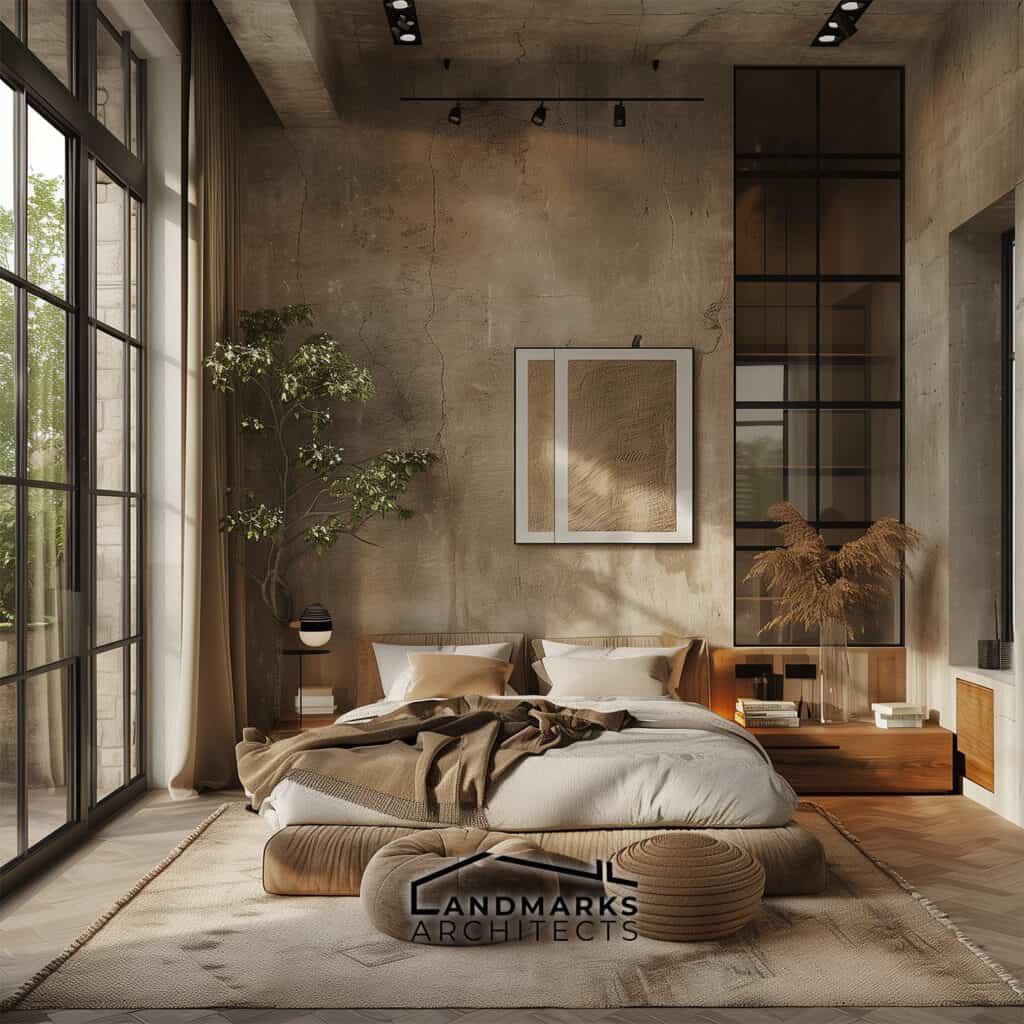

- 1. Prioritization of Practicality
- 2. Streamlined Aesthetics
- 3. Adoption of New Materials
- 4. Expansive Interior Layouts
- 5. Linear Forms and Horizontal Lines
- 6. Harmonization with the Environment
- 7. Elimination of Decorative Elements
- 8. Clarity and Order in Design
- What Are the Elements of Modernist Architecture? A Recap
1. Prioritization of Practicality

Modern architecture emerged in the early twentieth century with a focus on functionality. Architects followed a design philosophy that prioritized practical needs over decorative elements.
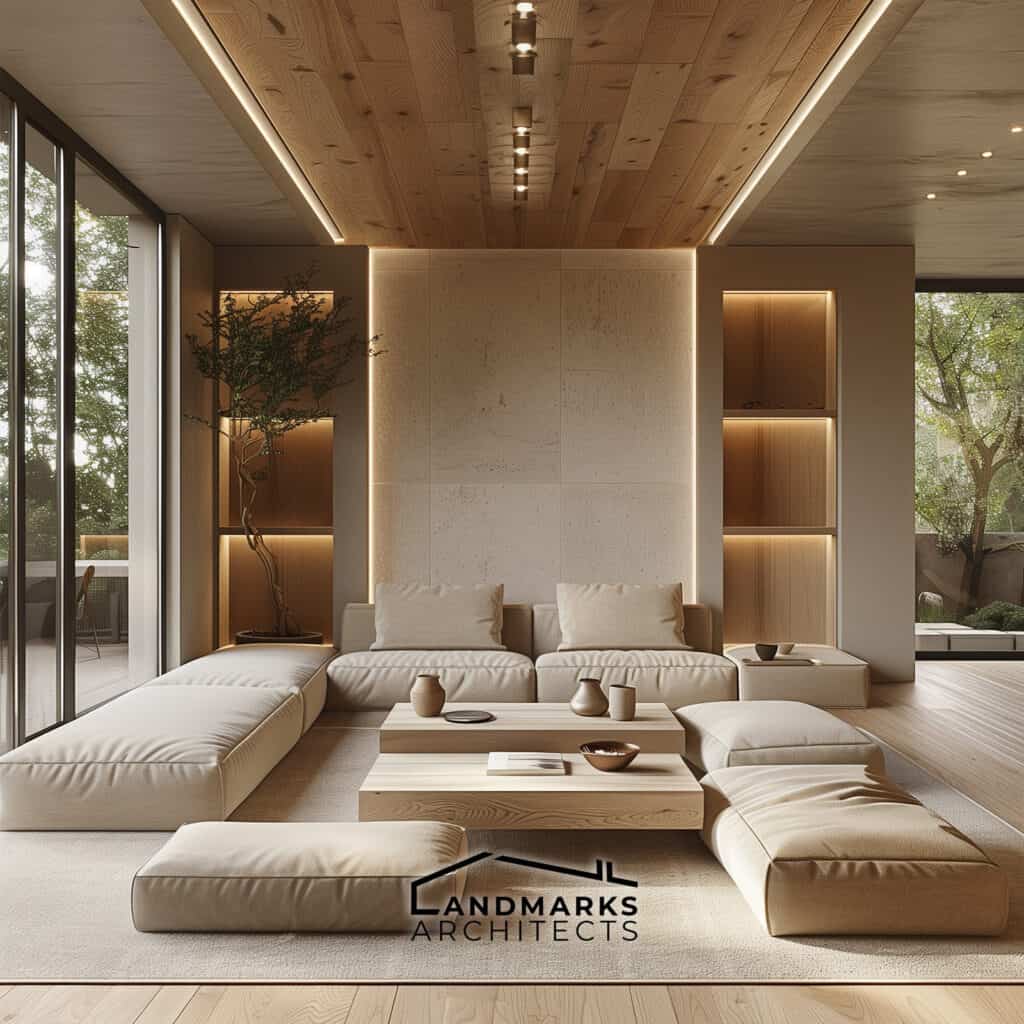

This approach shifts from traditional styles. It favors simple, straight-lined designs that meet modern living needs.
2. Streamlined Aesthetics
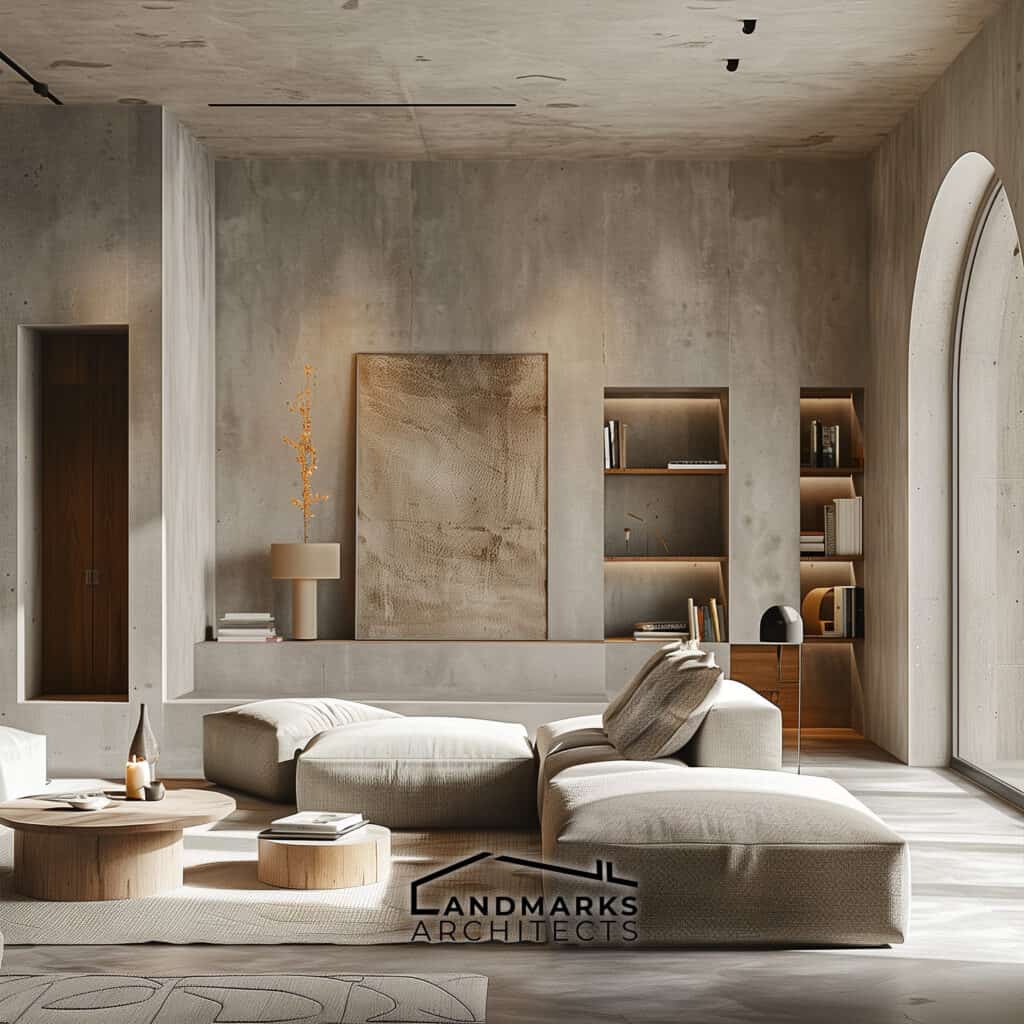

Streamlined aesthetics are a hallmark of modernist architecture, characterized by simplicity and functionality.
Asymmetrical compositions and geometric forms create a modern feel. Buildings often feature:
- Rectangular Forms: Promoting balance and functionality.
- Asymmetrical Designs: Creating visual interest without chaos.
- Straight Lines: Enhancing clarity and purpose.
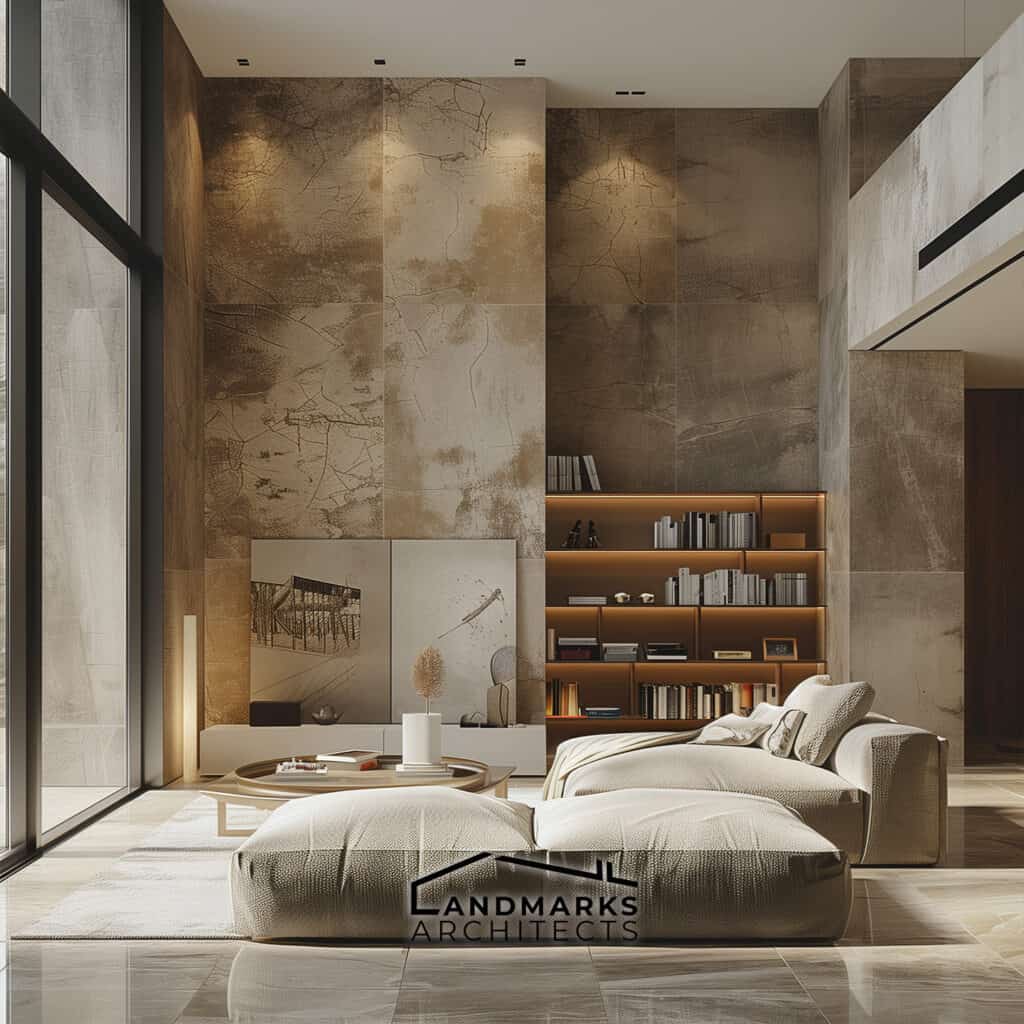

Architects use these principles to create practical, beautiful spaces. They reflect modernist design.
3. Adoption of New Materials
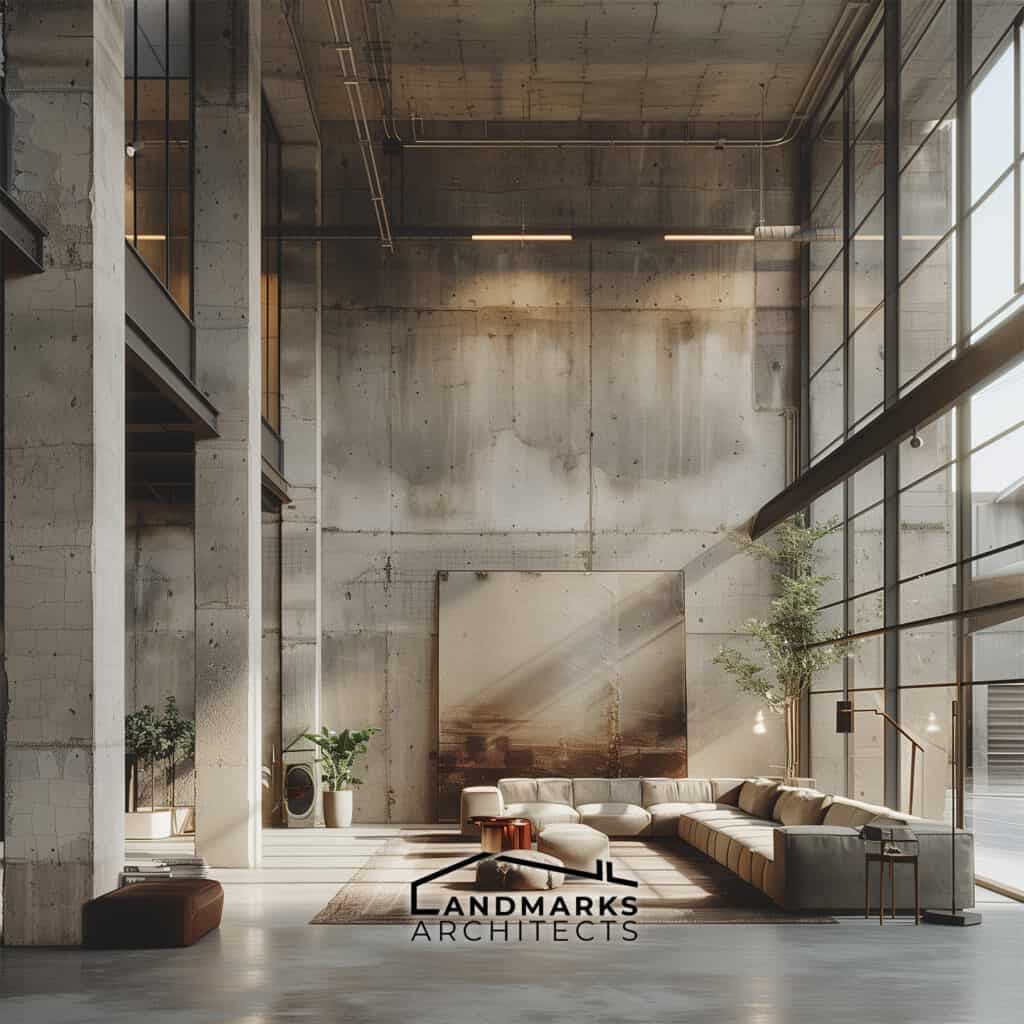

The modernist movement had new materials that transformed architectural design. This change boosted functionality and transformed the look.
- Industrial-Grade Materials: The use of reinforced concrete, steel, and glass became prevalent for their strength and versatility. These materials allowed architects to create innovative structures.
- Transparency and Light: Modern designs used large, clear glass and curtain walls. They let in natural light and offered clear views. This enhanced the link between indoor and outdoor spaces.

- Natural and Traditional Materials: While modernism emphasized industrial materials, it did not entirely abandon natural materials or traditional materials. Instead, it sought a balance, integrating these into the design where appropriate.

This combination of materials fostered a new architectural language that defined modernist and contemporary structures, showcasing clean lines and open space.
4. Expansive Interior Layouts
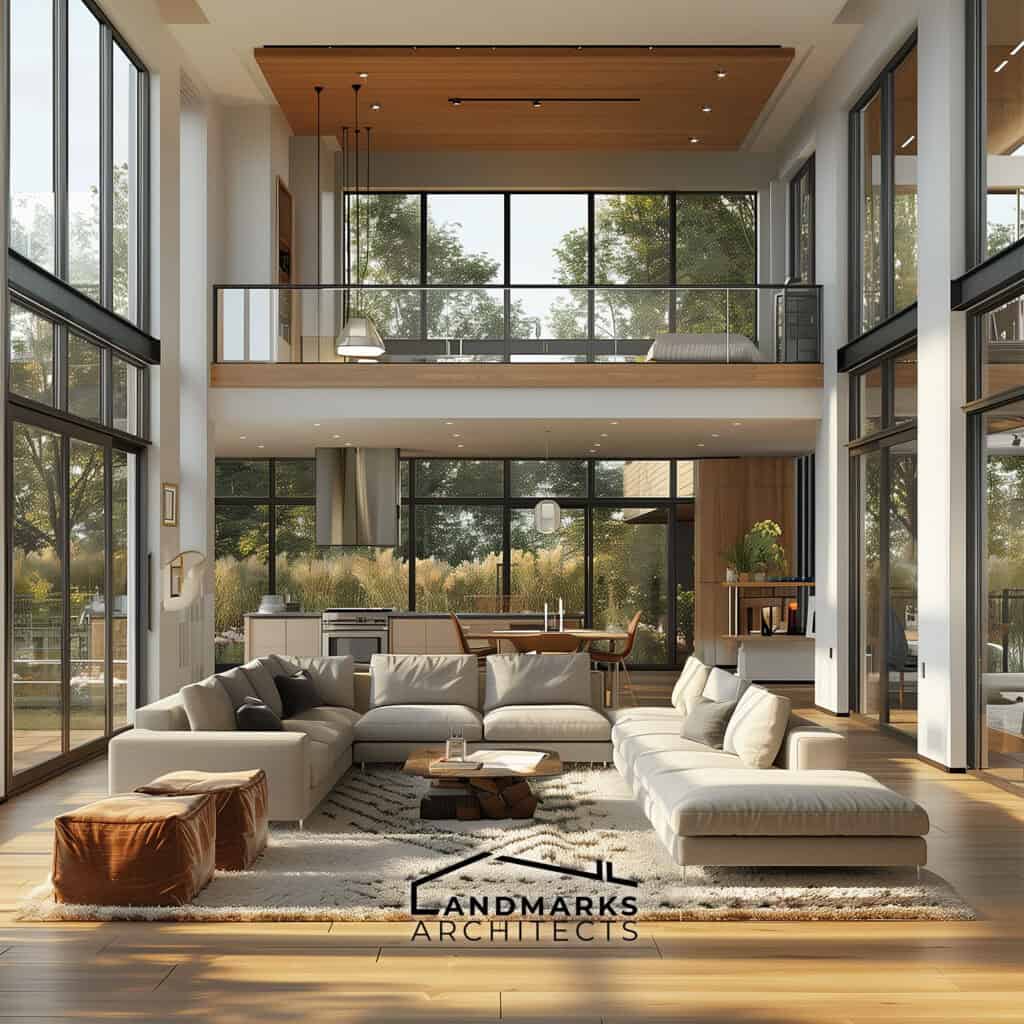

Modernist architecture initiated expansive interior layouts that encourage openness and connectivity. This design philosophy often features:
- Open floor plans: They create a flow between living areas. This boosts interaction and usability.
- Flexible spaces: Open, adaptable floor plans allow fluid movement within the building.
- Large windows: Maximizing natural light, they create a bright and inviting atmosphere.
- Glass doors: Sliding glass doors are often used. They give easy access to outdoor areas. They blur the line between indoor and outdoor living.
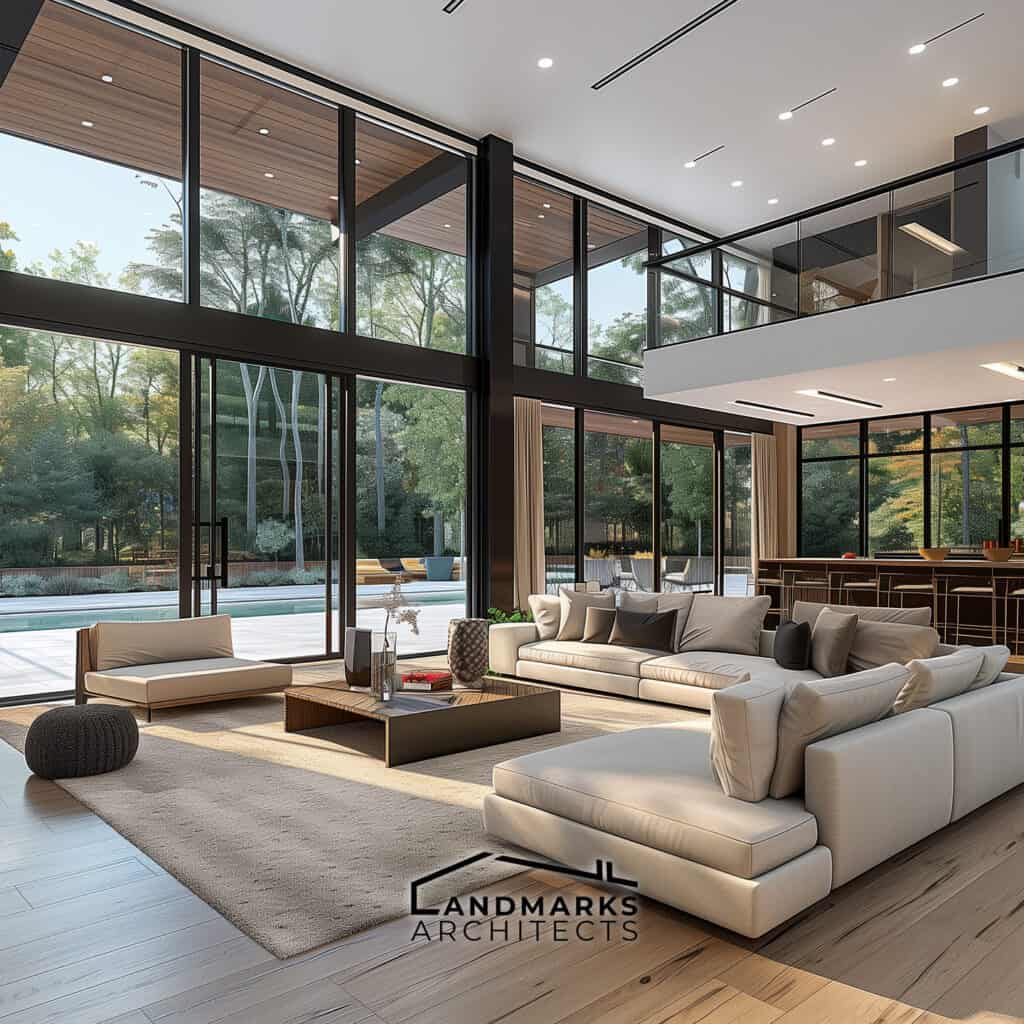

5. Linear Forms and Horizontal Lines
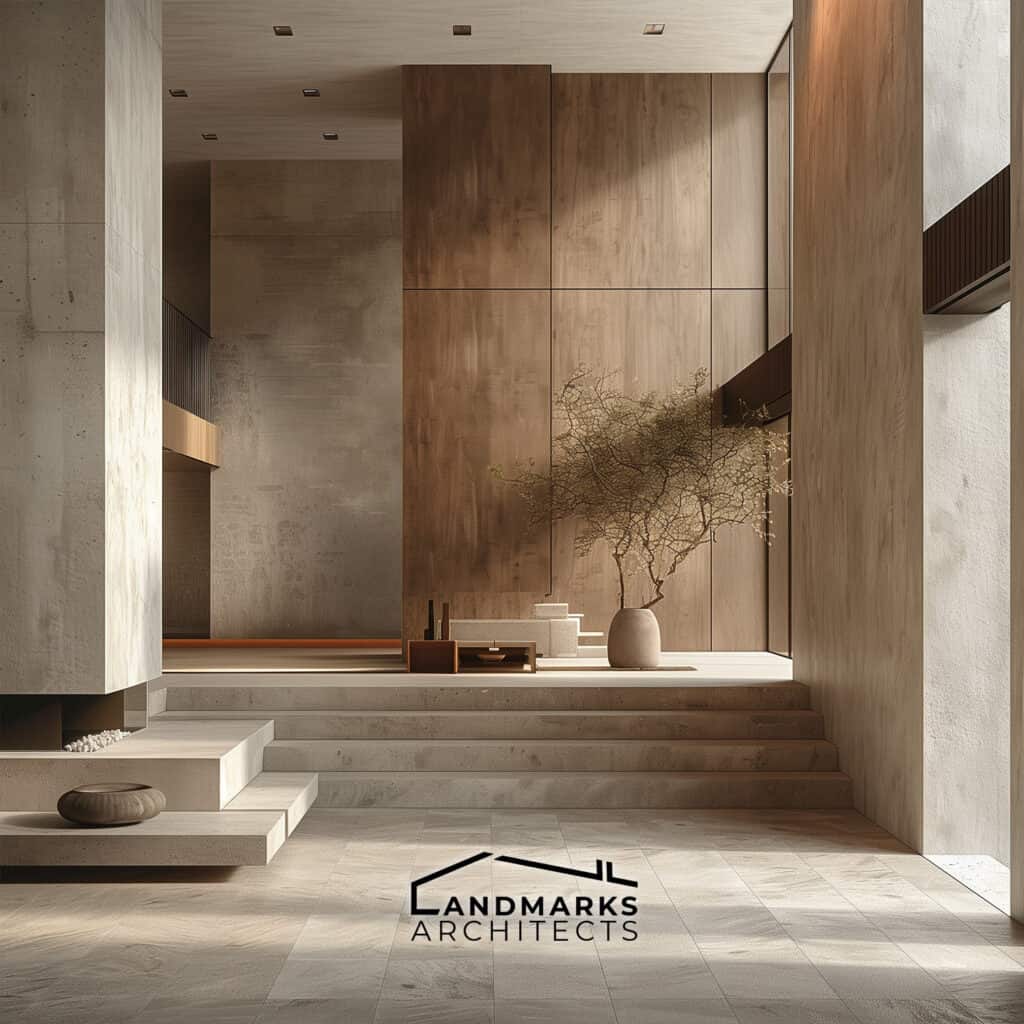

Modernist architecture has two key features: linear forms and horizontal lines. They create simplicity and elegance. Flat roofs and basic geometric shapes contribute to a streamlined appearance. Horizontal lines in modern buildings connect them to the landscape.
They reflect a belief in integrating with the environment.
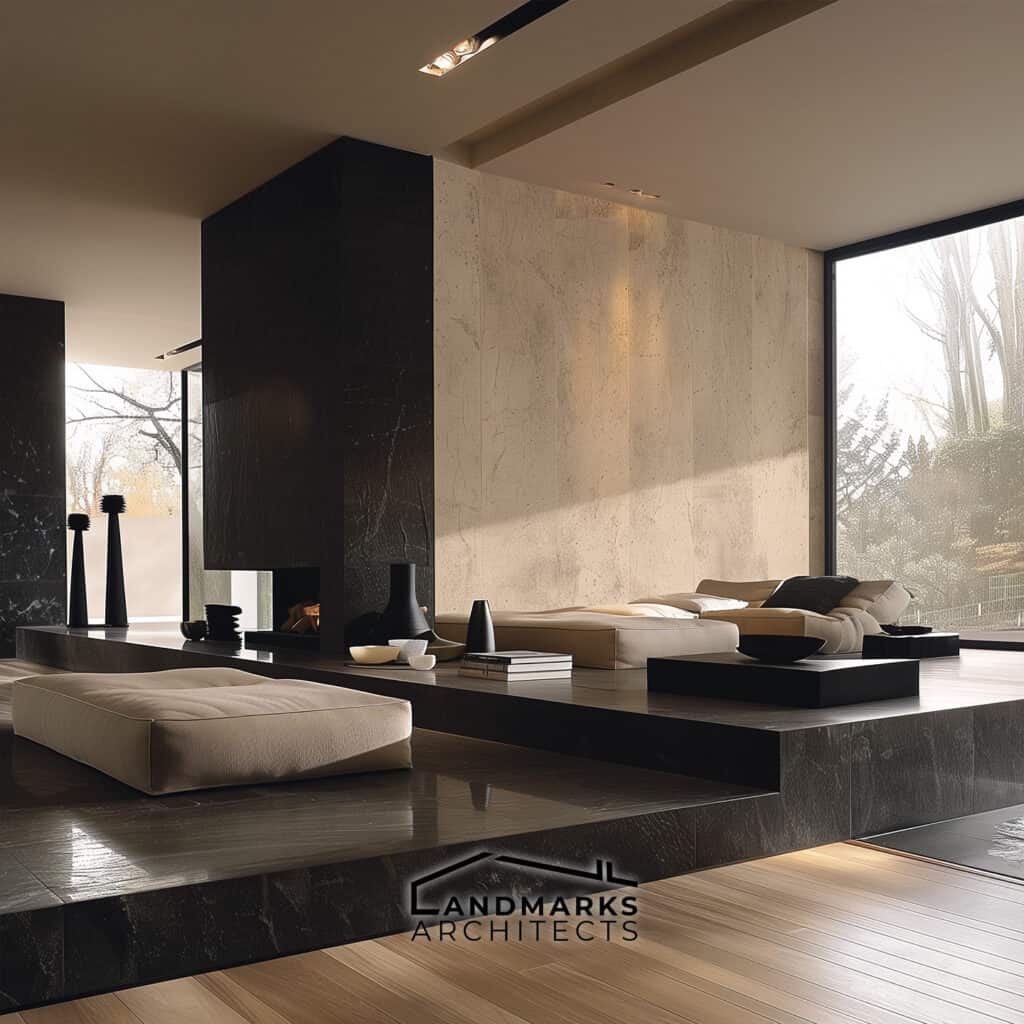

They promote a minimalist look. They highlight the movement’s focus on function and clarity. Together, they define modernist design and its enduring influence on contemporary architecture.
See also Modern Church Ideas: Exploring Modern Church Interior Design
6. Harmonization with the Environment
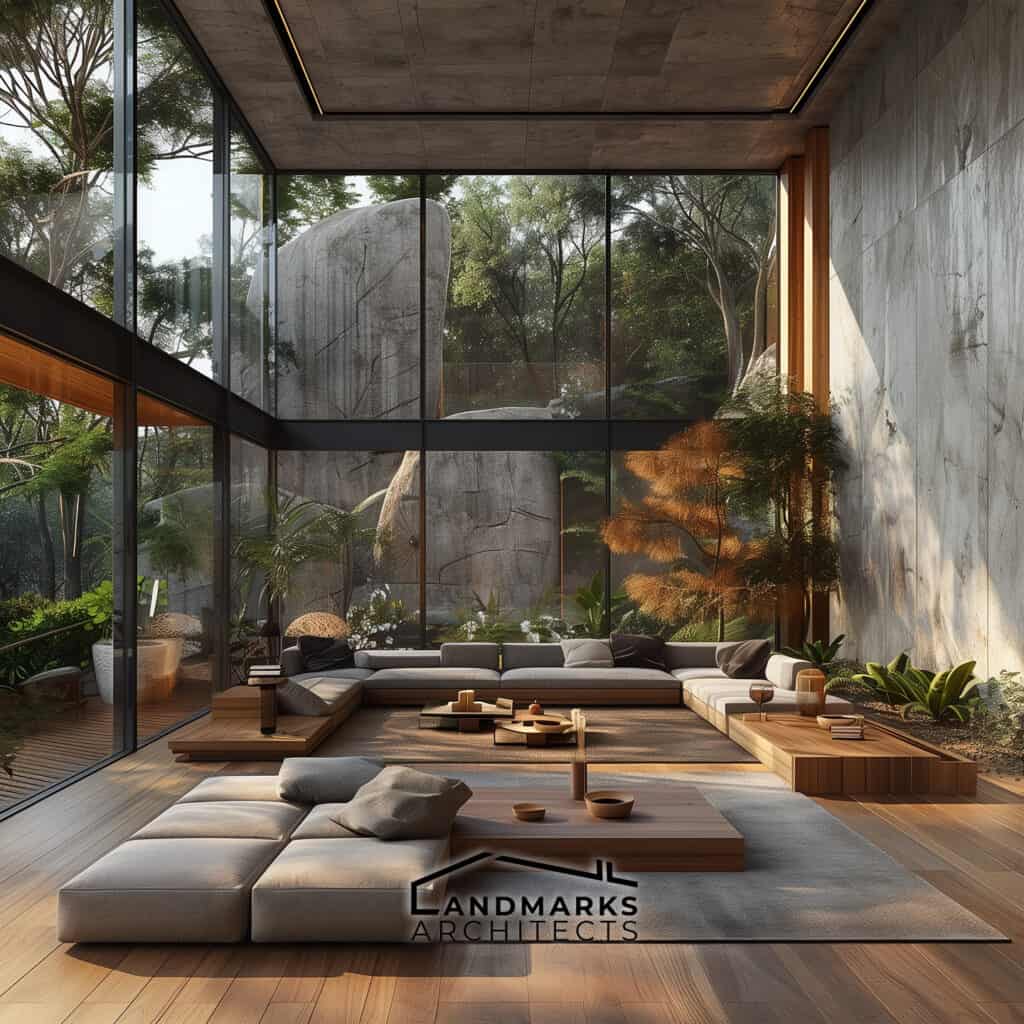

Modernist architecture often emphasizes a strong connection with the surrounding environment. This concept is a fundamental aspect of various architectural styles, particularly organic architecture.
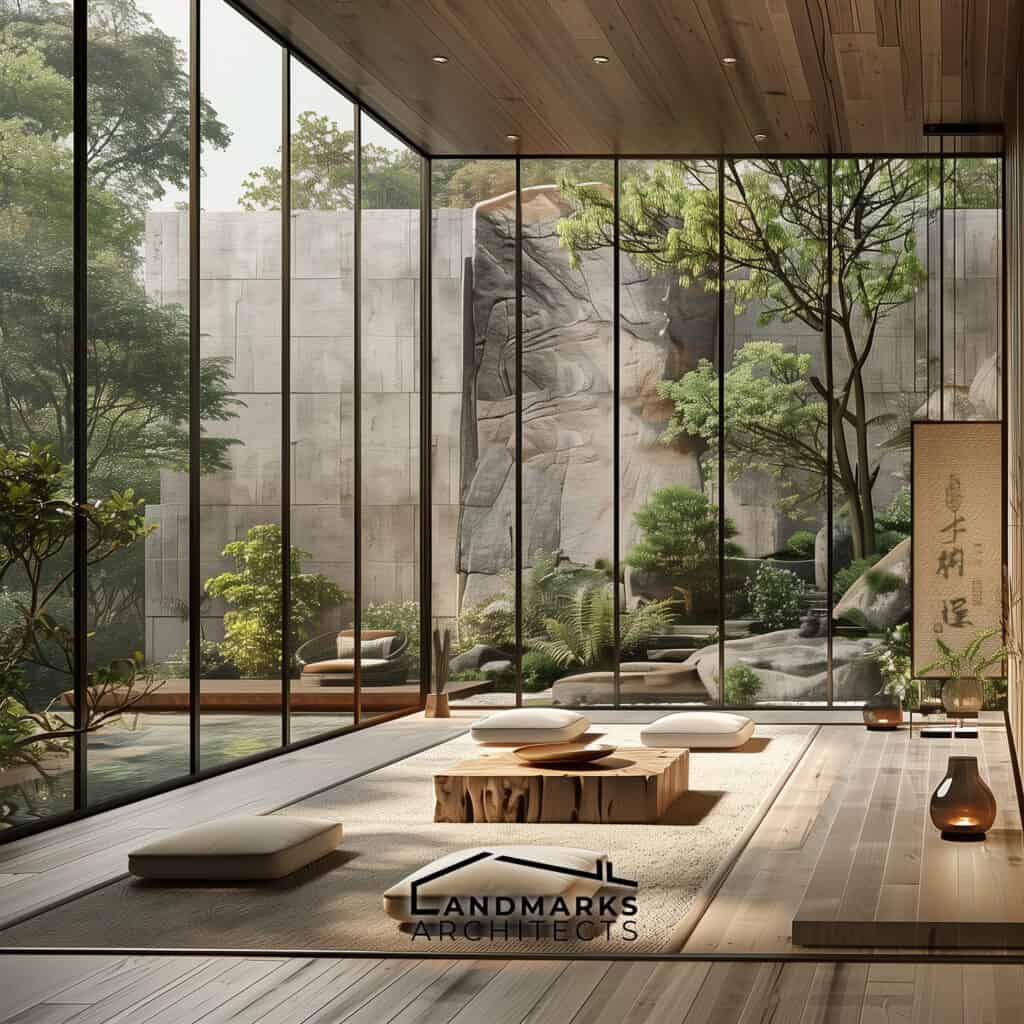

Architects, such as Frank Lloyd Wright, championed these principles in their designs. His work exemplifies the idea of blending with nature, creating spaces that harmonize with the landscape. This approach stresses the need to live in harmony with nature. It also values the natural elements in architecture.
7. Elimination of Decorative Elements

Modernist architecture emphasizes the rejection of ornamentation. This approach simplifies structures, drawing attention to their functional elements and materials.

The International Style indeed promoted minimalism and functionality in architecture. This types of architectural styles became globally recognized for its emphasis on volume over mass, balance rather than preconceived symmetry, and the absence of ornamentation.
Modernist architecture can express beauty through minimalism. Iconic works, like Ludwig Mies van der Rohe’s glass box designs, show this.
8. Clarity and Order in Design

Clarity and order are essential to modern design, as emphasized by modernist architects. These principles lead to simple forms. They prioritize clear, easy-to-understand designs. This enhances clarity.
Straight lines and geometric shapes improve clarity. Open floor plans promote flow and transparency. They reinforce a sense of order.
What Are the Elements of Modernist Architecture? A Recap

The modern style has left a profound impact on the architectural landscape, influencing various design approaches such as Modern Asian Architecture, Modern Georgian Architecture, Modern Victorian Architecture, and Modern Organic Architecture.
Its core elements continue to shape both modern and contemporary designs.
The modern movement rose to prominence during the Second World War, merging innovative styles with the spirit of the era. Today, modernist design continues to have a strong influence, demonstrating its lasting relevance.