Are you seeking a design philosophy that truly connects your space with nature and reflects your unique vision?
In a world of conventional, cookie-cutter buildings, finding modern architecture that harmonizes with the environment can be challenging. We are here to guide you through the process of creating a space that seamlessly integrates with its natural surroundings.
In this article, we’ll explore the eight essential elements of organic architecture, including:
- Achieving harmony with nature to create a tranquil, cohesive environment
- The principle of “form follows function” and how it influences design
- Incorporating sustainability to minimize environmental impact
- Ensuring unity and continuity between interior and exterior spaces
- The strategic use of natural materials for a harmonious aesthetic
- Embracing curvilinear forms and flowing lines to mimic natural patterns
- Designing with open floor plans for enhanced connectivity and openness
- Utilizing daylighting and natural ventilation to improve energy efficiency and comfort
Ready to explore how modern organic architecture principles can transform your design?

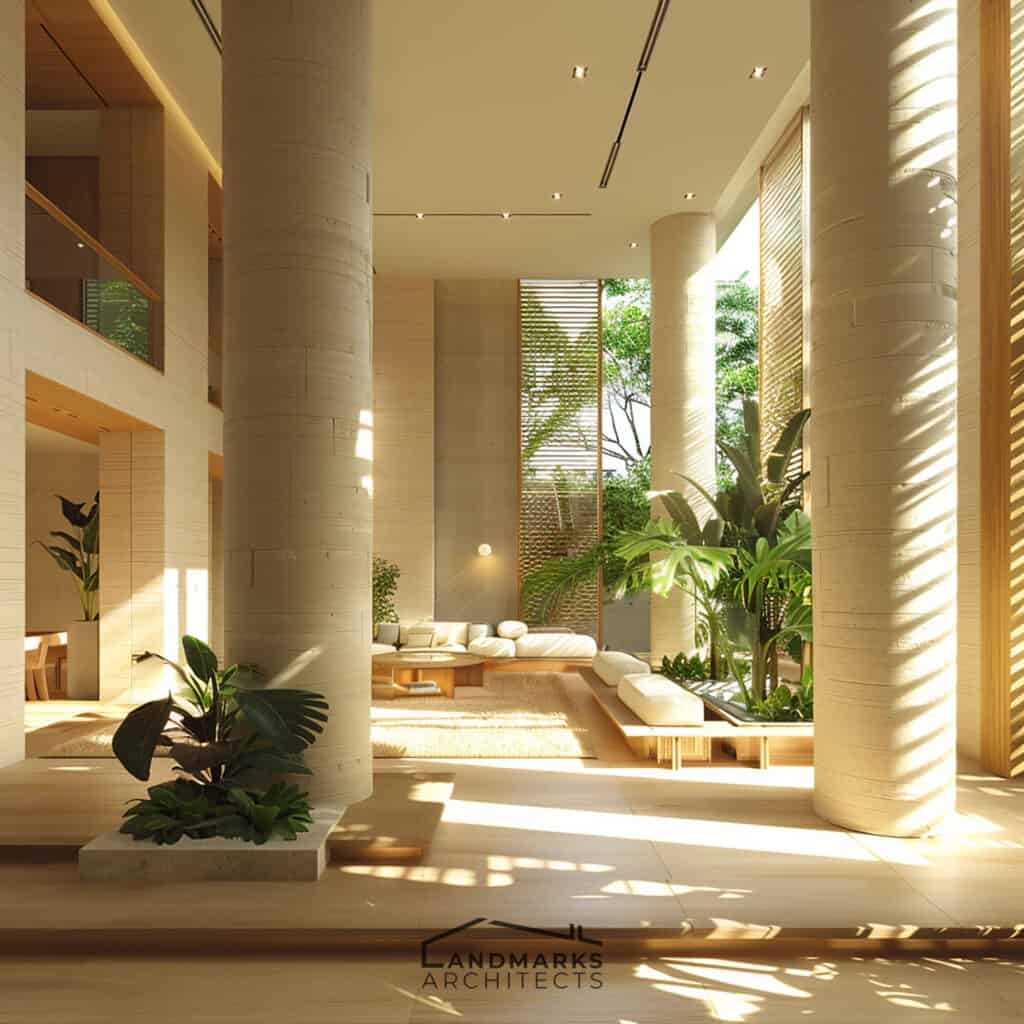
1. Harmony with Nature

Organic architecture aims to connect buildings with the natural world. This design creates a deep bond between the built environment and nature. This design philosophy blends buildings with their surrounding landscape. It creates a smooth transition between indoor and outdoor spaces.

The goal is to harmonize with the natural environment. Buildings should reflect the character of their sites. This approach respects the surrounding ecosystem. It also offers inhabitants a sense of tranquility and well-being.
See also What is modernist style in architecture? 10 key features
2. Form Follows Function
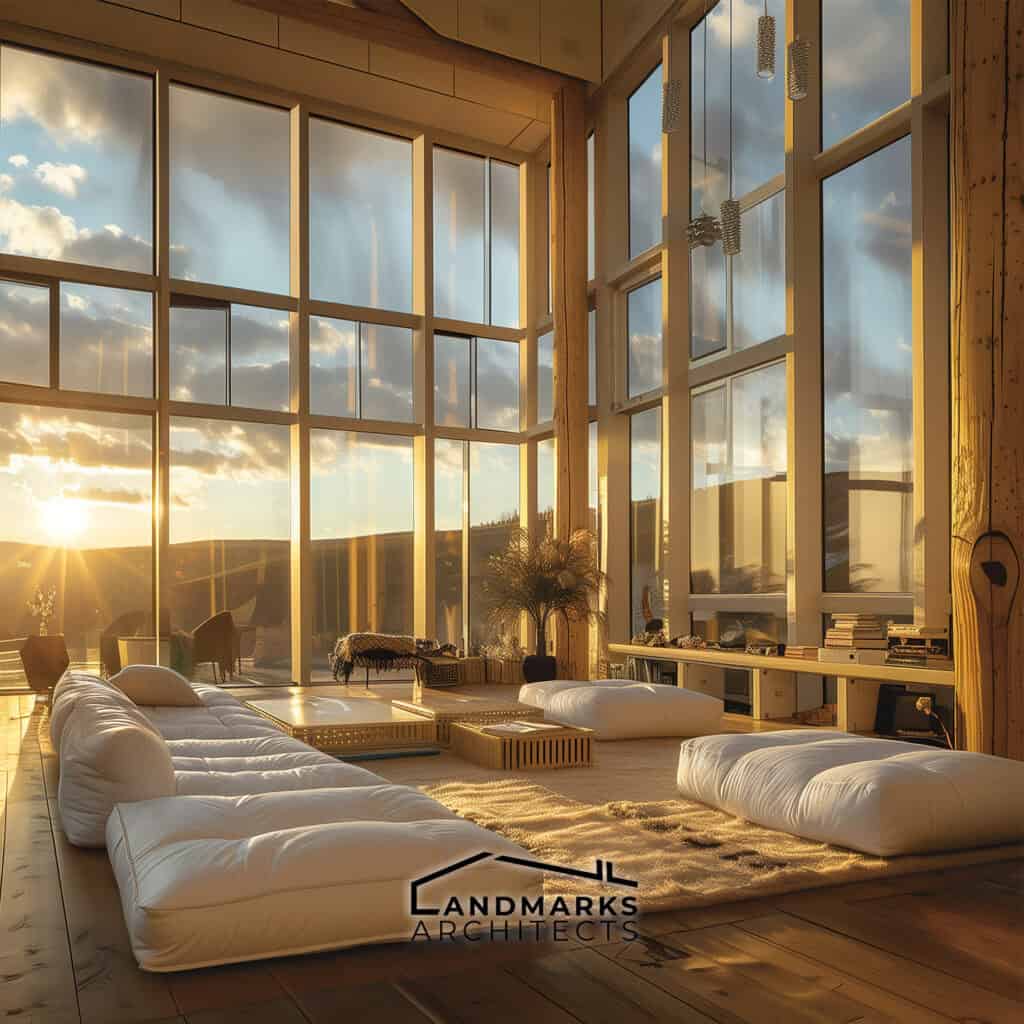

The principle of “form follows function” is key in organic architecture. It ensures that a building’s design is guided by its purpose. Organic architects prioritize functionality, strategically placing windows to maximize natural light and views. This approach balances practical beauty with environmental harmony, avoiding unnecessary ornamentation.
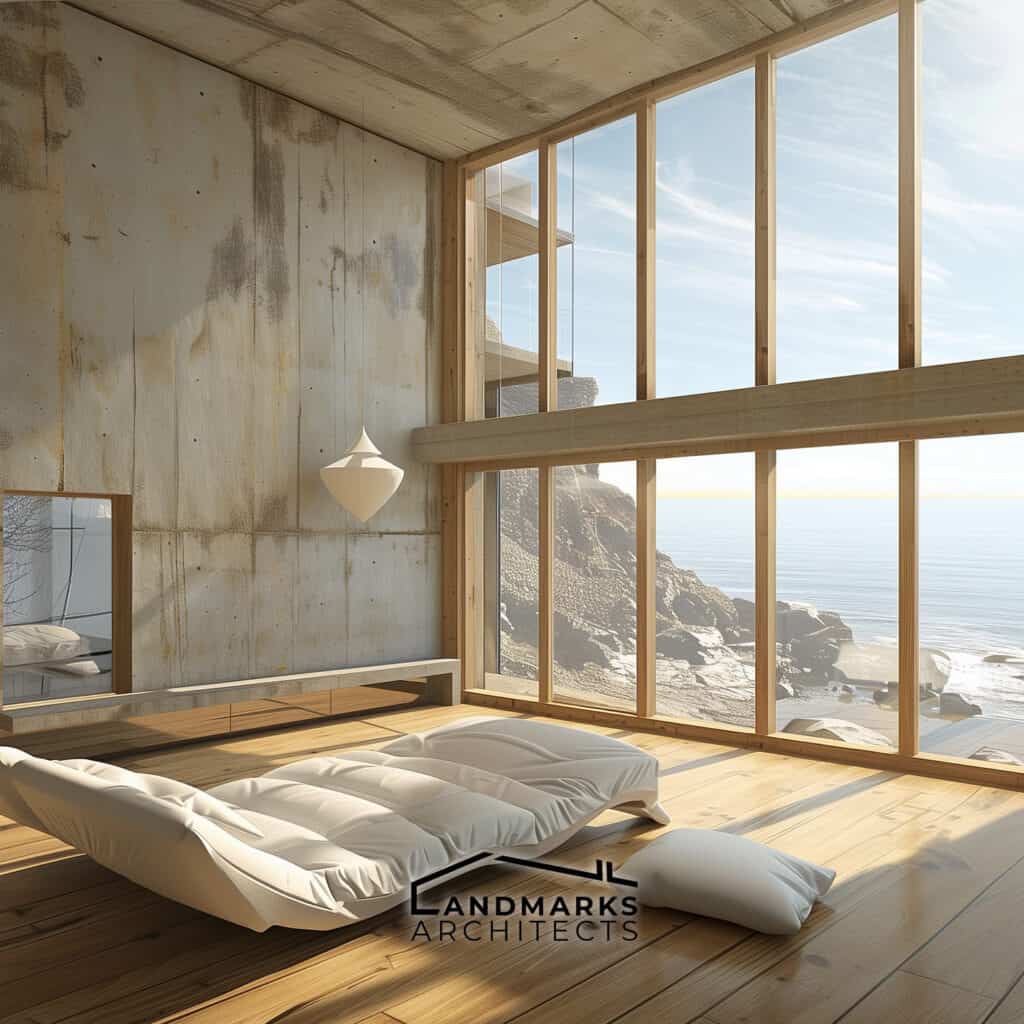

3. Sustainability in Organic Architecture

Organic architecture plays a crucial role in fostering a sustainable ecosystem by:
- Emphasizing the use of renewable, eco-friendly materials.
- Promoting energy-efficient design practices.
- Minimizing the carbon footprint of buildings.
- Reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Aiming for a reduced environmental impact.
This holistic approach ensures that architecture and the natural world coexist efficiently.
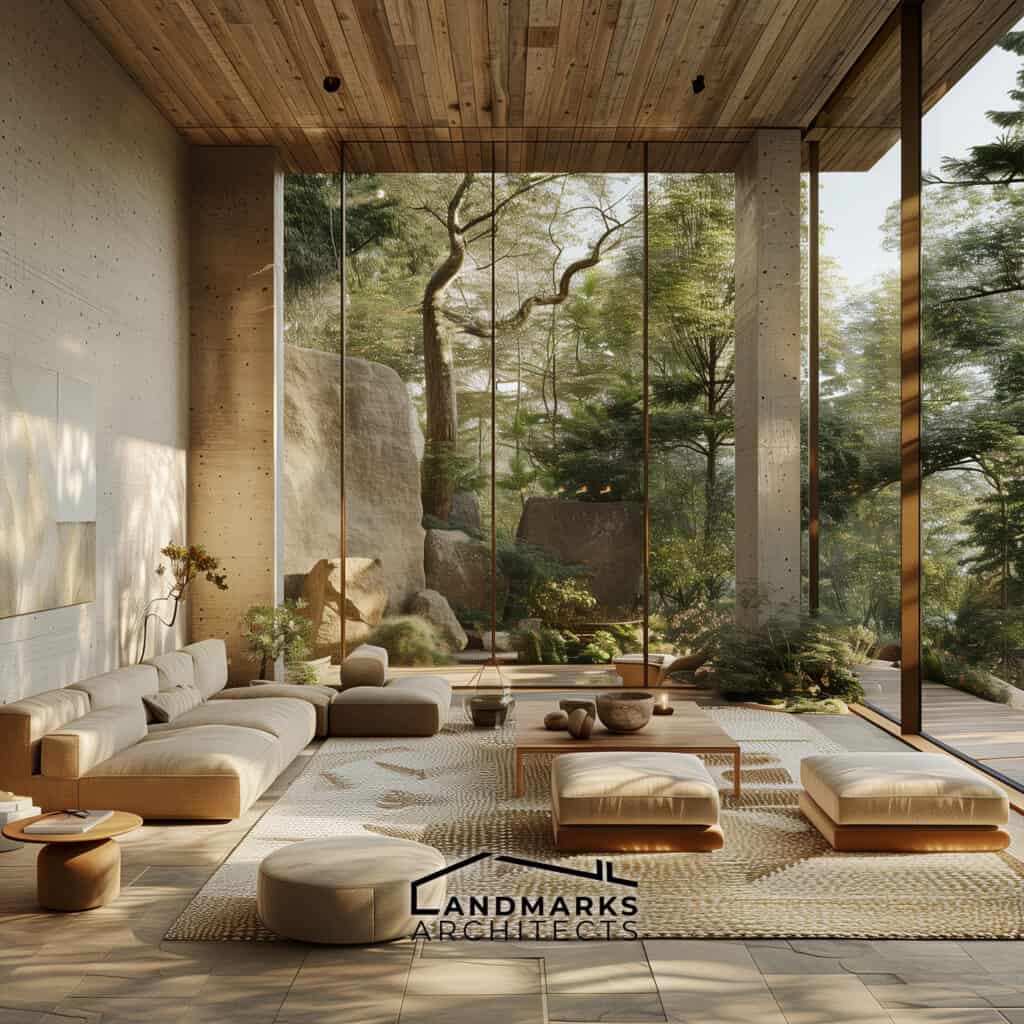
4. Unity and Continuity

Unity and continuity are key principles in organic architecture. This approach connects a building’s interior with its exterior. It integrates the built environment with nature. Organic designs improve beauty and functionality. They help spaces thrive in their natural context.

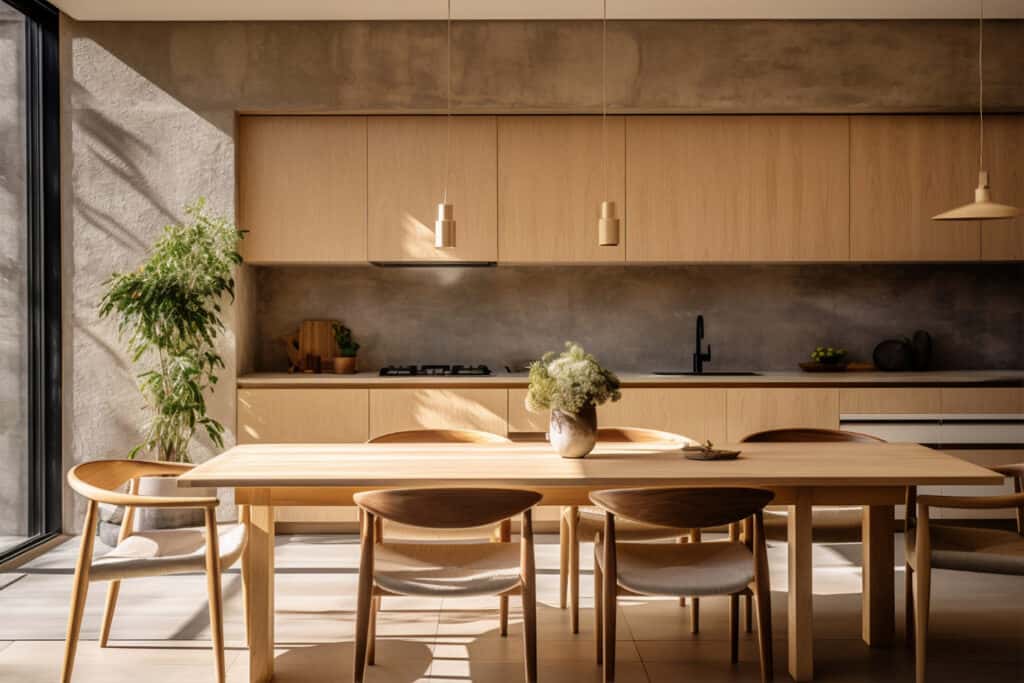
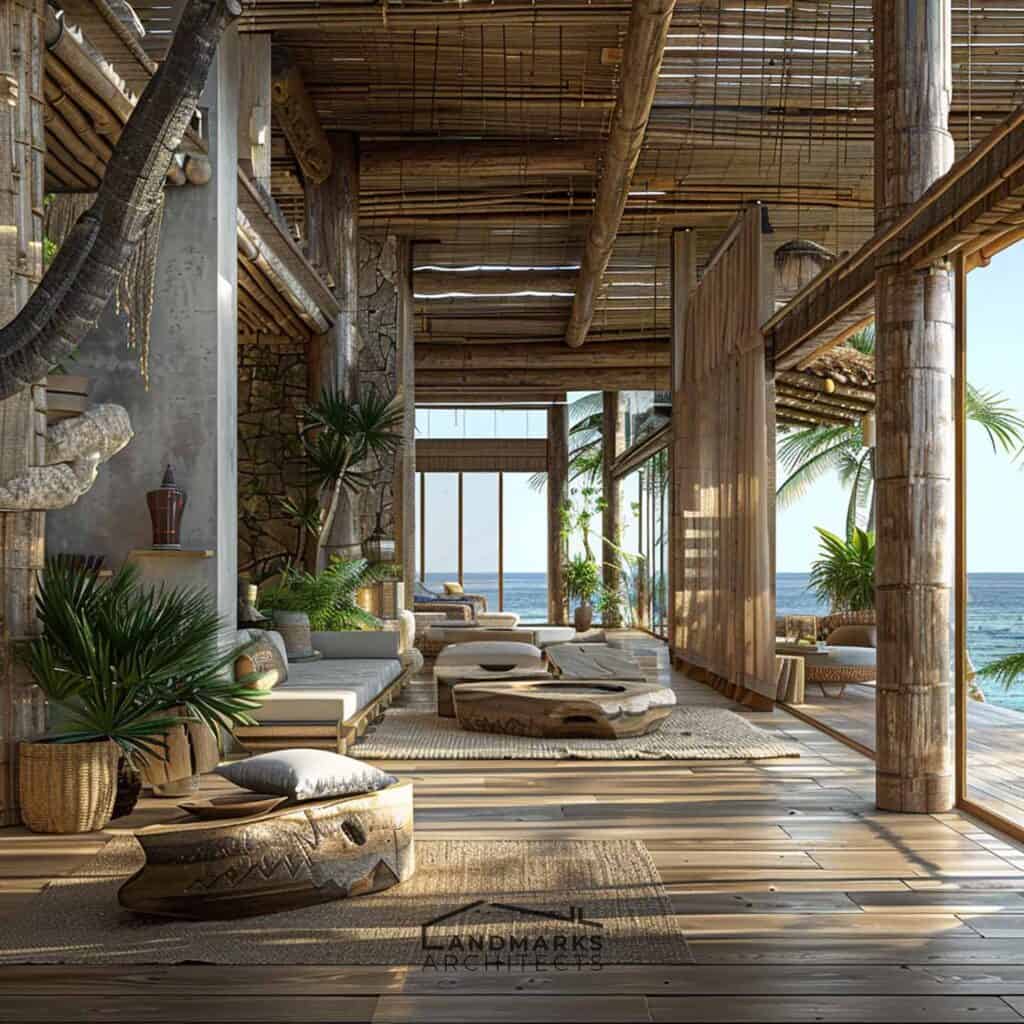
5. Use of Natural Materials
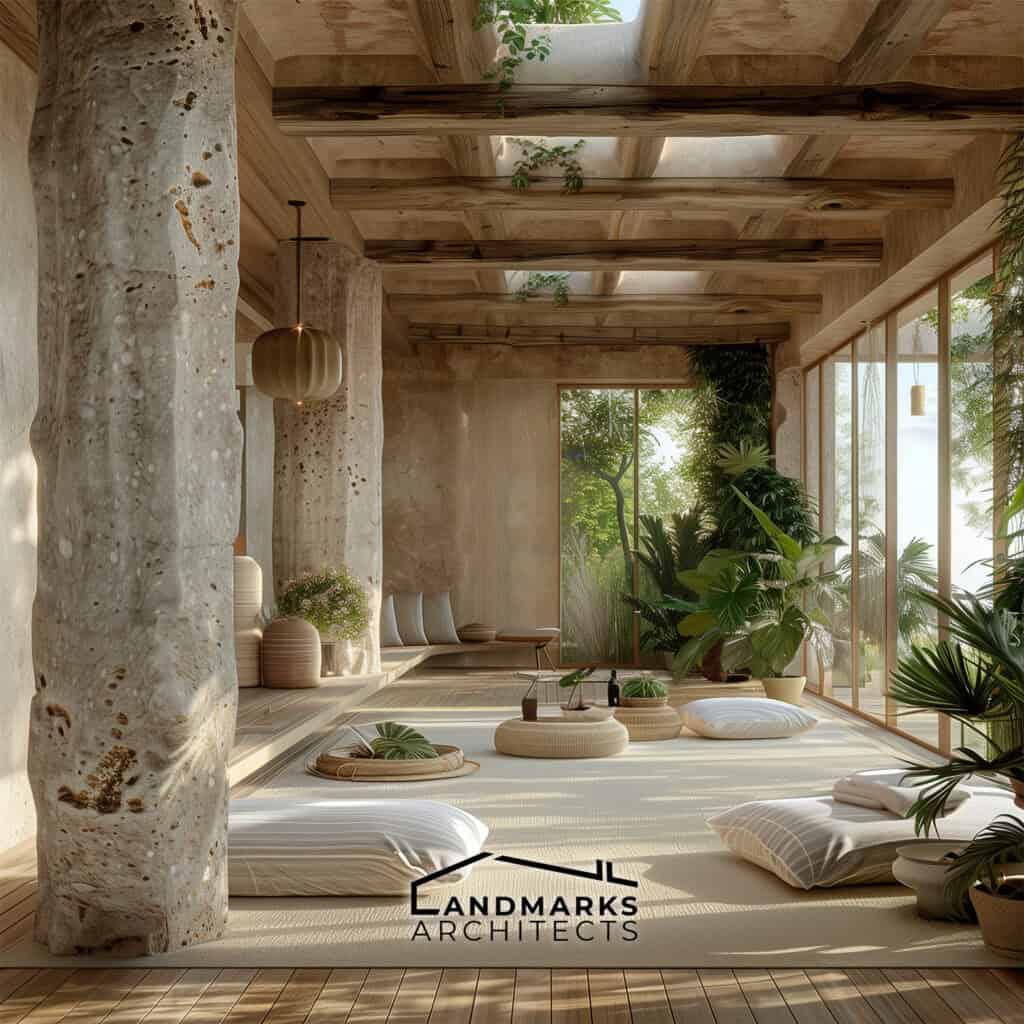

Natural materials are key in organic architecture. They help structures blend with their surroundings and support sustainability. Key elements include:
- Wood: Adds warmth and texture, promoting a natural aesthetic.
- Stone: Offers durability and integrates well with outdoor settings.
- Living Roofs and Plants: Improve air quality and connect buildings to nature.
Using bamboo or reclaimed timber lowers environmental impact. It also strengthens the structure’s link to nature.
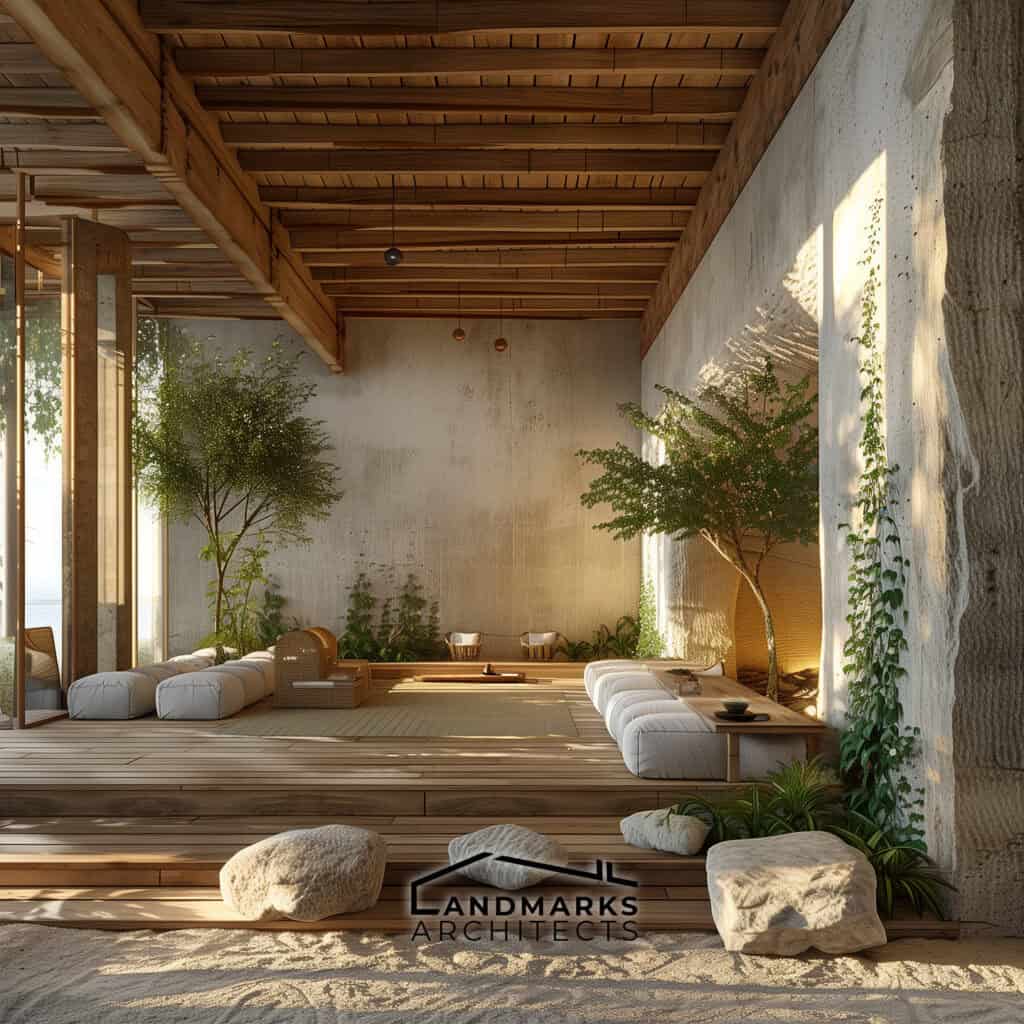

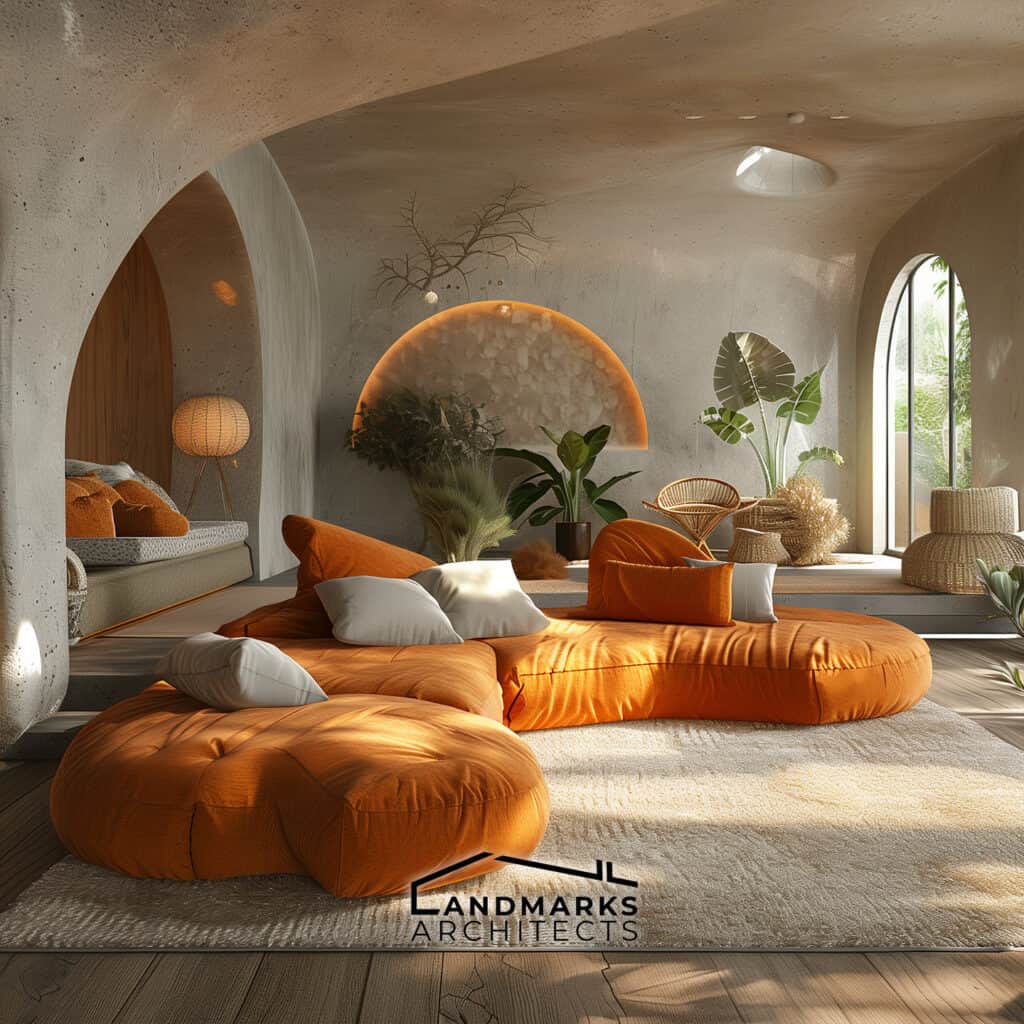
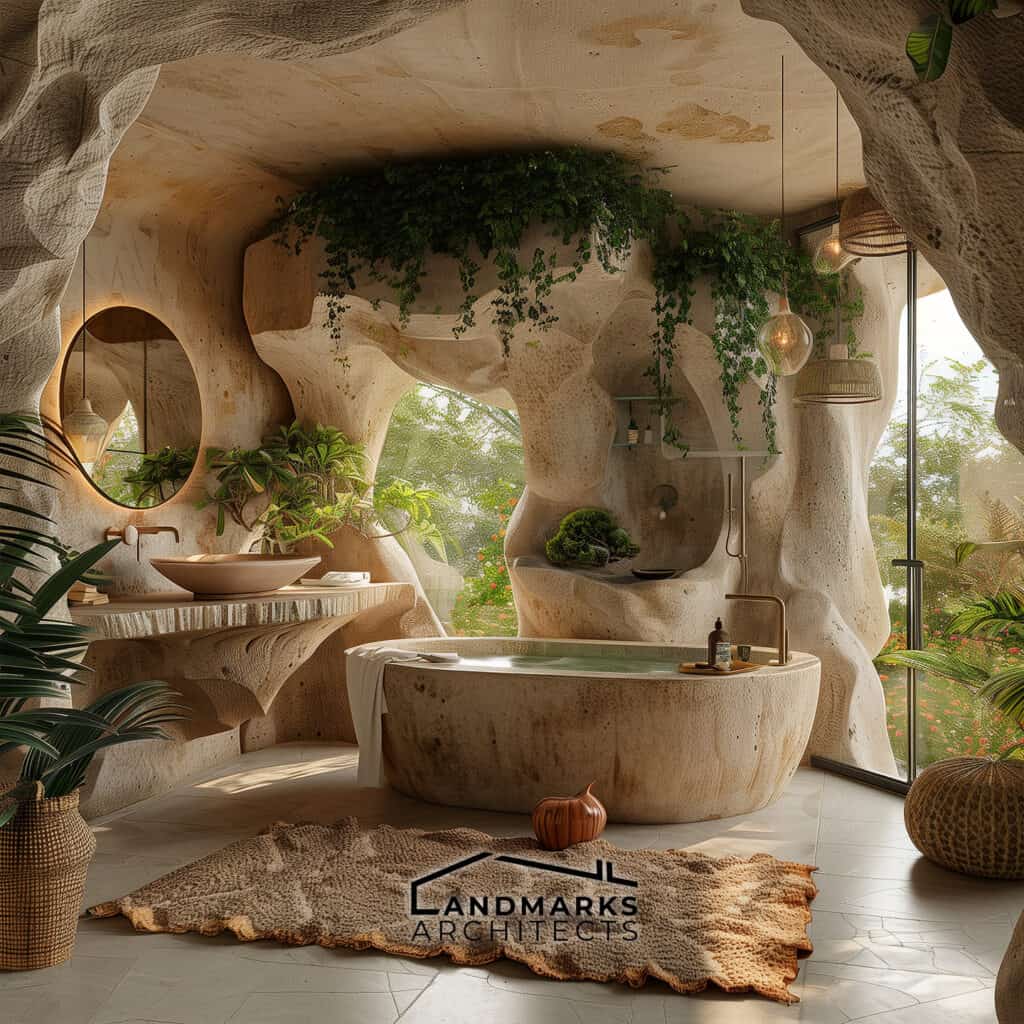
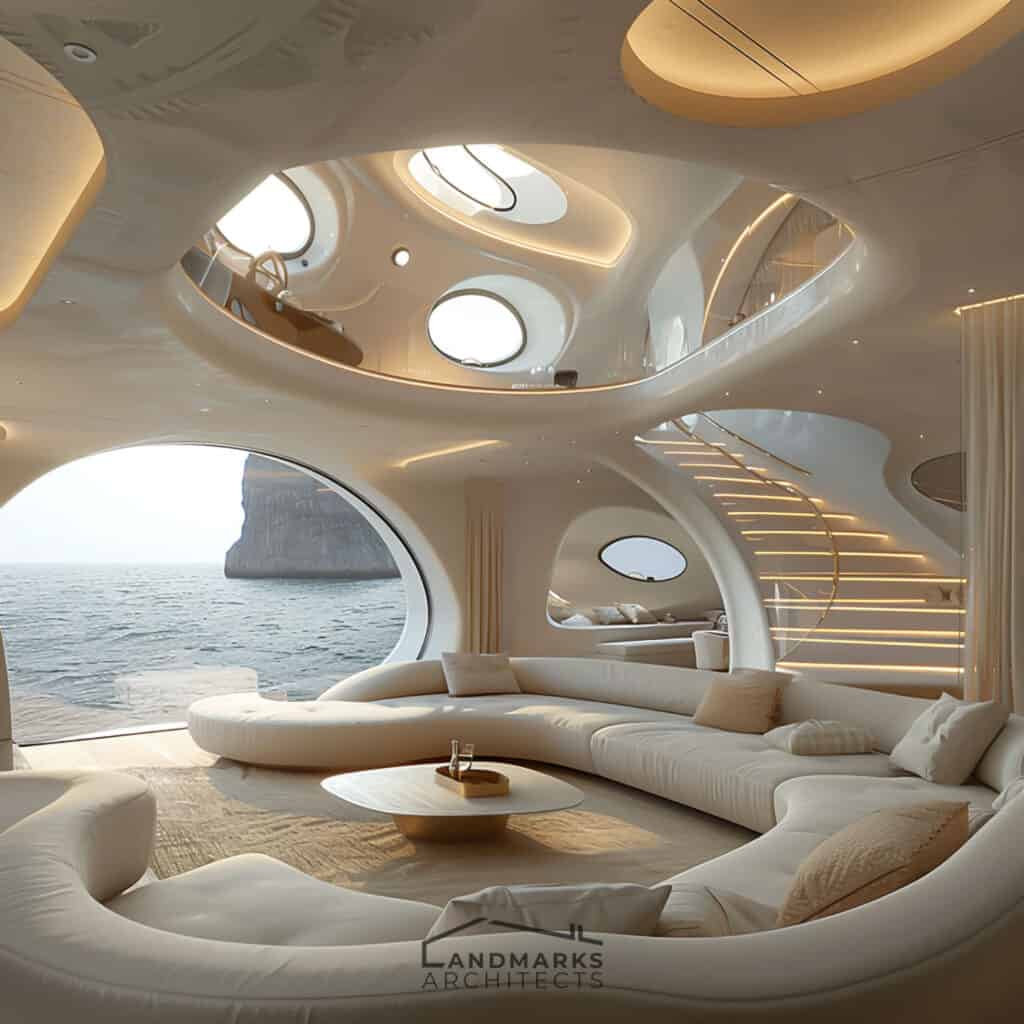
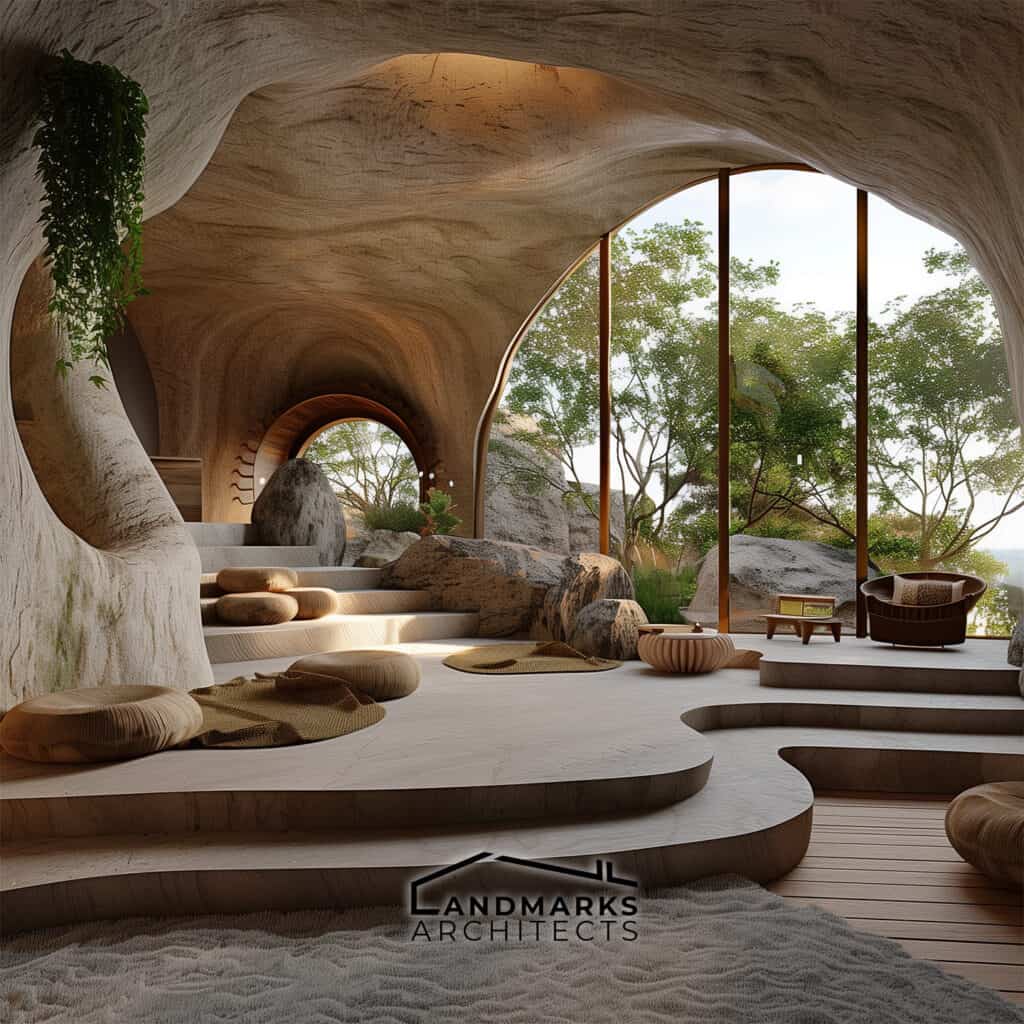
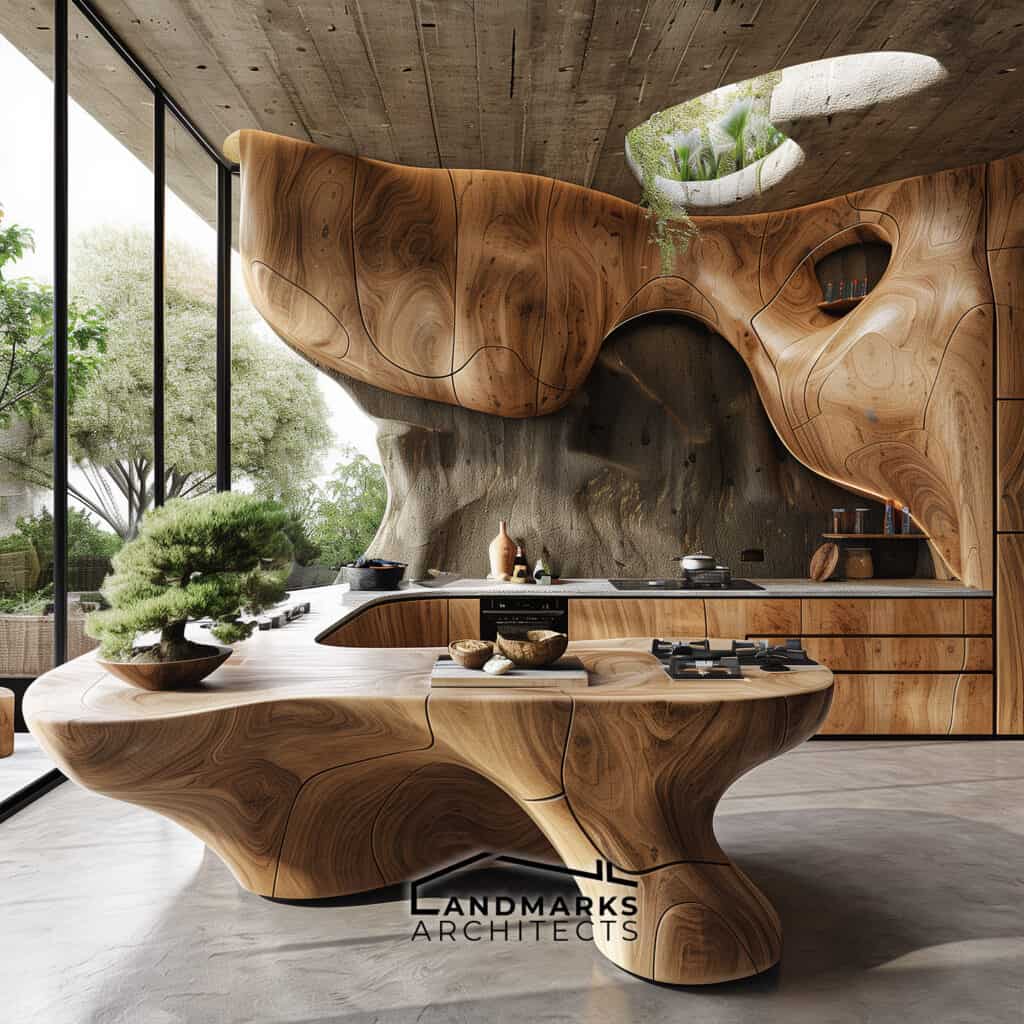
6. Curvilinear Forms and Flowing Lines
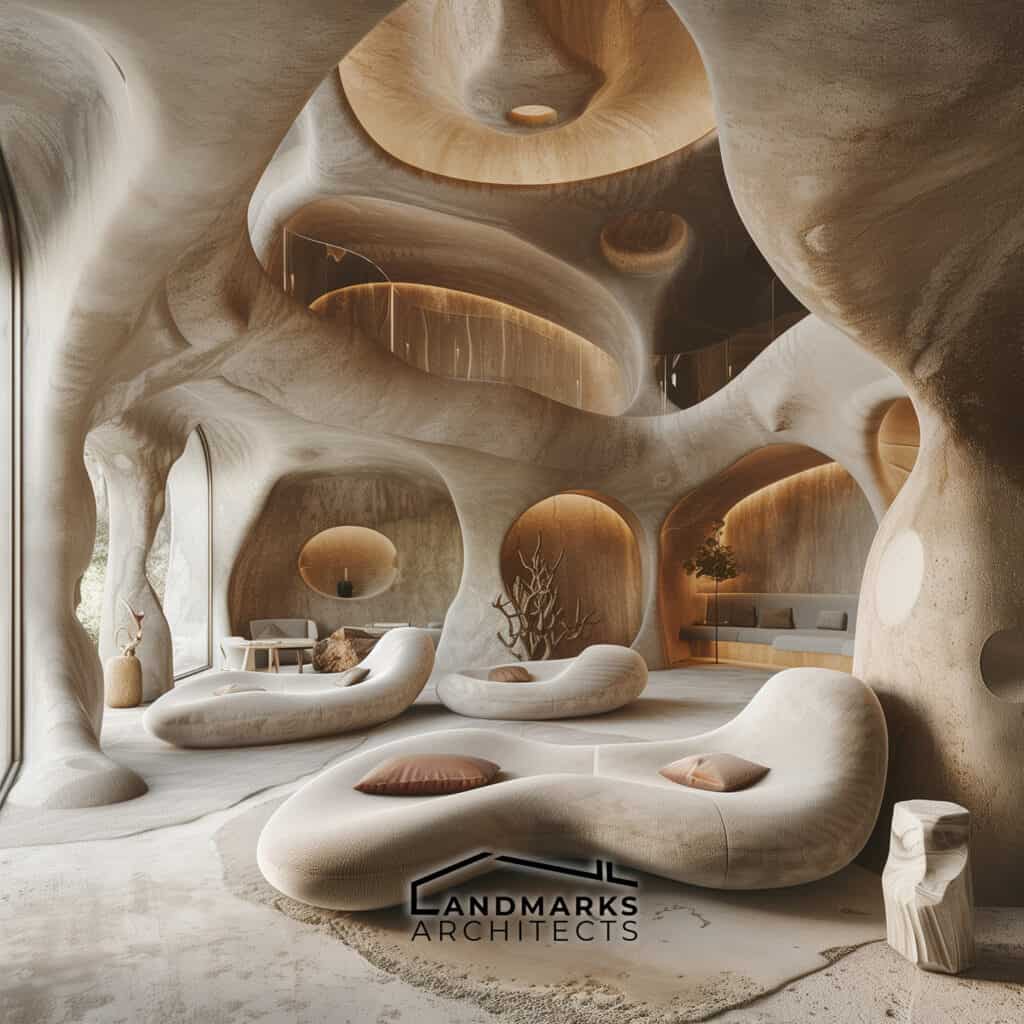

Curvilinear forms and flowing lines are essential in organic architecture. They set it apart from rigid, straight-line designs. Incorporating nature derived structures, including cave-like elements, enhances this integration. These features create cozy, intimate spaces that provide protection and comfort.
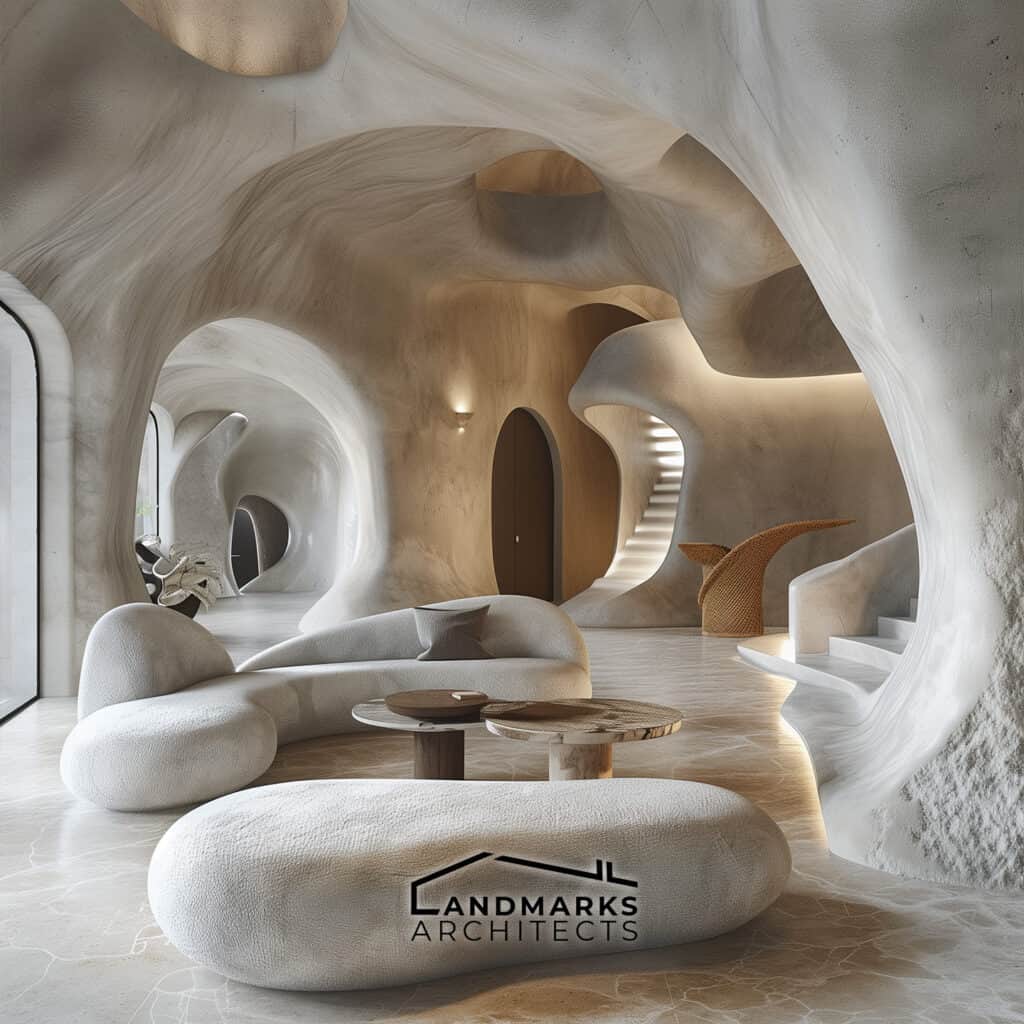

The flow of lines in the architecture mimics natural patterns, promoting a sense of calm. By embracing these design principles, spaces are not just functional. They become extensions of the natural world.
7. Open Floor Plans

Open floor plans, a hallmark of organic architecture, emphasize spaciousness and connectivity. This design removes unnecessary walls. It promotes a sense of community and enhances the connection between indoor and outdoor spaces.
It aligns with the principles of organic design, supporting harmonious living environments.
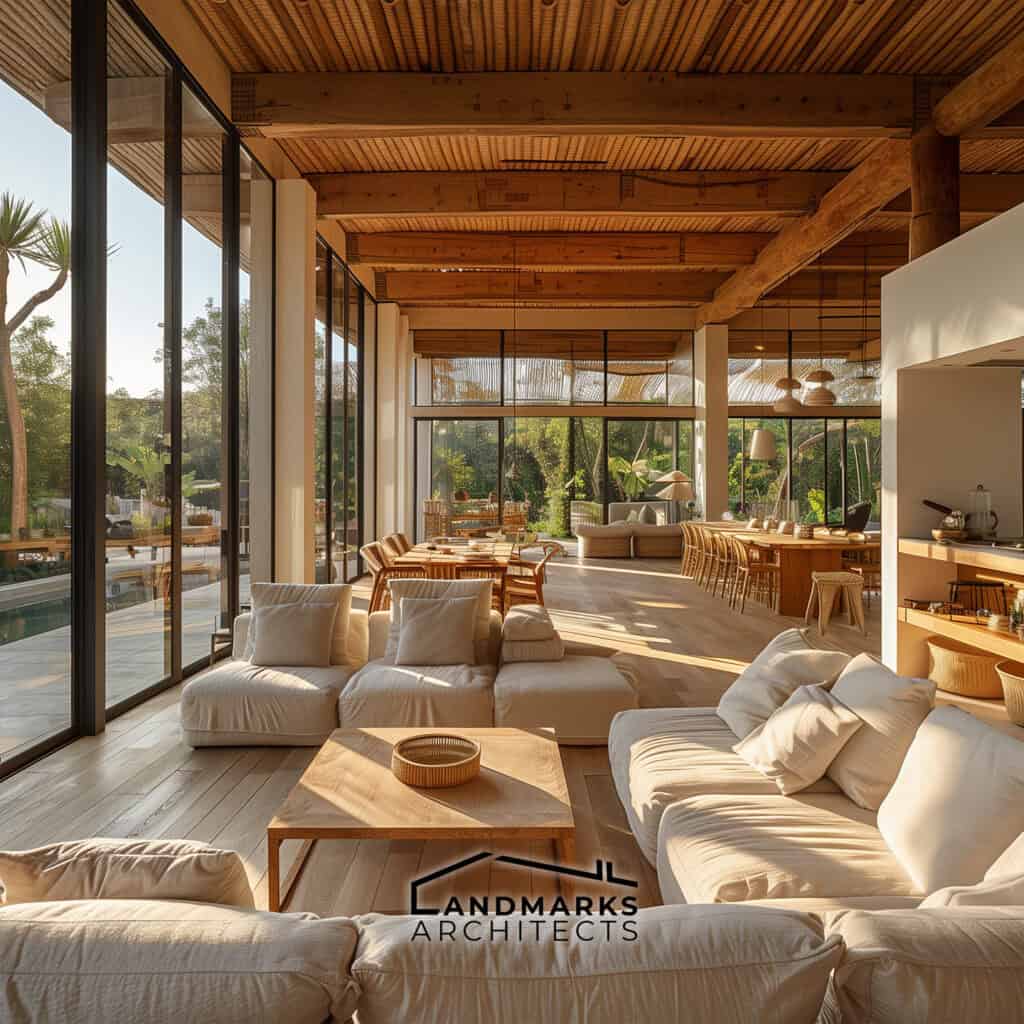

8. Daylighting and Natural Ventilation

Daylighting is key in organic architecture. It uses natural light to lessen the need for artificial lighting. This not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also improves energy efficiency.

Natural ventilation, through well-placed windows and vents, encourages airflow and natural cooling. This benefits both the environment and the well-being of inhabitants.
What Are the Elements of Organic Architecture? A Recap

Organic architecture represents a vital approach to integrating buildings with their natural surroundings.
Frank Lloyd Wright designed many examples of the organic building style, including Fallingwater. These works showcase principles he learned from Louis Sullivan. This architectural approach promotes a strong relationship between human habitation and the environment.
The enduring principles of organic architecture offer insights for creating living environments that integrate natural elements. This approach honors the earth and enhances human life.