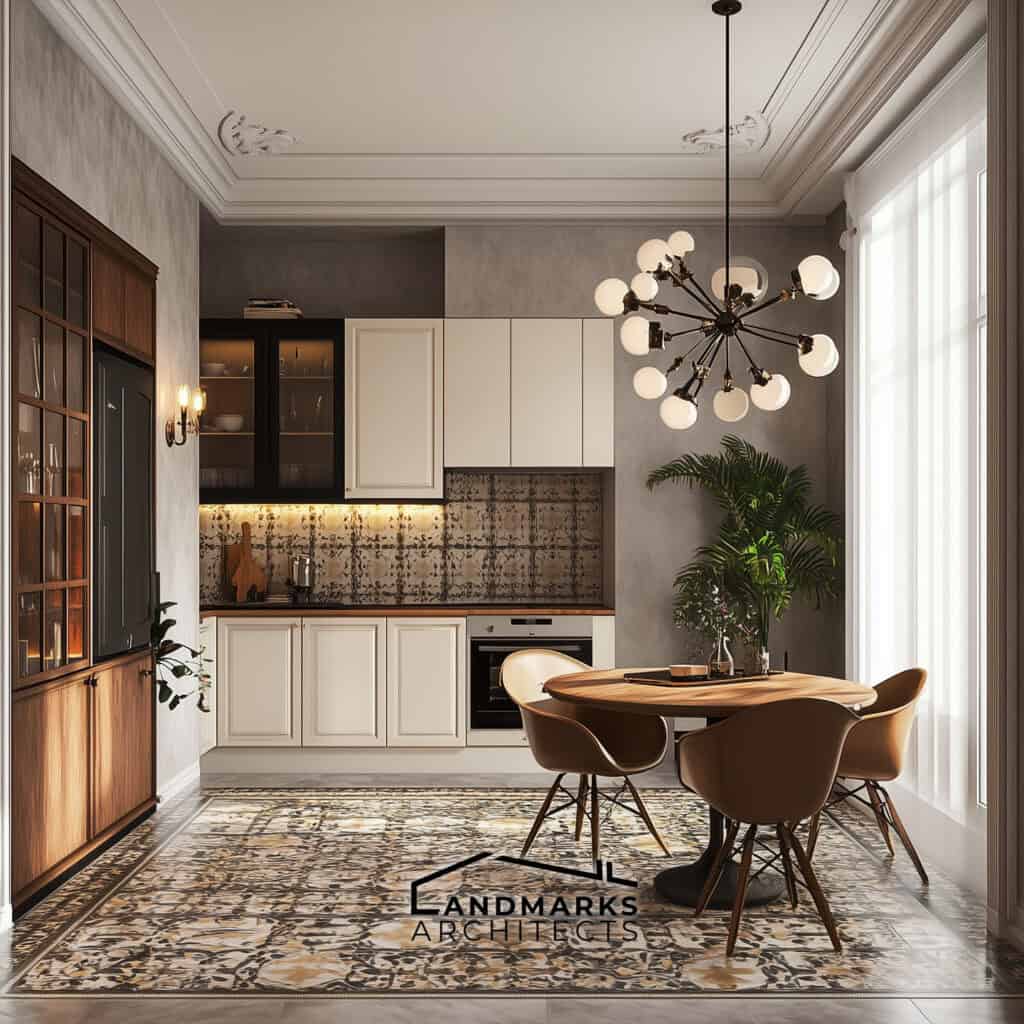
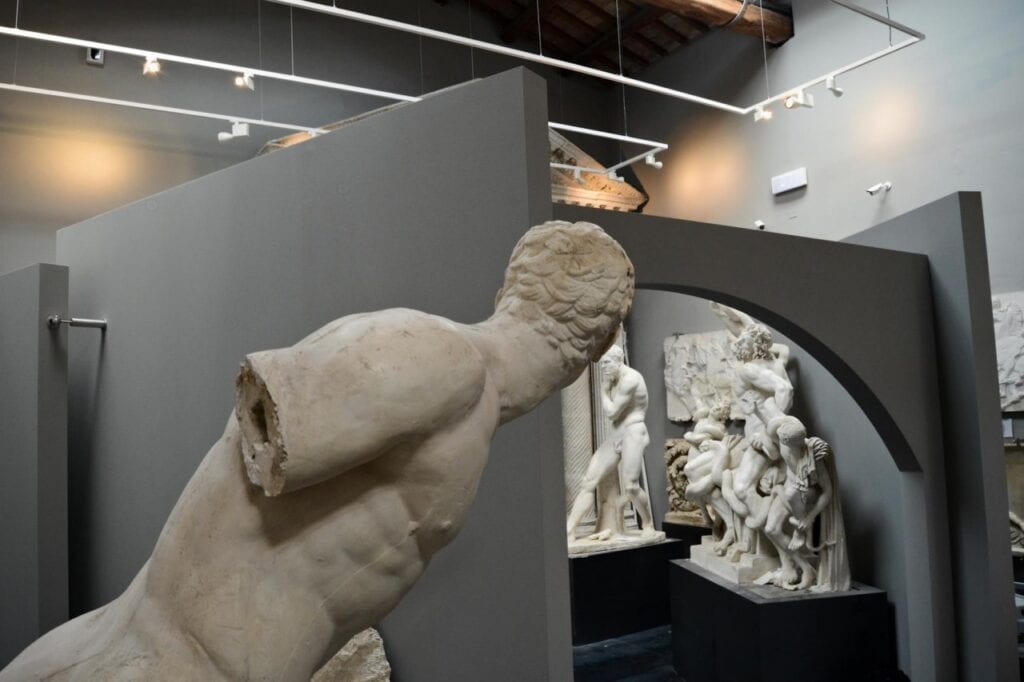
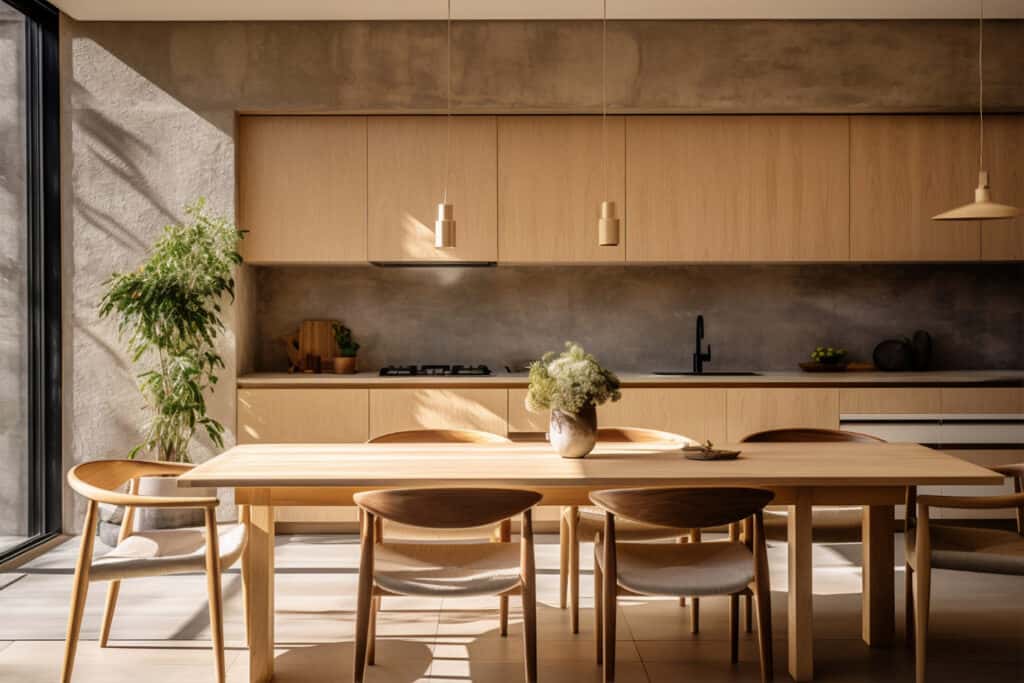
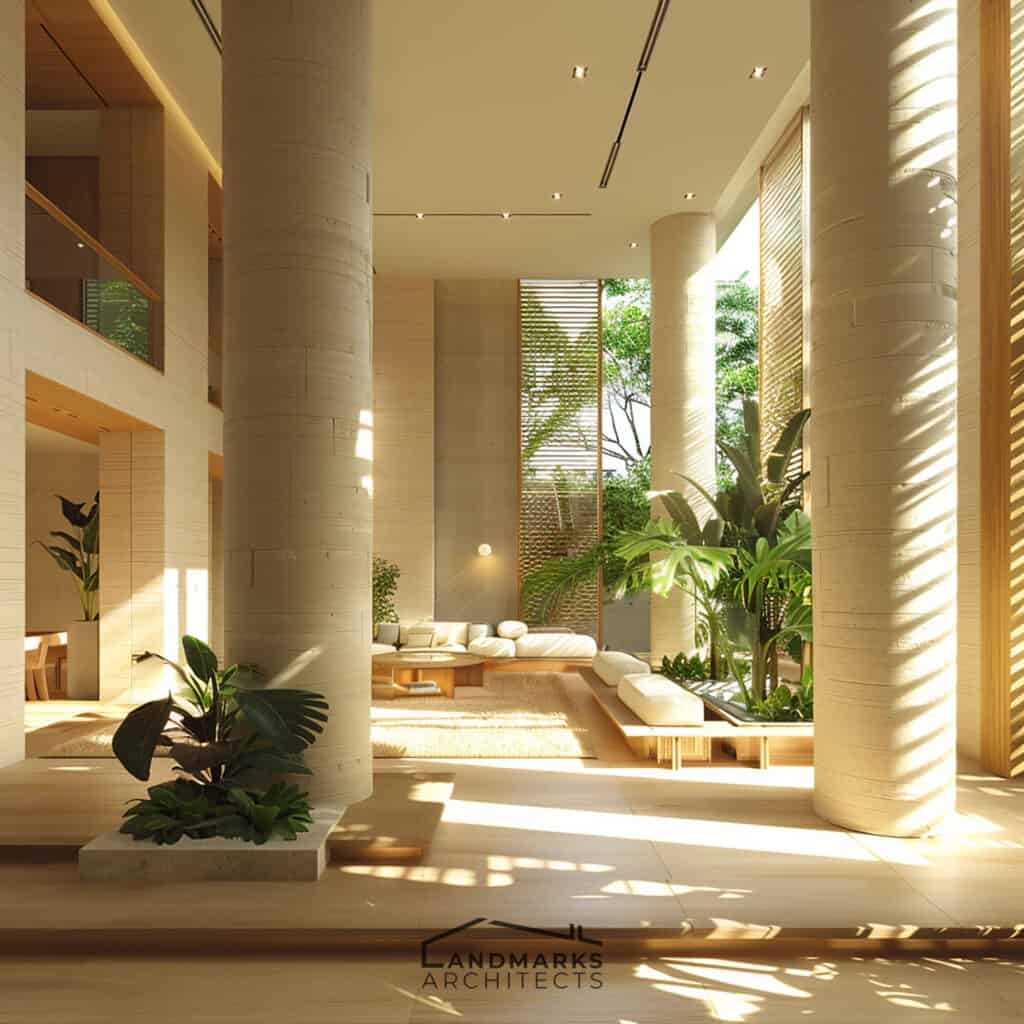
Are you drawn to architectural styles that offer more than just function, but also a touch of history and elegance?
As a discerning homeowner or design enthusiast, you strive for a space that not only meets your needs but also reflects your appreciation for timeless beauty.
At Landmarks Architect, we understand the difficulties of navigating modern architectural styles that may lack character and depth. With our expertise in vintage-inspired architecture, we assist you in combining historical charm with contemporary functionality.
In this article, we will explore:
- The essence of vintage style and its historical influences
- Key characteristics that define vintage architecture
- Common materials and color palettes that evoke nostalgia
- Architectural details and design elements that enhance vintage appeal
Ready to discover how vintage architecture can elevate your space?

Vintage Style

Vintage architecture refers to design elements that evoke a sense of the past. This architectural style often incorporates aesthetic characteristics and materials reminiscent of earlier eras, creating an inviting atmosphere.
This style has remained relevant due to its ability to blend old world charm with modern living spaces. By combining elements from various historical periods, vintage design creates unique, timeless spaces.
Historical Background
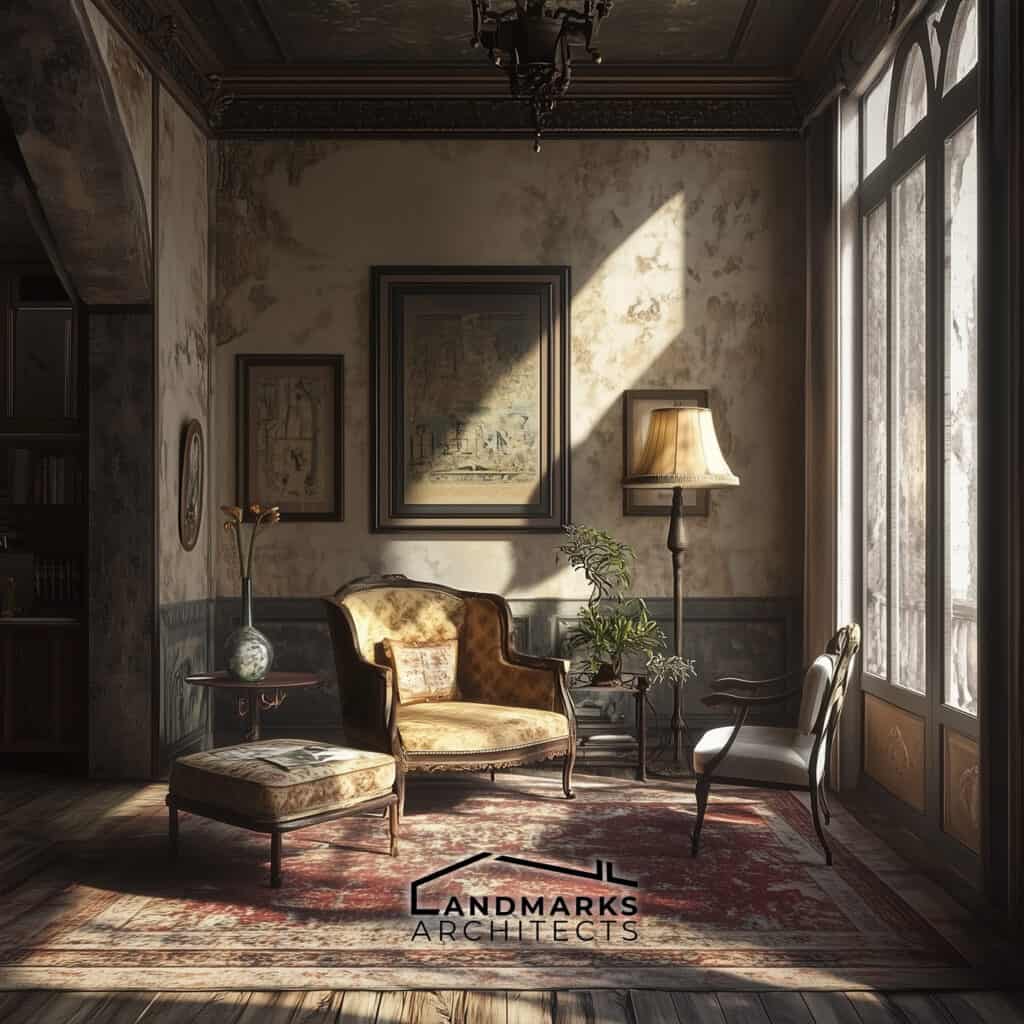

Vintage architecture draws inspiration from various historical periods and movements. These key influences are:
- Renaissance: Introduced symmetry and proportion, shaping balanced vintage designs.
- Ancient Greece: Added classical columns and structured forms, enhancing grandeur.
- Industrial Revolution: Enabled more elaborate designs, expanding vintage style.
- Modern Victorian architecture and Art Deco: Enriched vintage architecture with ornate details and bold aesthetics.
- Roaring Twenties: Infused opulence with geometric shapes and luxury finishes.
- Post World War II: Promoted clean lines and open spaces, streamlining vintage style.
- Northern Europe and British Empire: Blended local traditions with international influences, diversifying vintage architecture.
Characteristics of Vintage Style Architecture
1. Common materials
Vintage architecture often utilizes materials that reflect the building’s era and regional context. Common choices include:
- Brick: Provides durability and a classic aesthetic, often seen in colonial and federal styles.

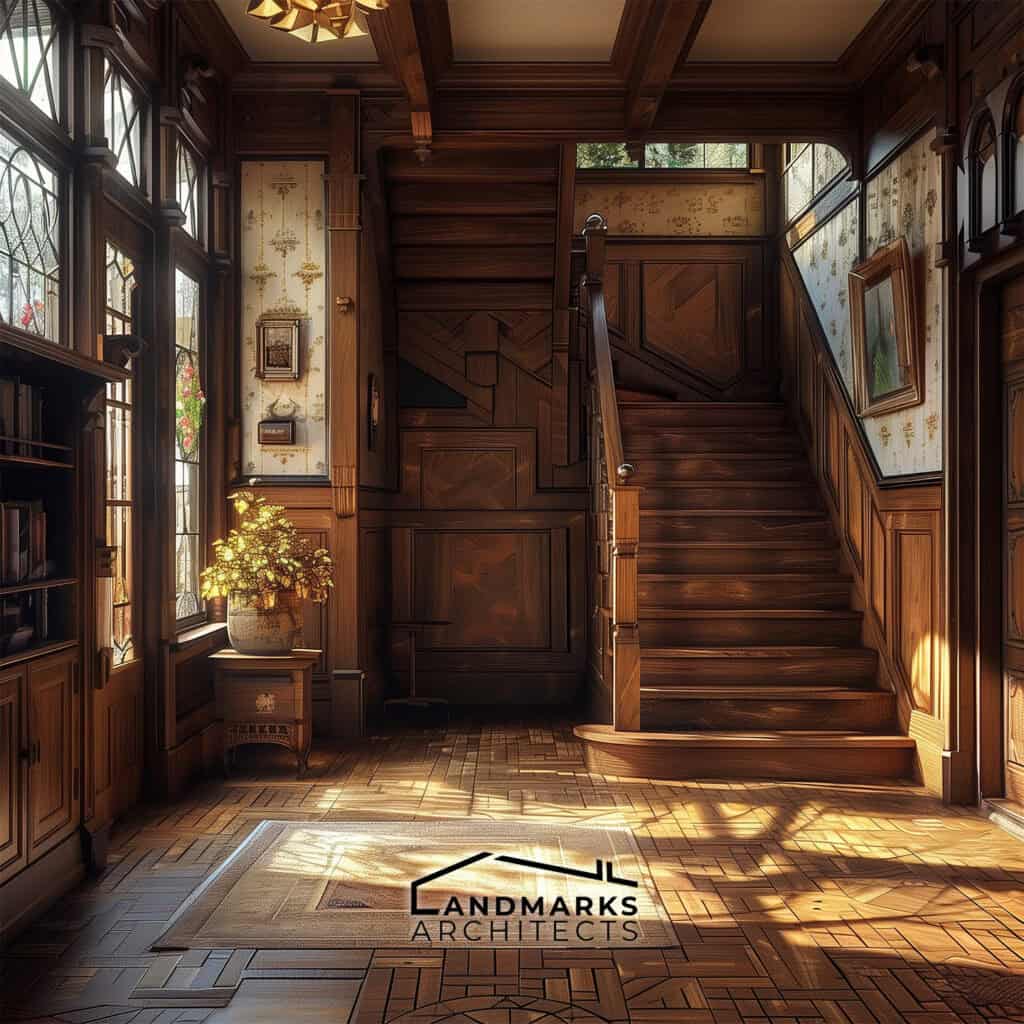
- Wood: Used for framing and siding, showcasing craftsmanship and warmth. It is prevalent in Craftsman and Victorian homes.

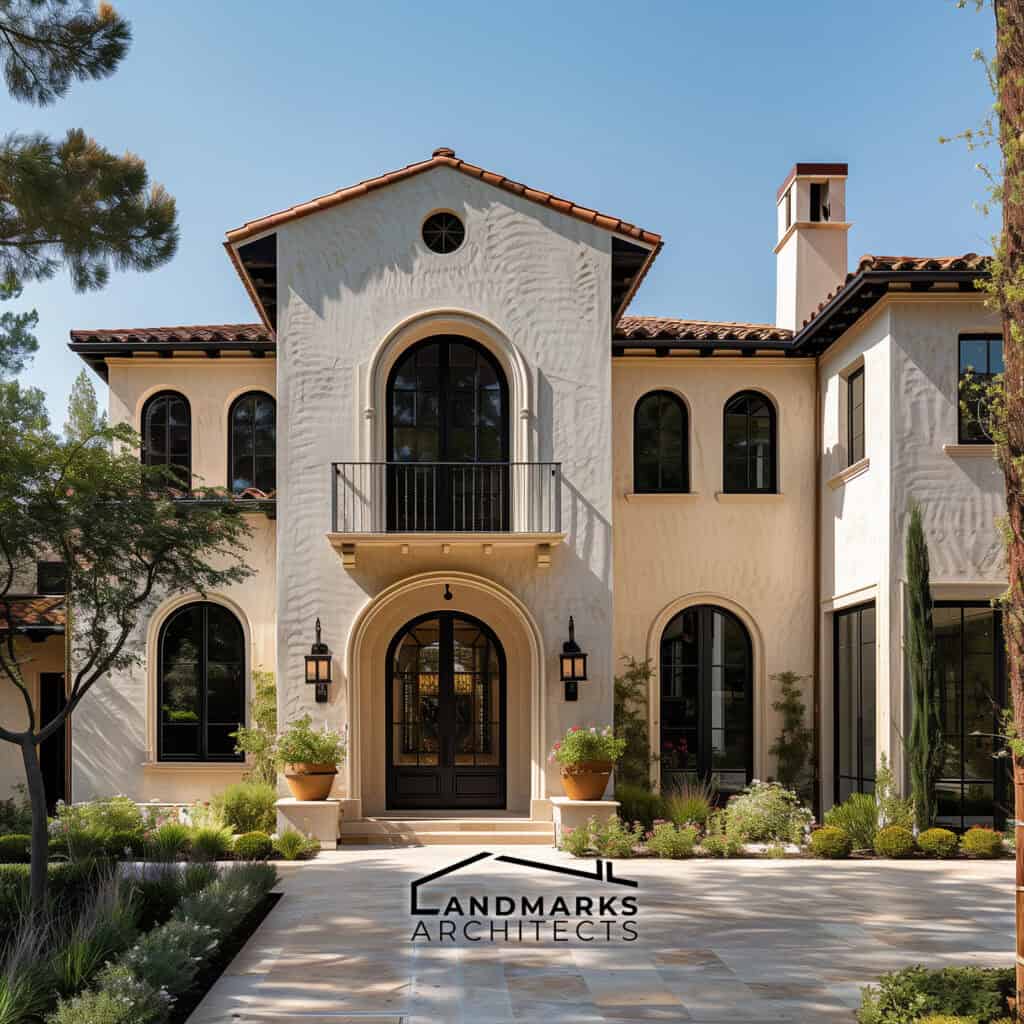
- Stucco: A common exterior finish in Mediterranean and Spanish-style architecture, it offers a smooth and textured appearance.

2. Typical color palettes
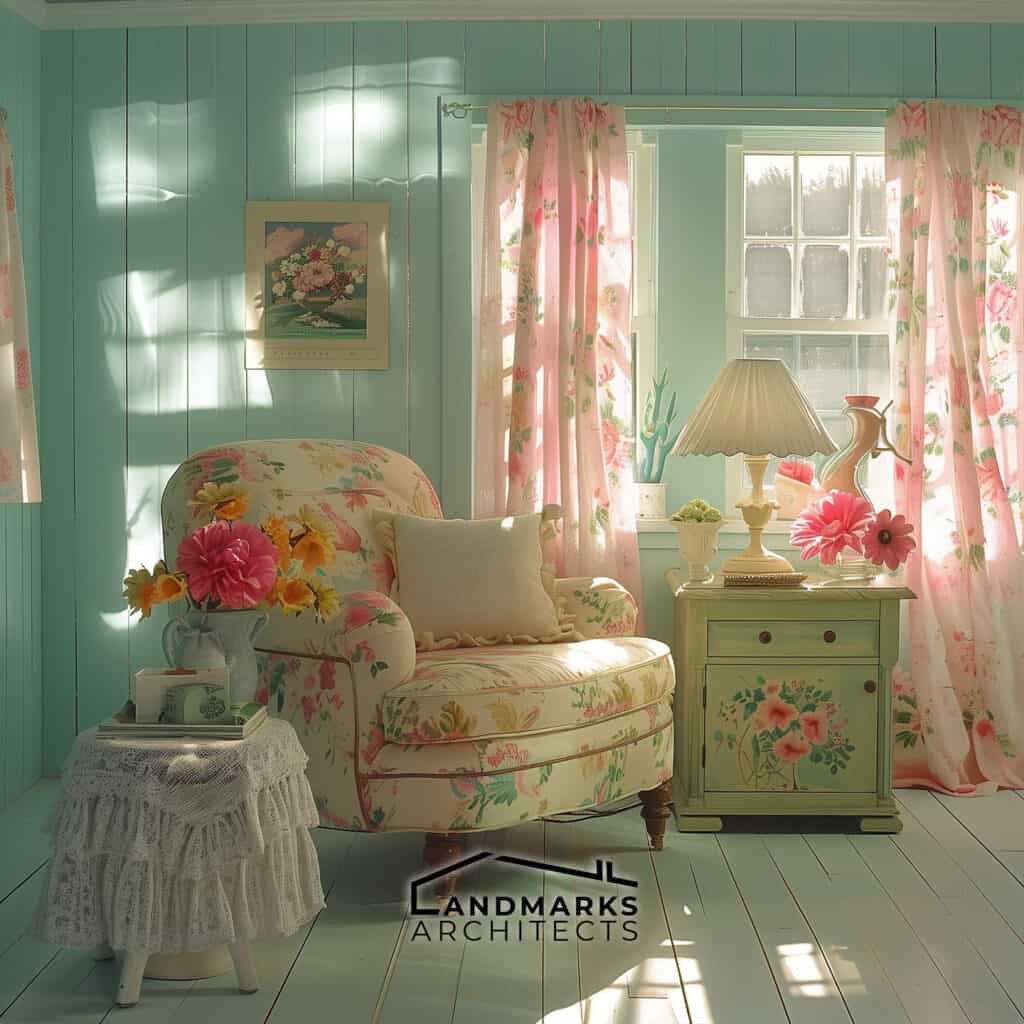
Vintage style architecture embraces a range of color palettes that evoke a sense of nostalgia. These typically include:
- Earthy tones: Shades of brown, green, and beige convey a natural look.
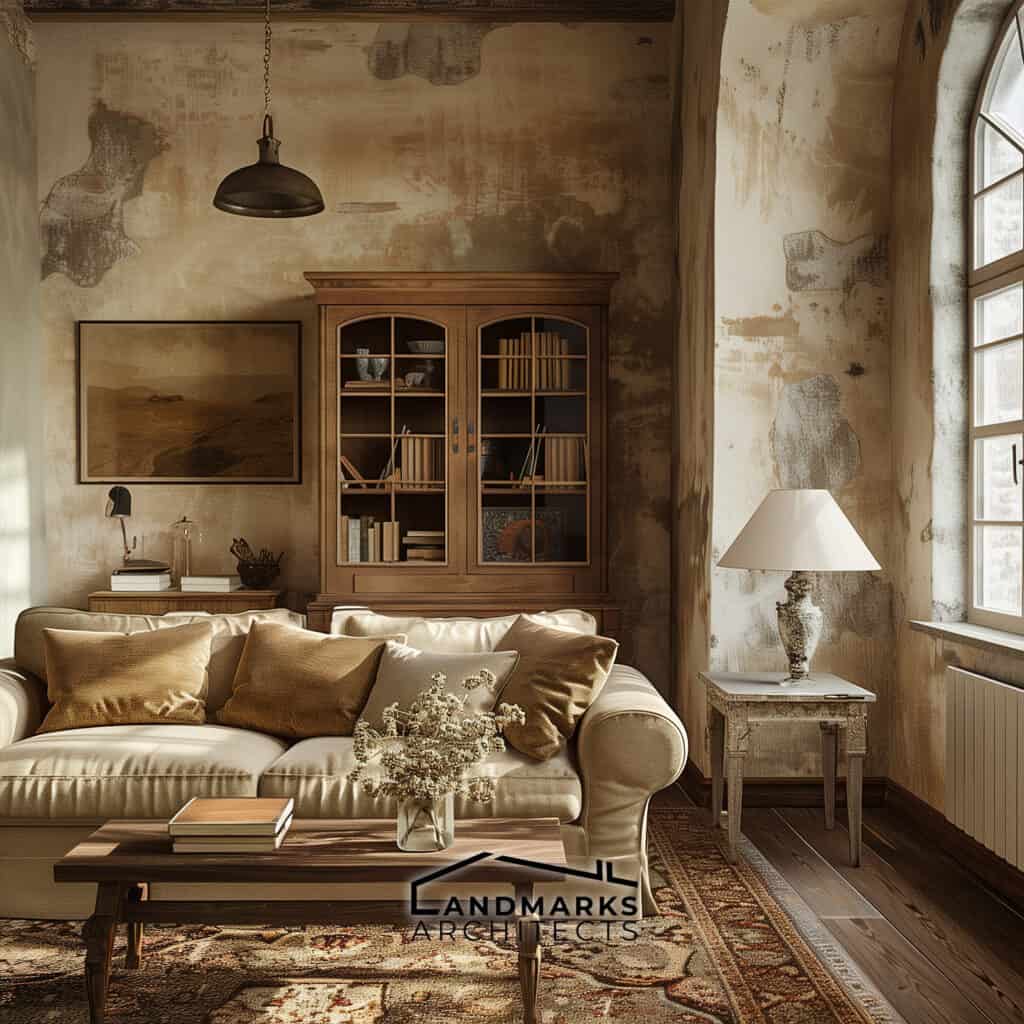

- Pastels: Soft colors such as light blue, pink, and yellow are commonly found in coastal designs.

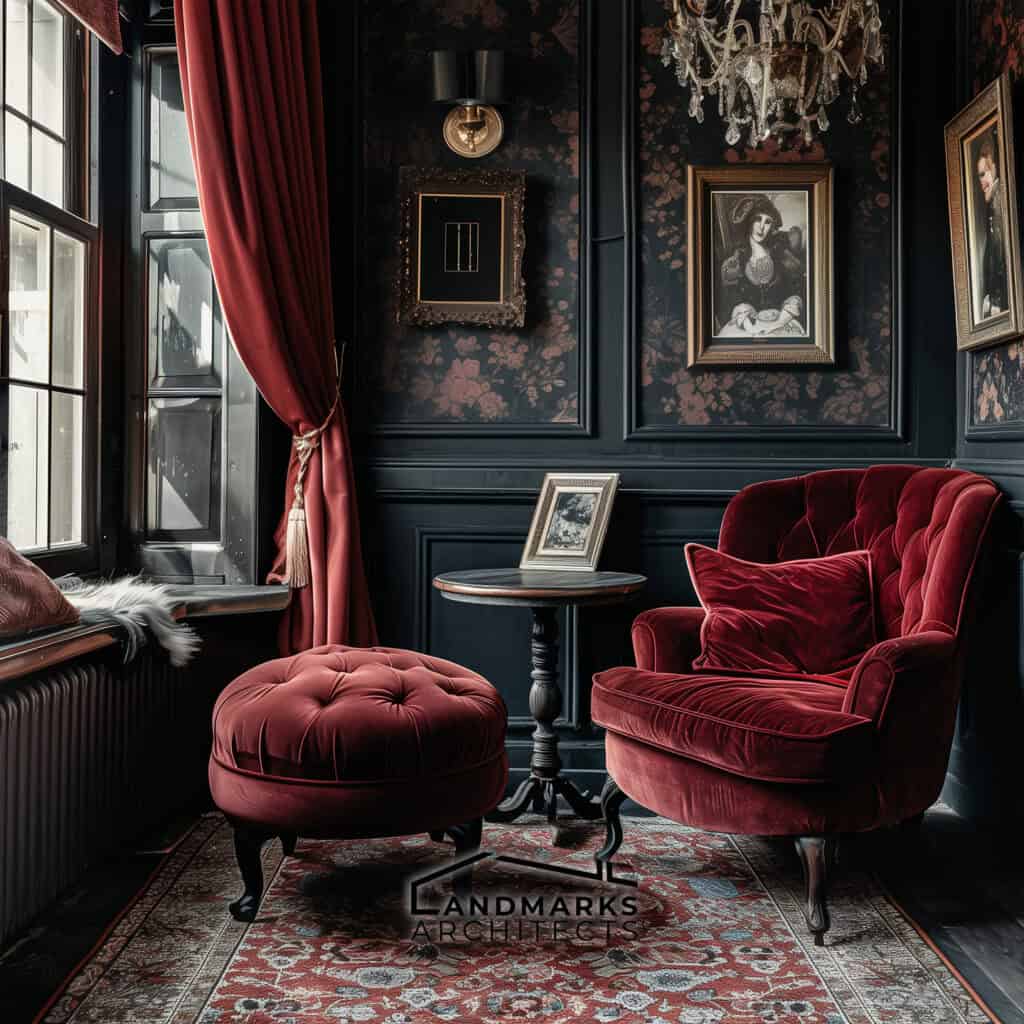
- Deep hues: Rich colors like burgundy or navy often enhance ornate features.

See also: 1970s Style in House Architecture: 10 Must-Know Features
3. Ornamentation and detailing
Detailing is a significant aspect of vintage architecture. Key features include:
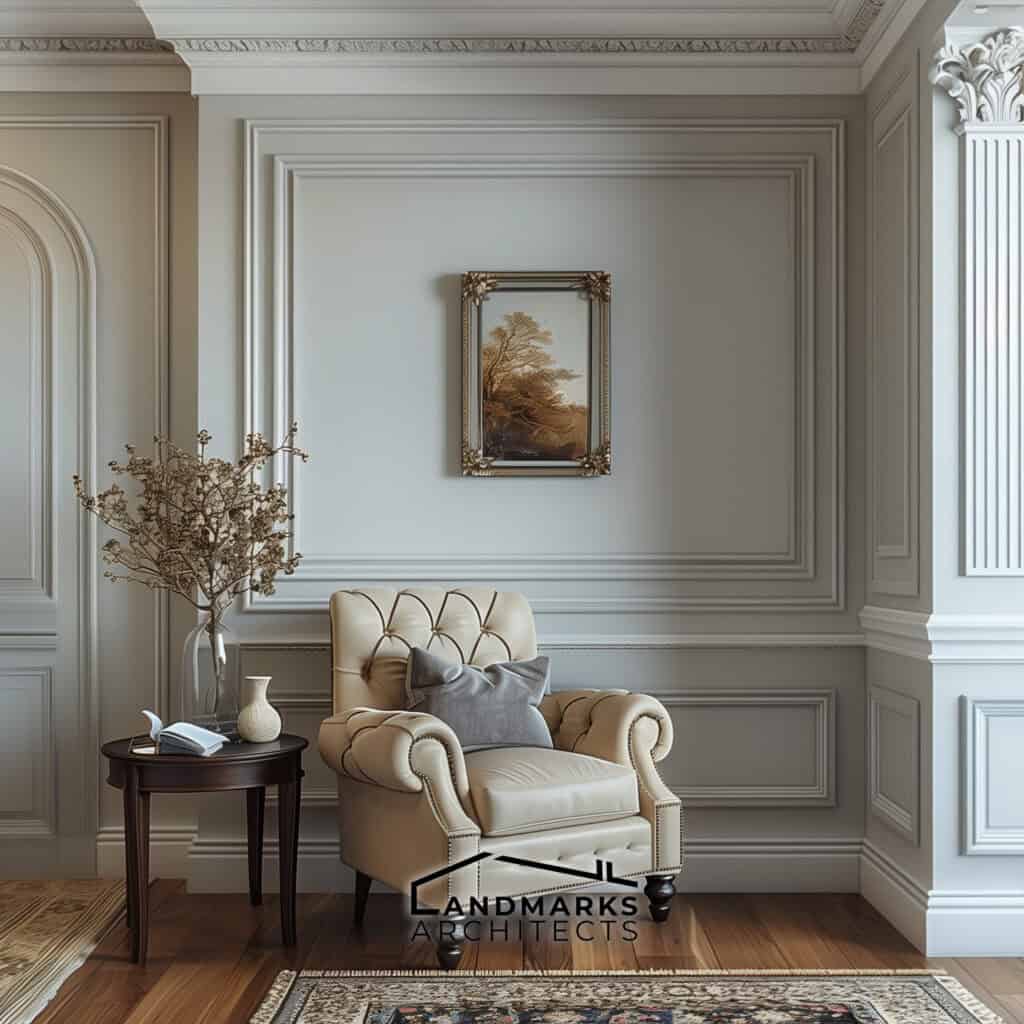
- Moldings: Crown and base moldings add dimension and elegance to rooms.

- Carvings: Intricate designs on doors and mantels serve as focal points and reflect craftsmanship.
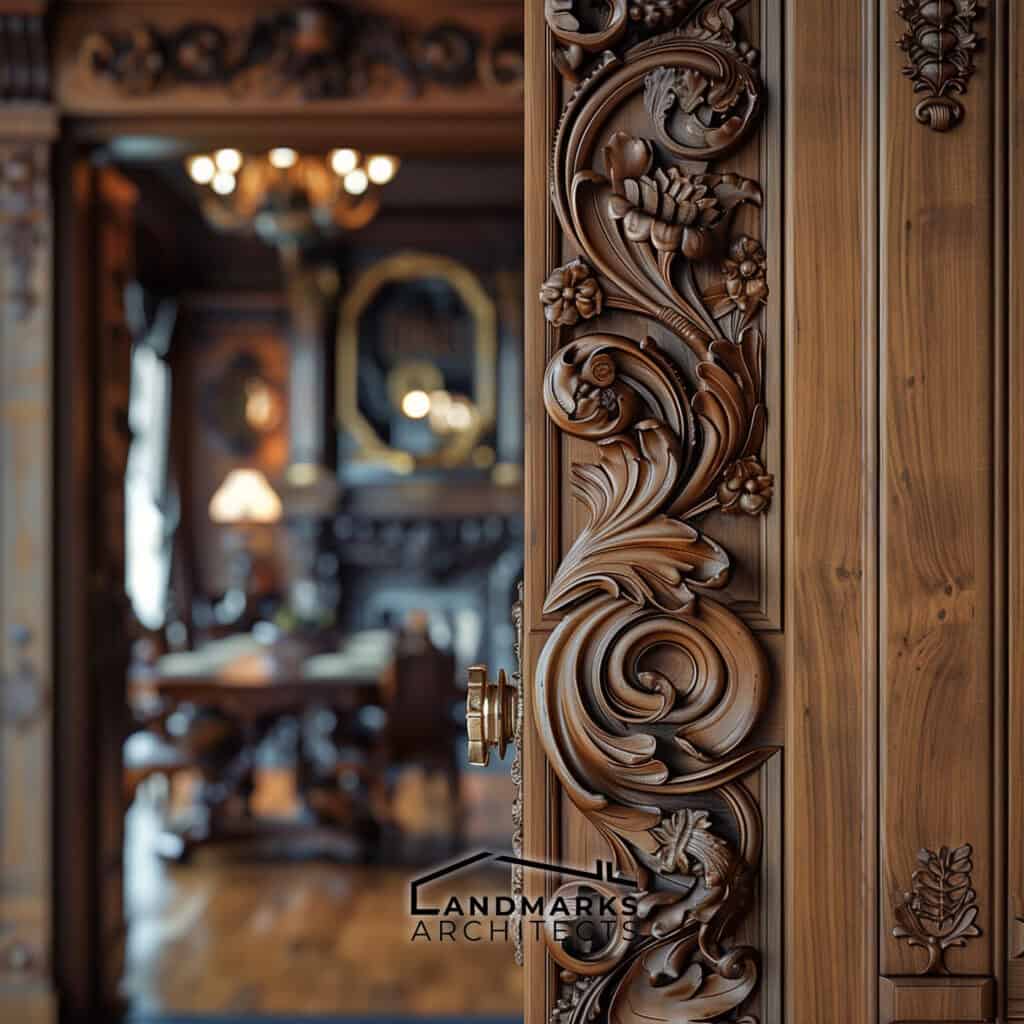

- Elaborate door surrounds: These enhancements draw attention to entryways and emphasize architectural style.

4. Roof styles
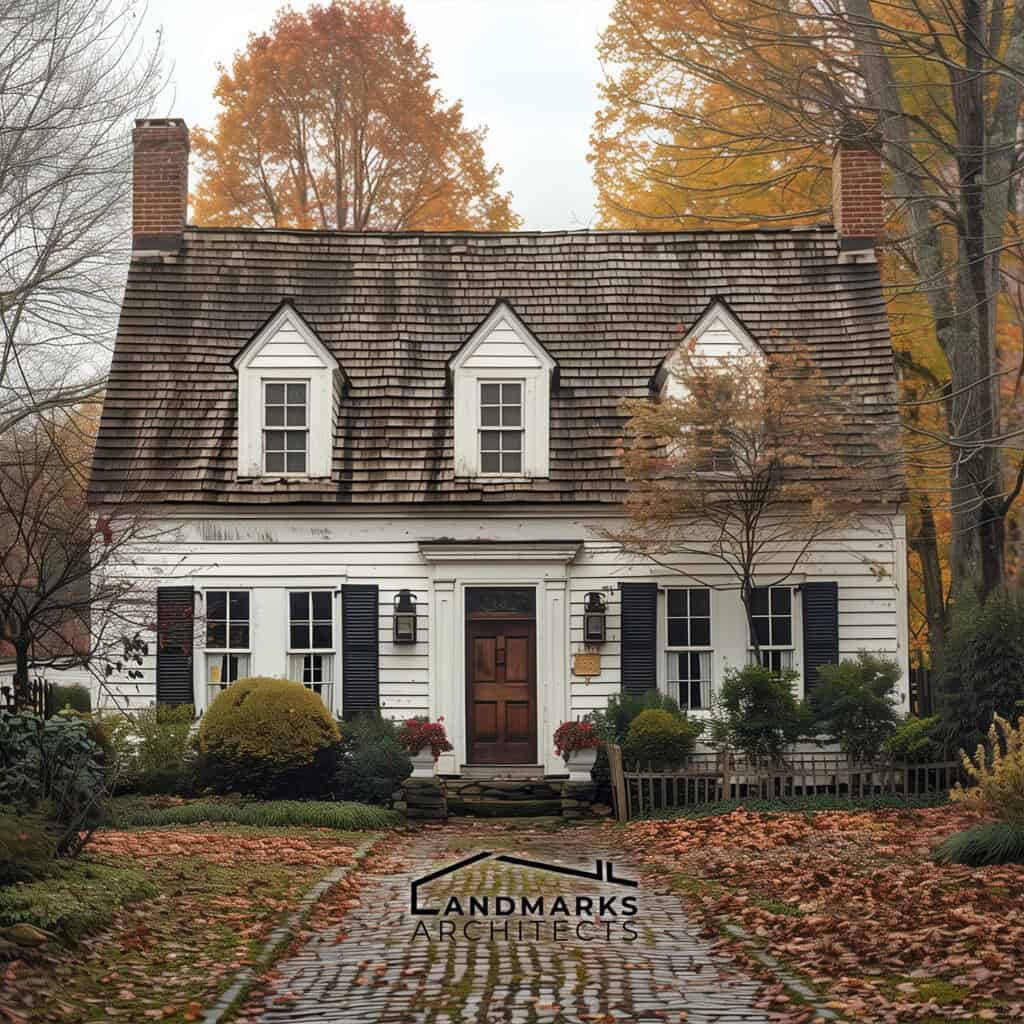

Roof design is crucial in vintage architecture, influencing both aesthetics and functionality. Common styles include:
- Gabled roofs: Characterized by their triangular shape, these roofs are common in colonial and farmhouse designs.
- Hipped roofs: Featuring slopes on all sides, these roofs provide stability and are often seen in Victorian architecture.
- Flat roofs: Common in modern interpretations, they can be found in some mid-century designs and offer a minimalist look.
5. Window styles
Windows play an essential role in vintage architecture, both functionally and aesthetically. Typical styles are:
- Sash windows: These double-hung designs are prevalent in colonial and federal homes, offering practicality and period charm.

- Casement windows: Hinged on one side, these windows provide excellent ventilation and are often used in Mediterranean styles.
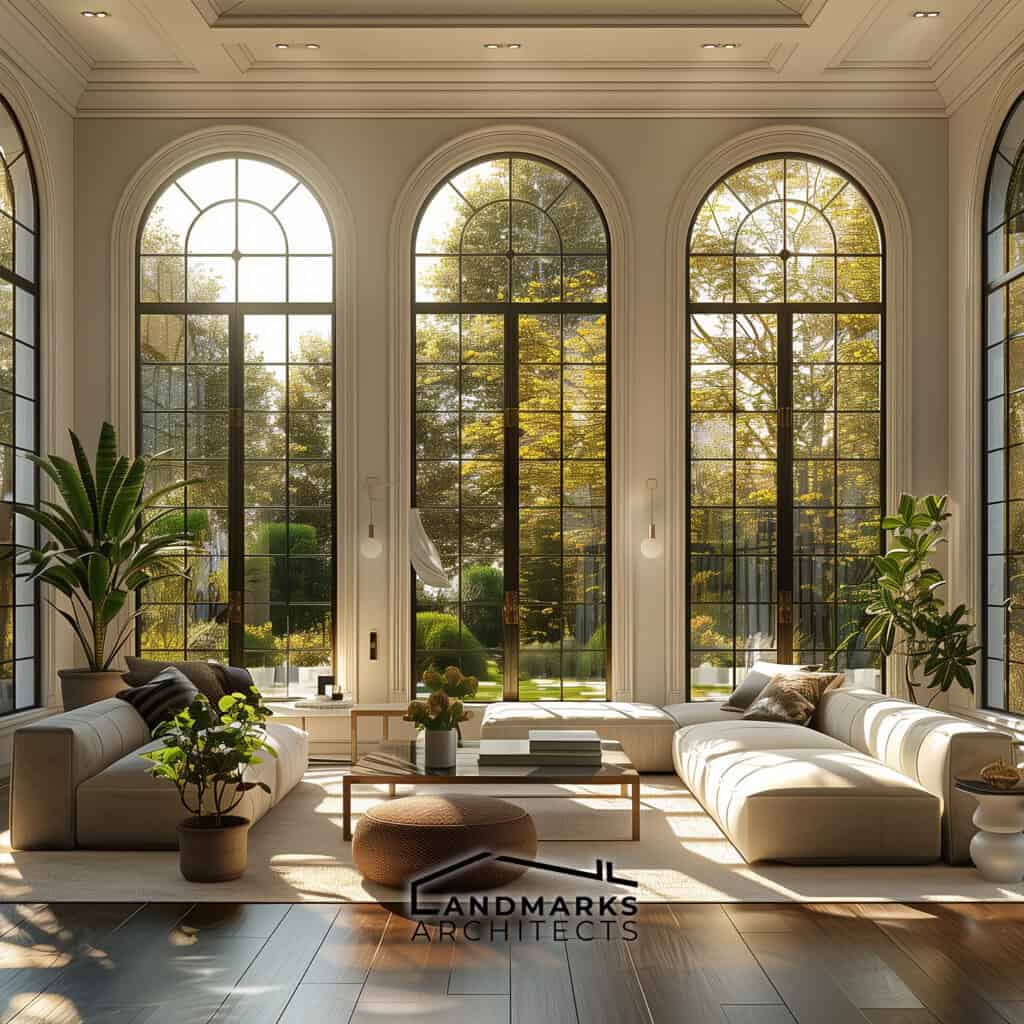

- Large windows: Frequently seen in early 20th-century designs, they allow for abundant natural light and connection to outdoor spaces.
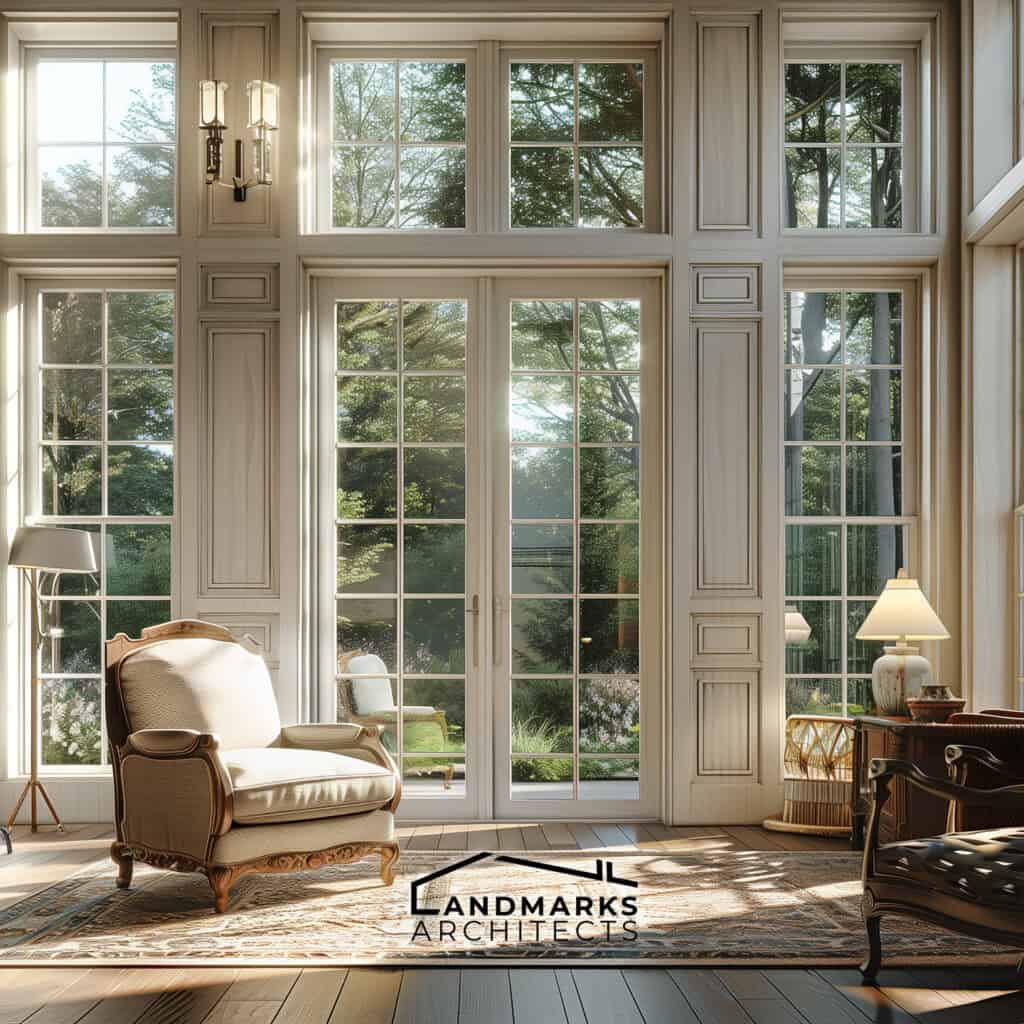

6. Interior features
Interior design plays a crucial role in defining vintage spaces. Notable features often include:
- Built-in furniture: Shelving and seating built directly into walls create functional and efficient living areas.
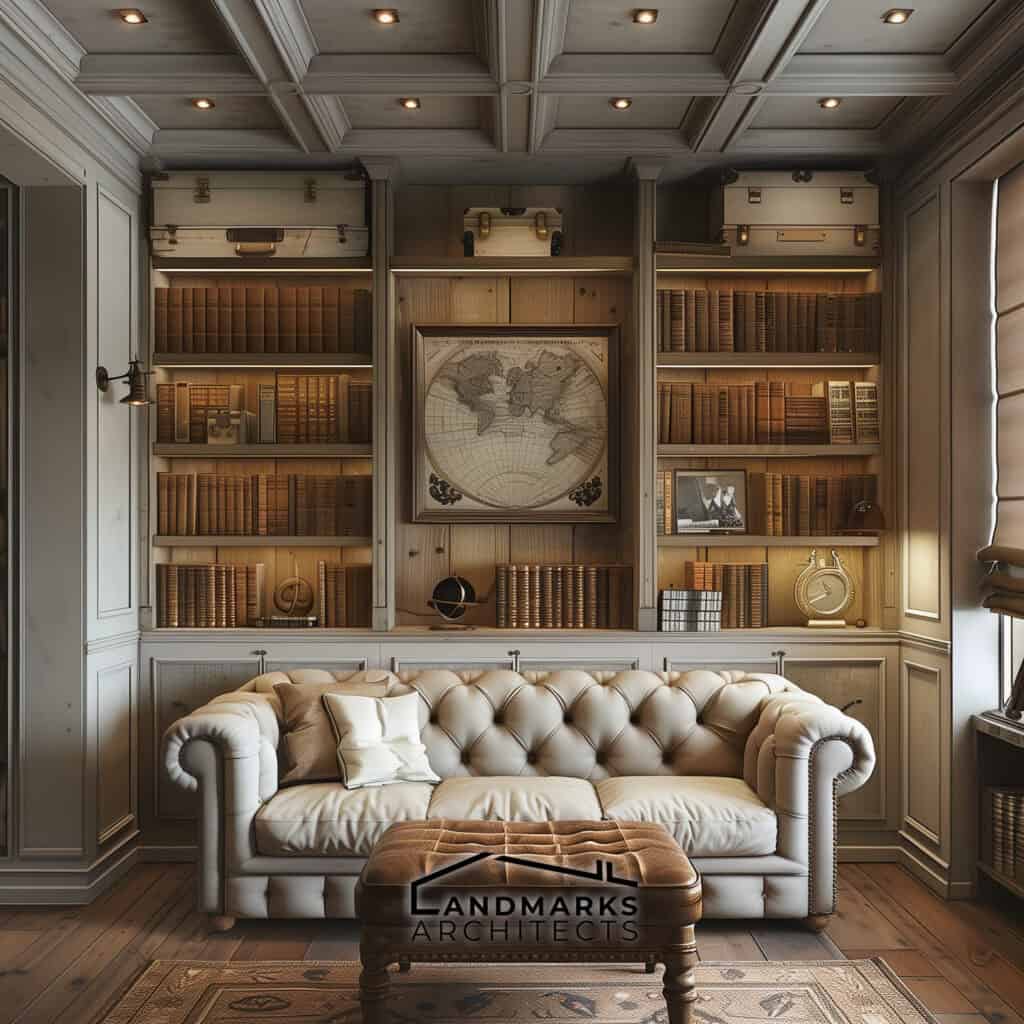

- Fireplaces: Ornate mantels and decorative tiles highlight communal spaces, often serving as the room’s focal point.

Architectural Styles Influencing Vintage Architecture
Examining any building style reveals its historical significance, evolution and types of architectural styles, offering insights into how it shapes vintage style in contemporary contexts.
- Beaux Arts Buildings: These structures are celebrated for their grandiosity and classical elements. They emphasize symmetry, elaborate ornamentation, and the use of natural materials, representing a harmonious blend of art and architecture that continues to influence vintage designs.
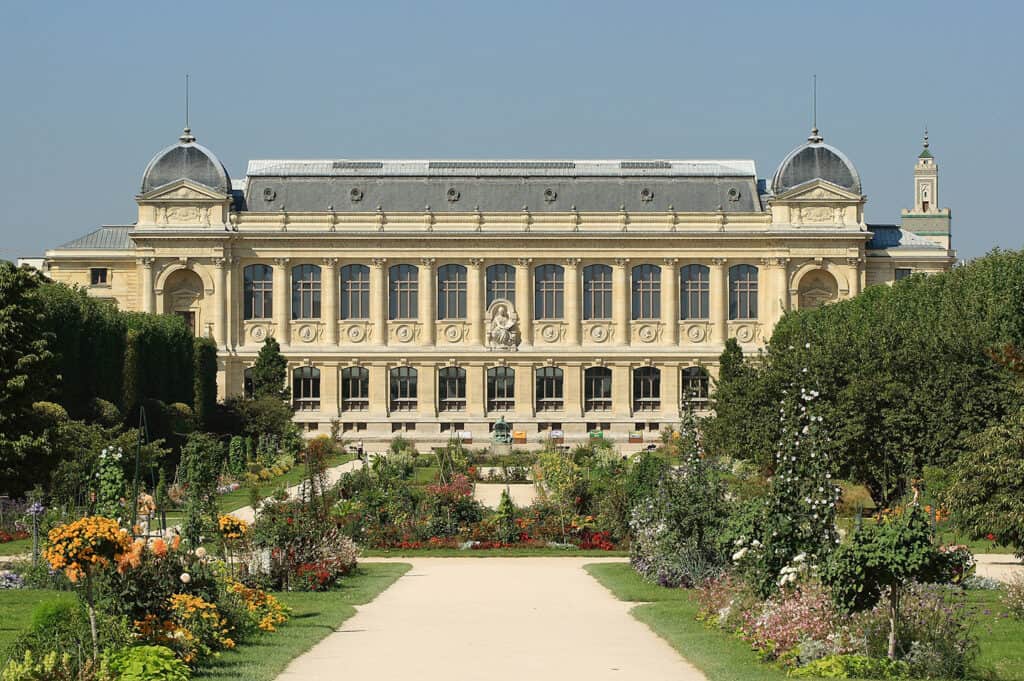

- Colonial Revival Style: This style encapsulates the charm of early American architecture, with homes featuring columned porches and gabled roofs. It creates inviting living spaces that bridge modern designs with historical roots, making it a key influence on vintage architecture.
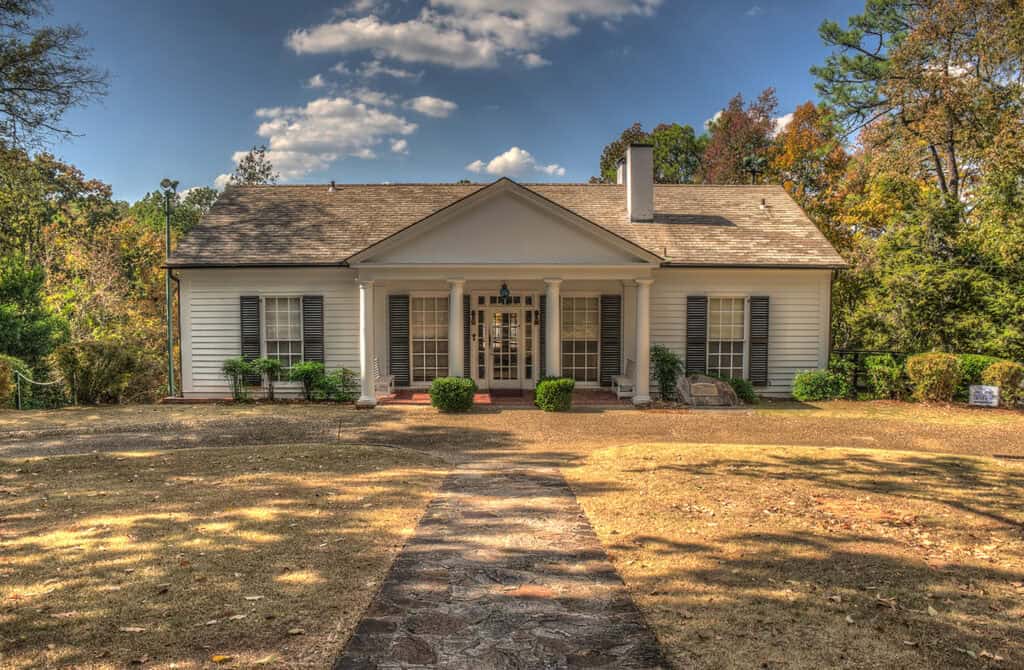

- Italianate Style: Known for its wide eaves and tall windows, Italianate architecture exudes elegance. Popular in urban settings, these buildings enhance neighborhood aesthetics while preserving their historical identity, contributing significantly.

Vintage Style in Architecture: A Recap

Vintage style in architecture, shaped by modern architects and thoughtful architectural design, weaves together diverse influences from the International Style to Colonial Revival. Key elements often include:
- Geometric shapes and clean lines
- Use of natural materials and light
- Architectural details like elaborate door surrounds
This style’s enduring appeal lies in its ability to evoke old-world charm and character, continuing to resonate with those who value history in their living spaces.