Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Architectural Site Planning! If you’ve ever wondered how architects and planners transform a bare piece of land into a functional, aesthetically pleasing space, you’re in the right place. Are you curious about the essential steps in site planning? Do you want to understand how architects balance practical considerations with creative vision?
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of creating an effective site plan, breaking down the process into four essential steps. We’ll also investigate the critical components and factors that make up a successful site plan, from understanding property boundaries to considering environmental features and accessibility requirements.
What is an Architectural Site Plan?
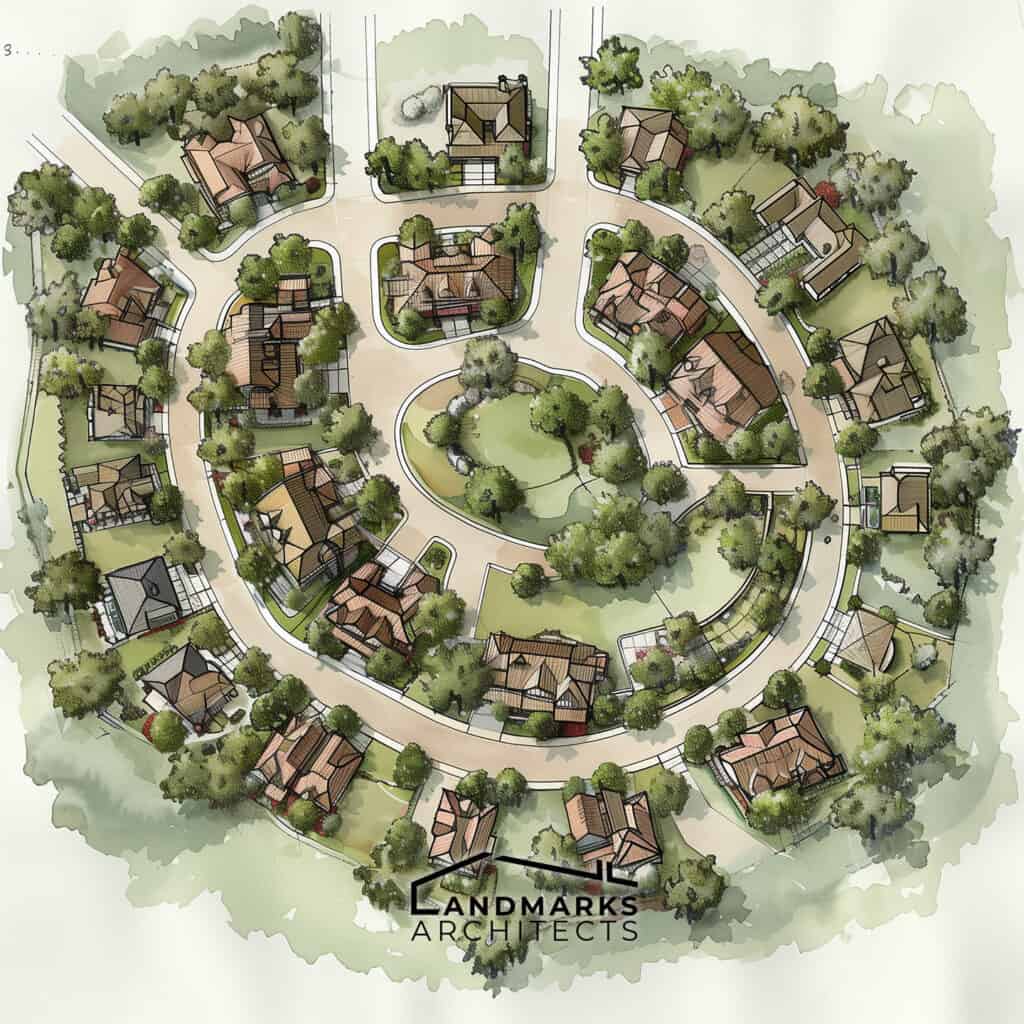
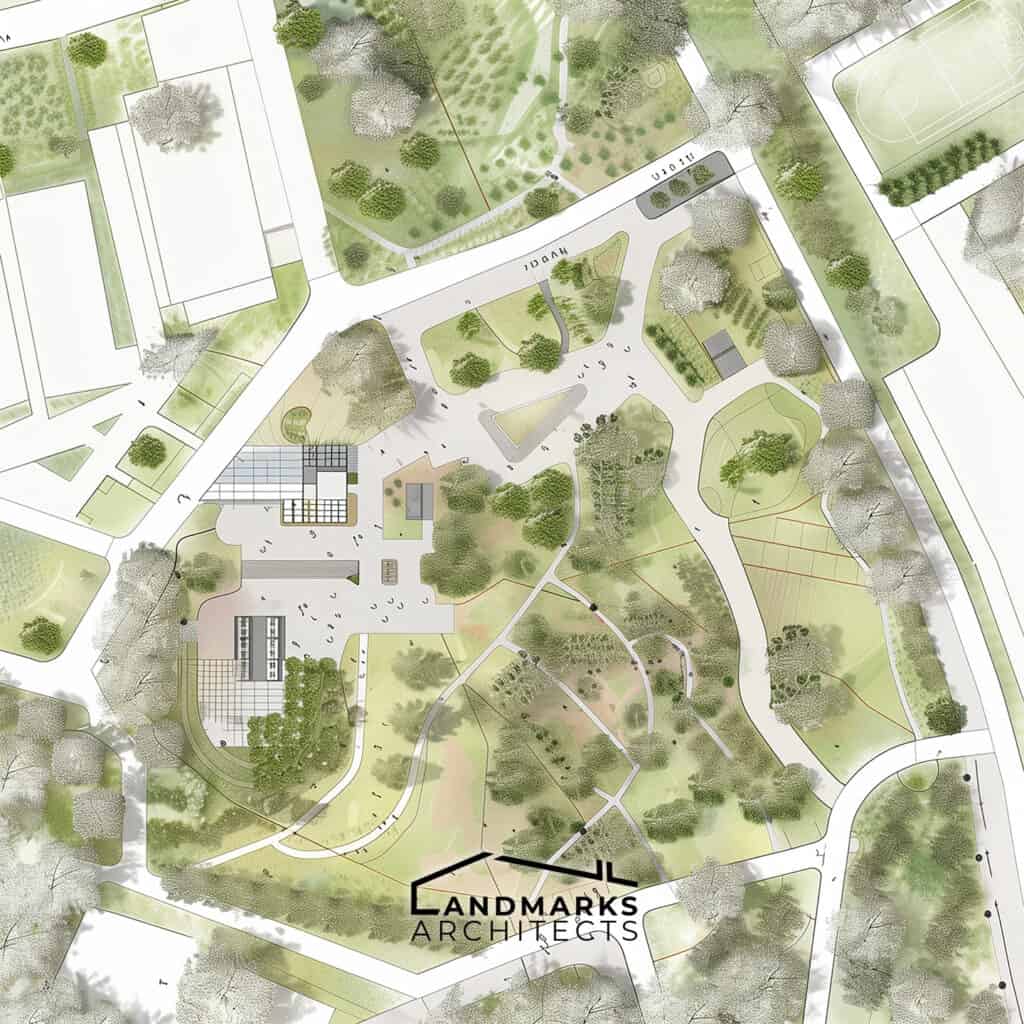
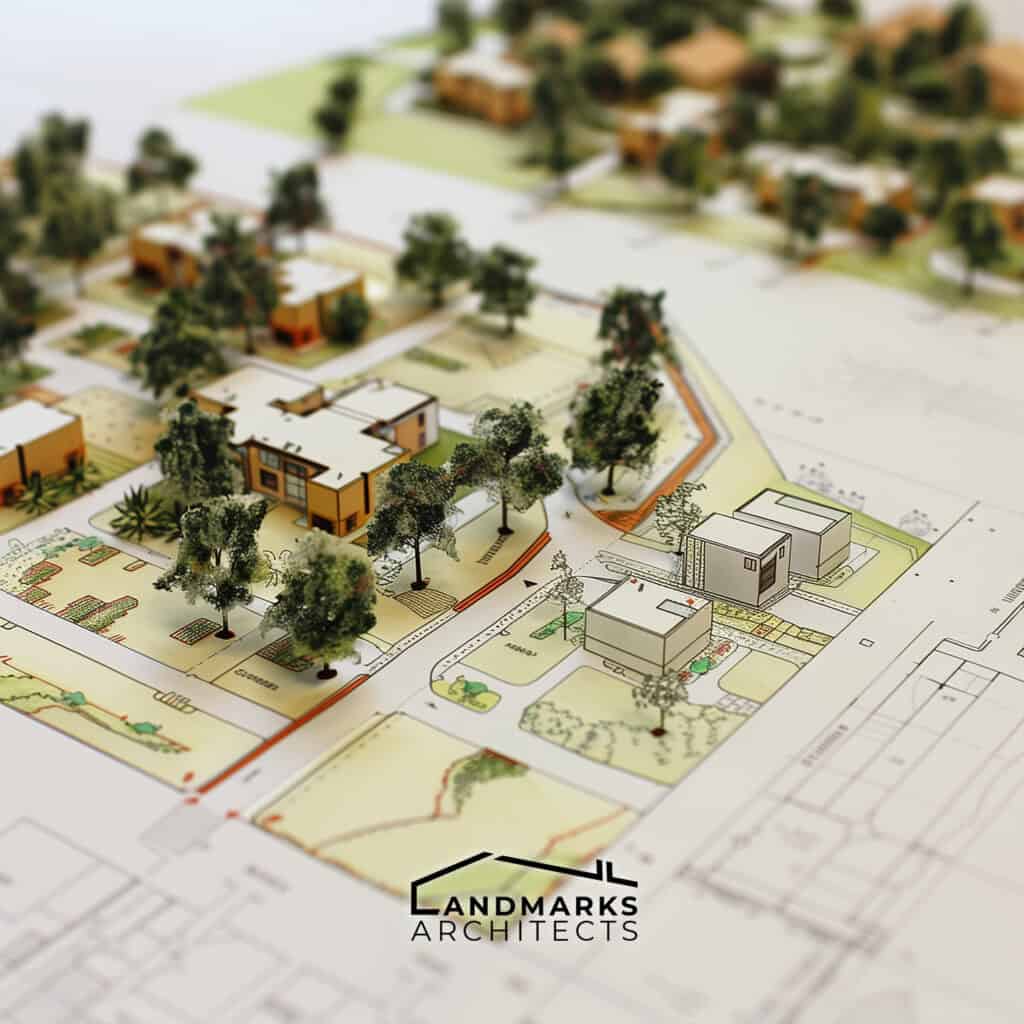
An architectural site plan is a comprehensive, detailed drawing used by architects, engineers, urban planners, and landscape architects to show the existing and proposed conditions of a specific area, usually a parcel of land that is being modified. It is an essential tool in the site planning process and the entire project’s design and construction process, as it provides detailed information about the site’s existing features, natural factors, and construction limits.

A site plan is different from other types of architectural plans, such as floor plans, elevations, and sections, as it shows the site’s property lines, existing landscape features, and proposed buildings’ locations. It is a scaled representation of the site and includes information about the site’s topography, drainage, vegetation, and other relevant features.
Architectural site plans utilize symbols and graphics to illustrate the existing and proposed conditions, including buildings, land use, and other features. Visual examples of site plans help professionals understand the plan’s contents and its relation to the overall project.
Why Architects Use an Architectural Site Plan

Architectural site plans are also used to facilitate coordination among architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. They provide a common language and visual reference point for all parties involved in the construction project. Additionally, site plans ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations, legal orders, historic landmarks, historical district rules, cultural factors, and natural beauty.
By using an architectural site plan, architects can also facilitate resource management and sustainability. They can identify opportunities to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and utilize renewable resources. Furthermore, site plans can enhance safety and accessibility by identifying potential hazards and providing solutions to mitigate them.
Components of an Architectural Site Plans
1. Property boundaries and lot lines
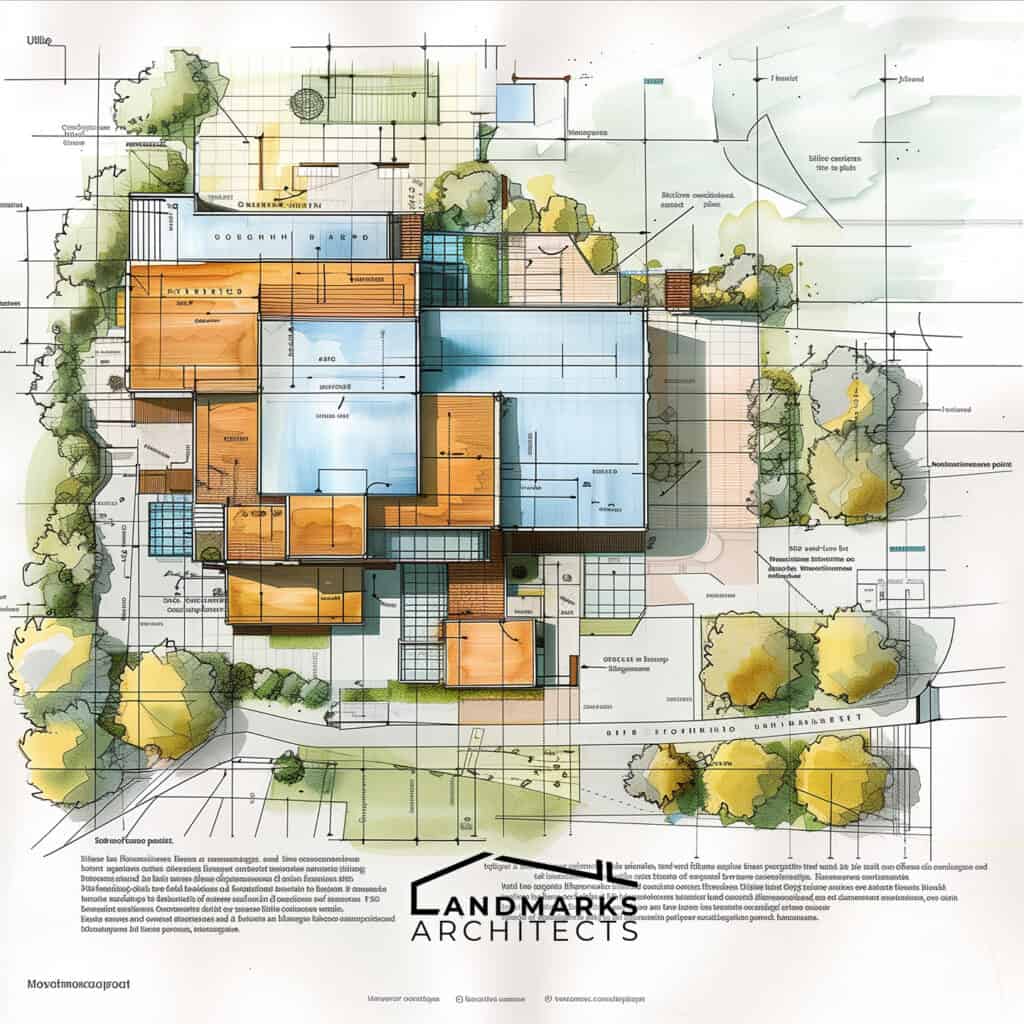
Property boundaries and lot lines are crucial aspects of an architectural site plan as they define the boundaries of the property and determine construction limits.
2. Topographical features and landscape elements
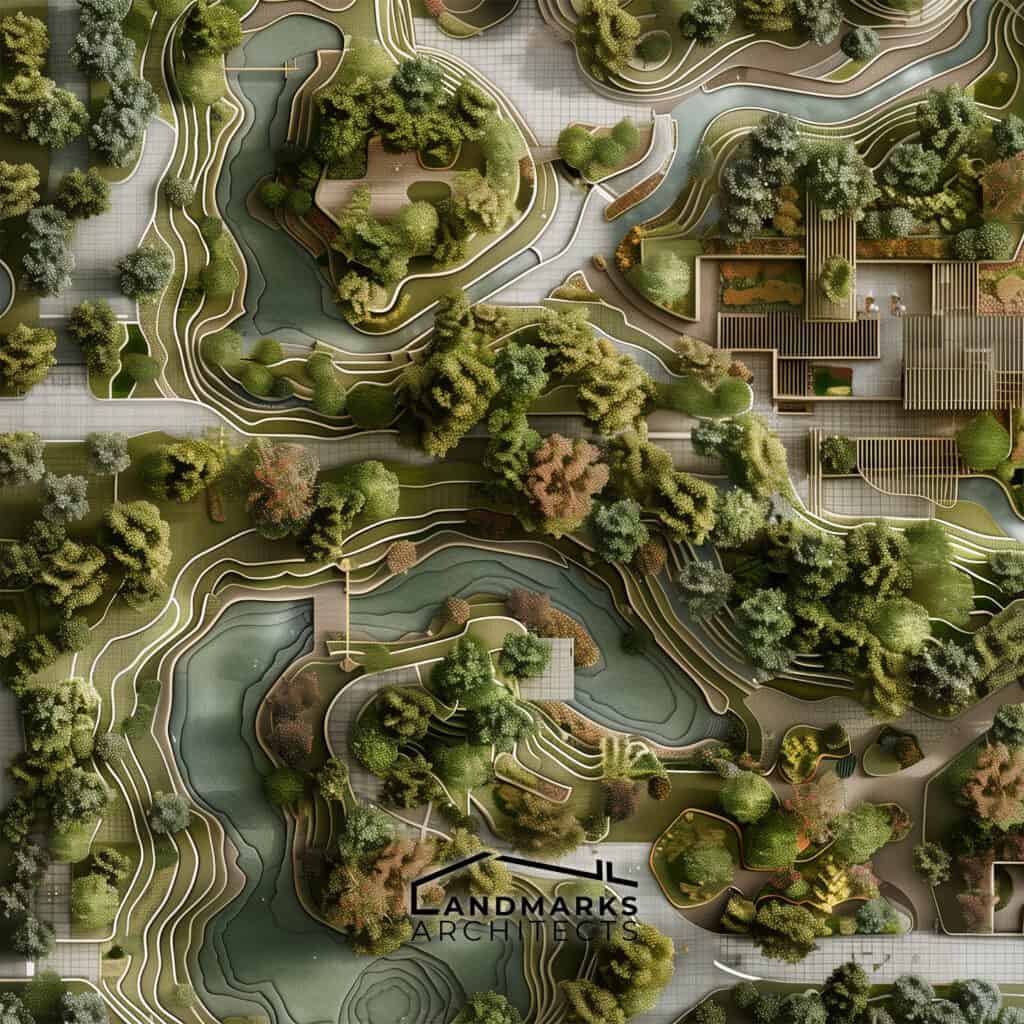

These elements depict the contours, elevations, and slopes of the land, along with existing landscape features such as trees and water bodies, aiding in site analysis and design decisions.
3. Environmental features (trees, water bodies)

Highlighting the presence and layout of trees and water bodies, environmental features inform the site’s natural characteristics and influence building placement and site design.
4. Utilities and infrastructure (water, sewage, electrical lines)
Including utilities and infrastructure like water, sewage, and electrical lines in the site plan indicates existing and proposed service routes, guiding the placement of buildings and structures.
5. Access points (driveways, walkways, entrances)

Mapping access points such as driveways, walkways, and entrances helps define circulation patterns and facilitates efficient movement within the site.
6. Zoning information and setback lines
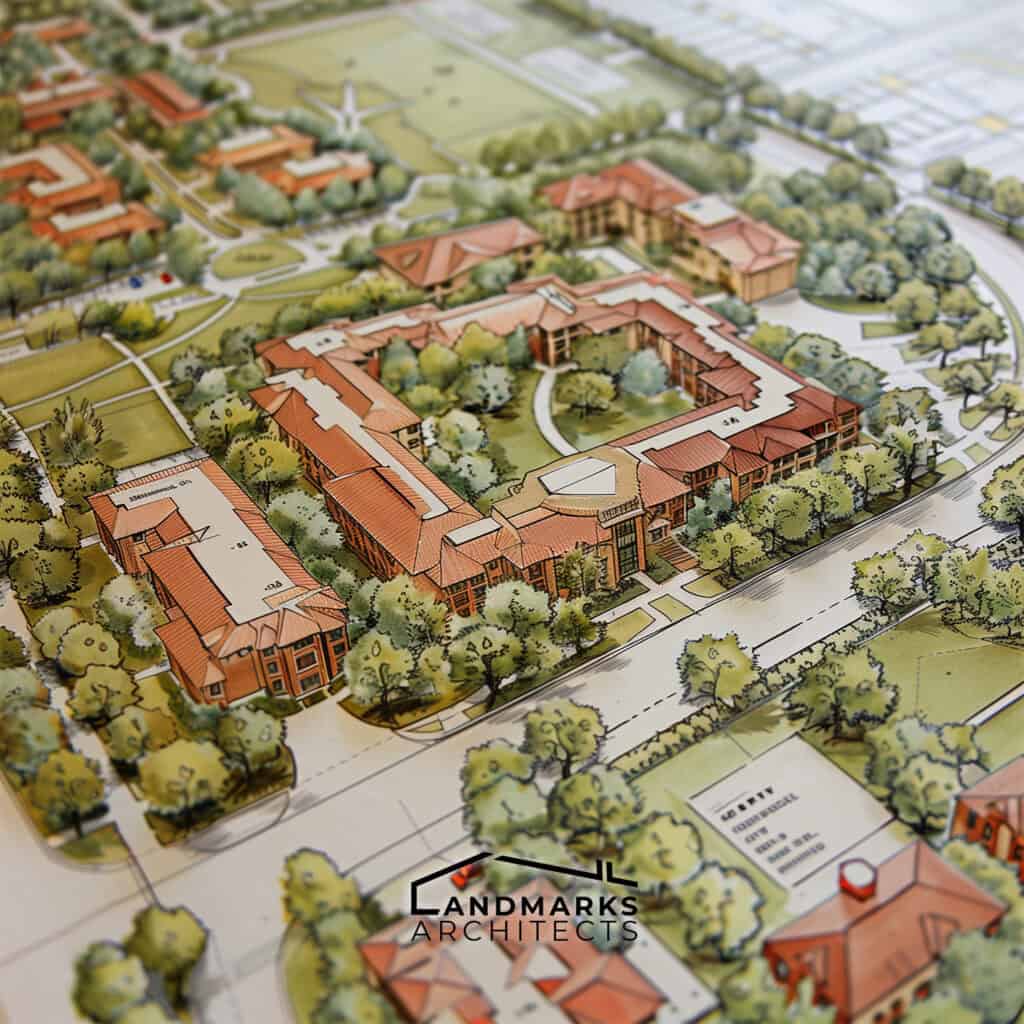

Zoning information and setback lines display relevant regulations and restrictions, guiding development decisions and ensuring compliance with local laws.
7. Easements and rights-of-way
Easements and rights-of-way delineate areas designated for specific uses or access, influencing site layout and development options.
Important Factors in a Site Plan

- Understanding the site context involves assessing existing land use, buildings, and natural elements like plants and predators. Including the north point in the site plan ensures correct orientation.
- Compliance with local zoning laws and regulatory requirements is essential to avoid legal issues and ensure the project is completed on time and within budget.

- The site plan should take into account climatic factors, drainage systems, and other natural factors that may impact the environment. This will ensure that the project is sustainable and has a minimal impact on the environment.
- The site plan should reflect the client’s needs and preferences, ensuring that the project meets their expectations.
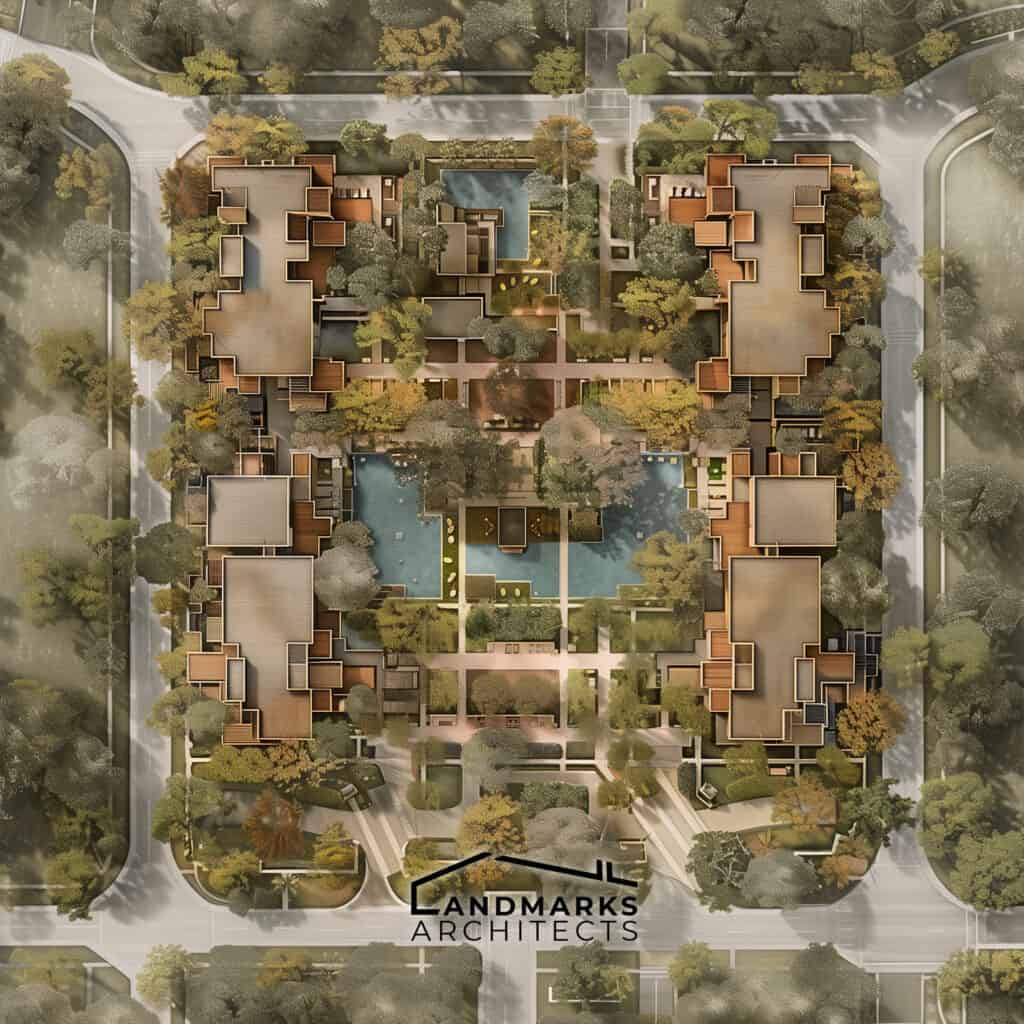

- Ensuring accessibility and compliance with ADA standards is also important. The site plan should take into account the needs of disabled individuals. This will ensure that the project is accessible to everyone.
- The site plan should take into account the potential for future expansion and scalability, ensuring that the project can grow and evolve with the client’s needs.
How to Create an Architectural Site Plan

- Site Analysis and Surveying: The initial stage of architectural site planning involves conducting a thorough site survey to collect data on topography, soil, climate, and other natural factors. This analysis also identifies existing buildings and landscape features crucial for planning.
- Initial Design and Conceptualization: After gathering detailed site information, the next step is to initiate the initial design phase, drafting preliminary sketches and ideas detailing proposed buildings, construction limits, and other relevant aspects, with stakeholder collaboration for feedback.
- Development: Following the initial design phase, the detailed plan development stage commences, utilizing CAD/BIM software for precision and integrating structural, electrical, and mechanical plans. This stage involves selecting building materials and incorporating other relevant details into the plan.
- Review and Revision: The final step in creating an architectural site plan is reviewing and revising the plan as needed. This includes reviewing the plan for accuracy, completeness, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Architectural Site Planning

An effective architectural site plan considers existing buildings, land, proposed structures, and landscape features, aiming for clarity, accuracy, and detailed graphics.
Overall, the key points covered in this article emphasize the critical role of a site plan in successful architectural projects. By following best practices and considering all factors, architects can create effective site plans that provide a solid foundation for the construction process.