Are you fascinated by the elegance of historical architecture? Dutch architecture is unique. It blends classic elements with innovative design. It captures both tradition and modernity.
At Landmarks Architects, we appreciate the beauty and intricacies of Dutch architecture. We’re here to help you uncover the unique qualities of these styles.
In this article, we will explore:
- The historical evolution of Dutch architecture
- Key characteristics that define the Dutch style
- Famous examples that showcase this architectural legacy
- Insights into future trends in Dutch architecture
Interested in learning more about how Dutch architects shaped the world? Check out our guide to Dutch Colonial homes.
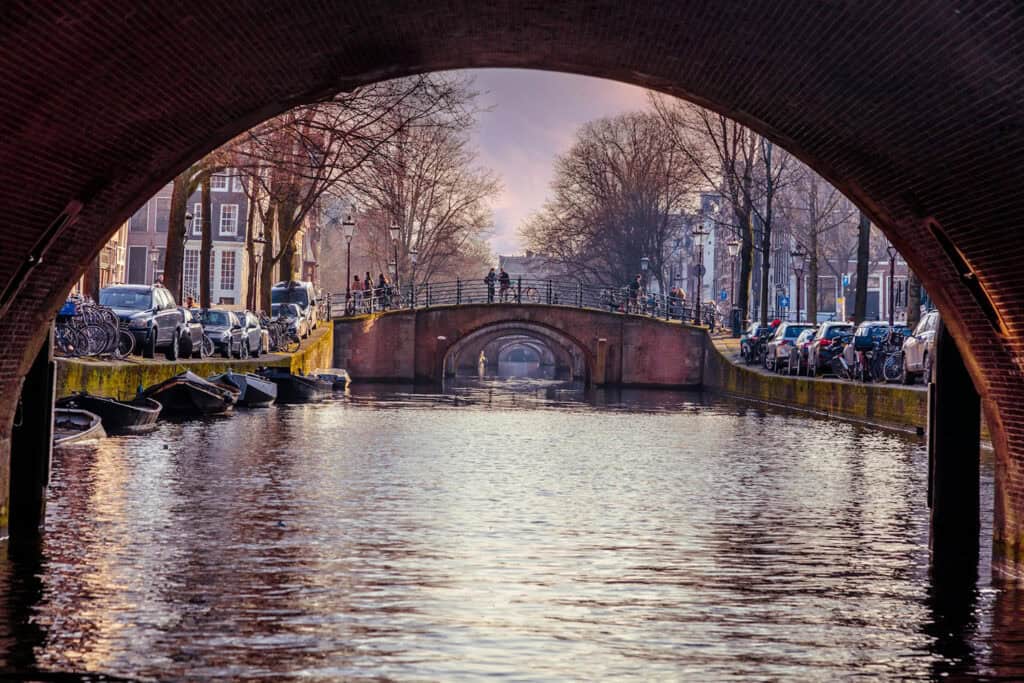


Historical Evolution of Dutch Architecture
Dutch architecture has evolved over the centuries. It reflects cultural, economic, and political changes. Key phases include:
Dutch Golden Age Architecture (17th Century)

In the Dutch Golden Age, the Dutch Republic built many grand public buildings and town halls. Architects like Jacob van Campen played a pivotal role in shaping unique Dutch buildings.
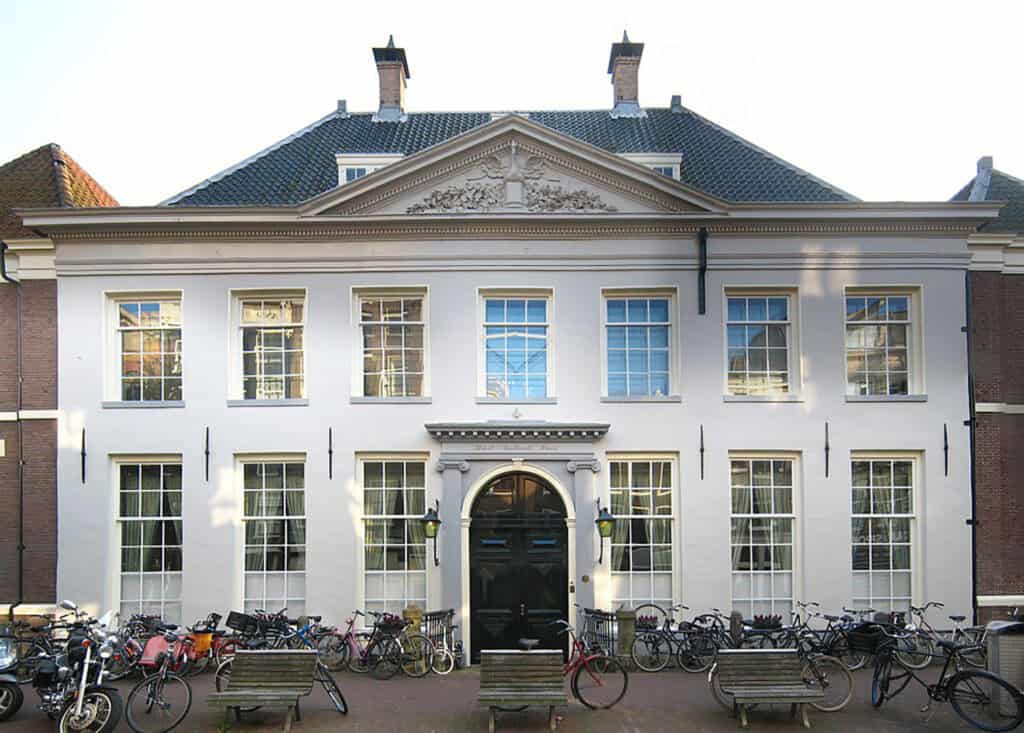

This building has straight lines, large windows, and local materials. Gambrel roofs, shaped like a bow, became iconic in homes. They conveyed elegance and functionality.
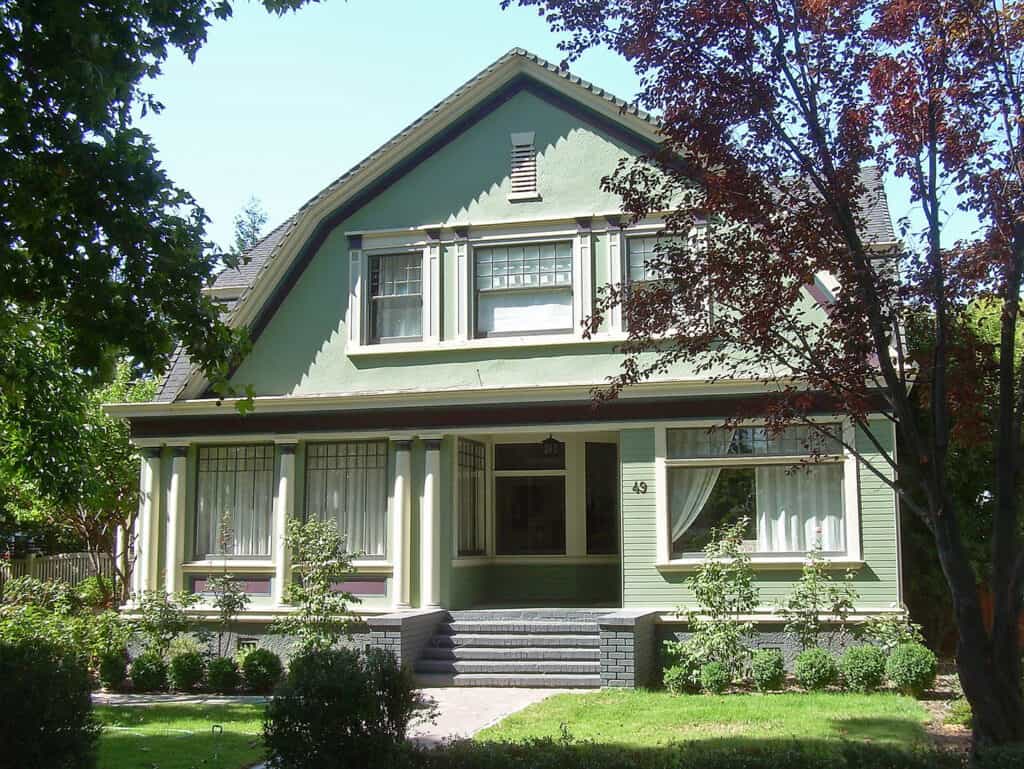
Dutch Colonial Period (Early America and Dutch East Indies)
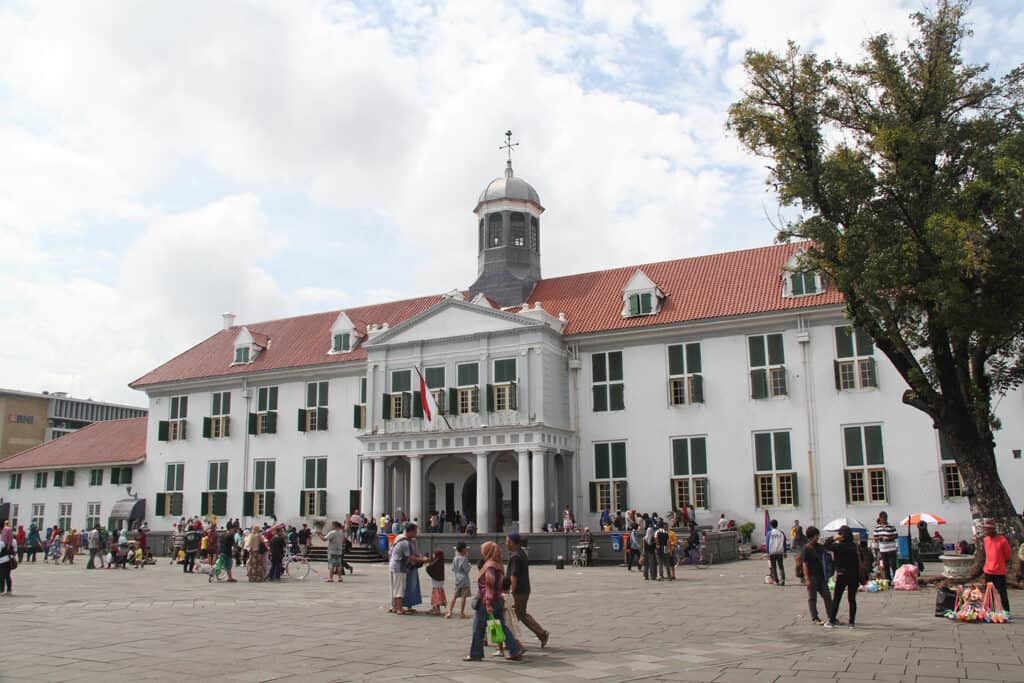

The Dutch Colonial period marked the spread of architectural styles to regions such as America. An early American Dutch Colonial house had distinct gambrel roofs, flared eaves, and symmetrical façades. Settlements adapted these styles to local climates and available materials.
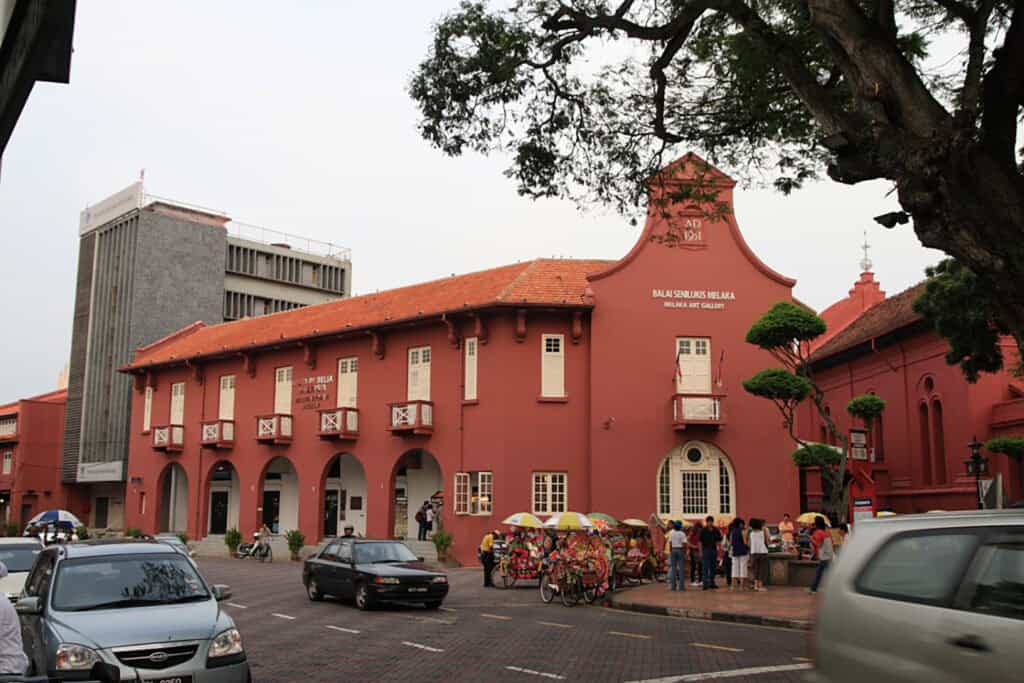

In the Dutch East Indies, the Dutch Colonial style emerged. It was a blend of local influences and traditional Dutch elements. It led to unique architecture with ornate gables and decorative façades.
20th Century Revival Styles
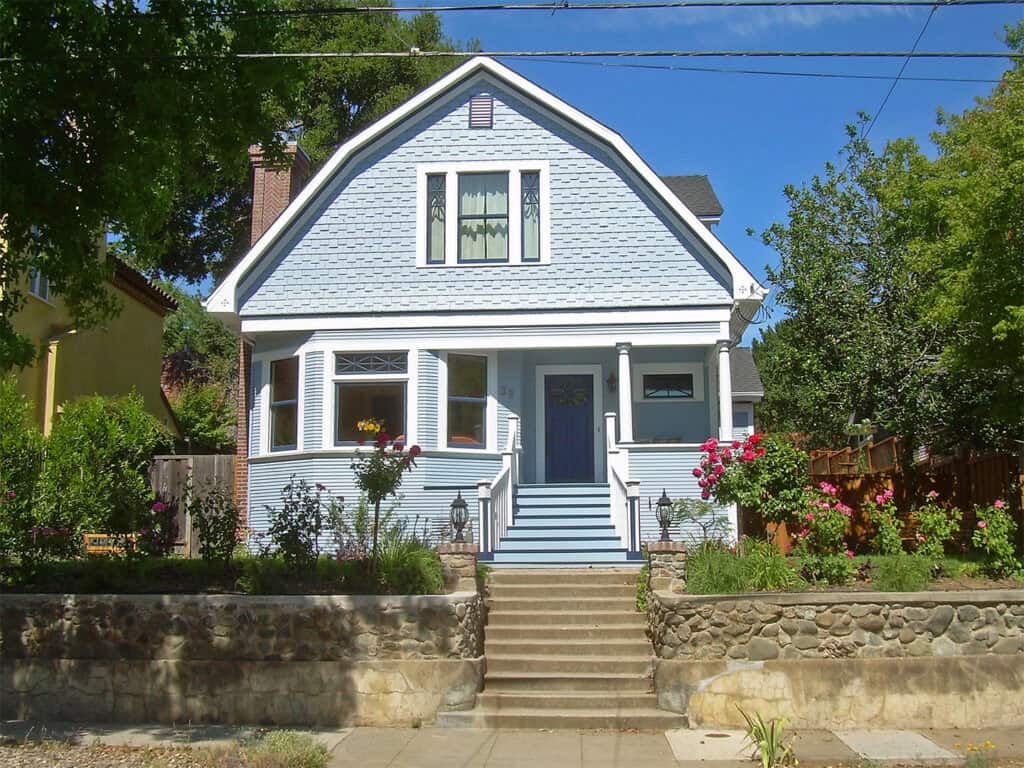

In the 20th century, interest in Dutch Colonial architecture grew, especially in the United state. The Dutch Colonial Revival style began as architects sought inspiration from early colonial homes. With their gambrel roofs and large porches, these homes aimed to evoke nostalgia and history.
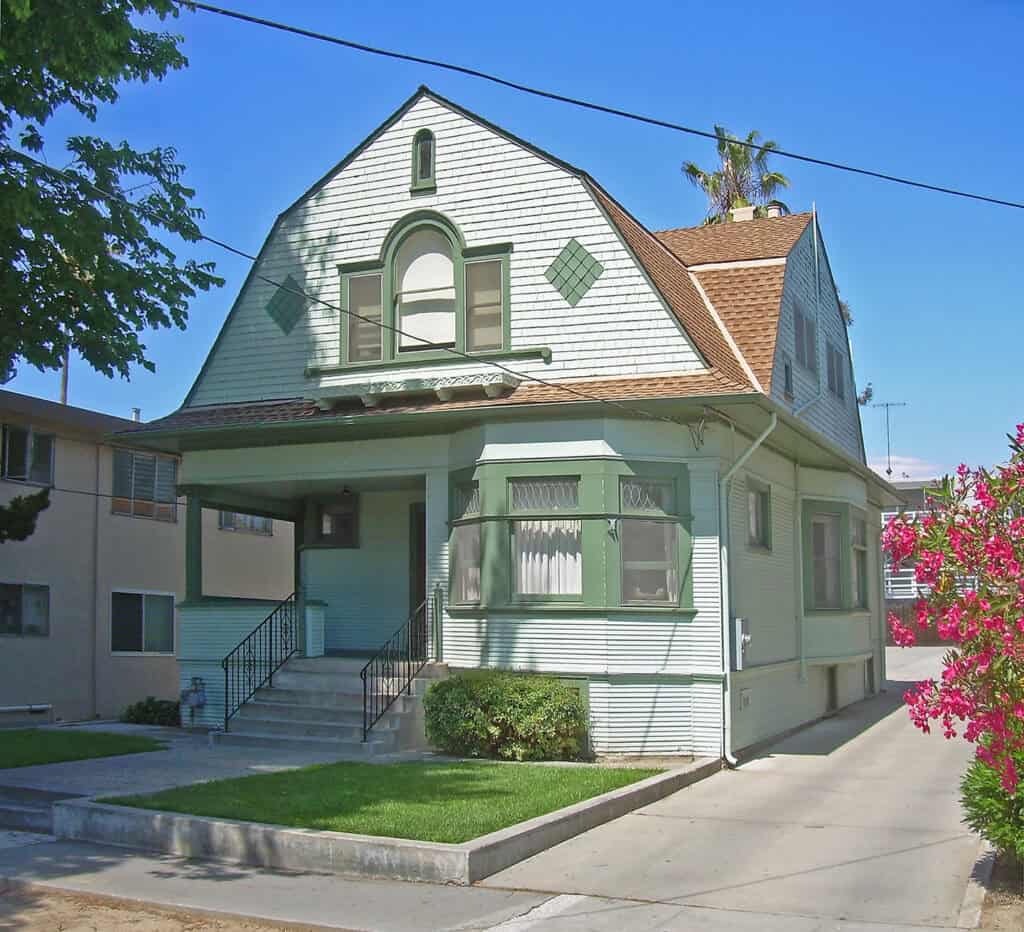

This revival lasted into the late 20th century. It showed a lasting love for Dutch architecture’s history and beauty.
See also: Miami’s Architectural Styles: 6 Iconic Designs to Know
Key Characteristics of Dutch Architecture
Dutch architecture is notable for its unique features. They reflect the country’s history, culture, and environment. This architectural style has unique features. They are: roof styles, brick use, and large windows. They make it both functional and beautiful.
1. Roofs

The Dutch gambrel roof, with its two slopes, is a hallmark of Dutch Colonial homes. It adds elegance and practicality to the structure.
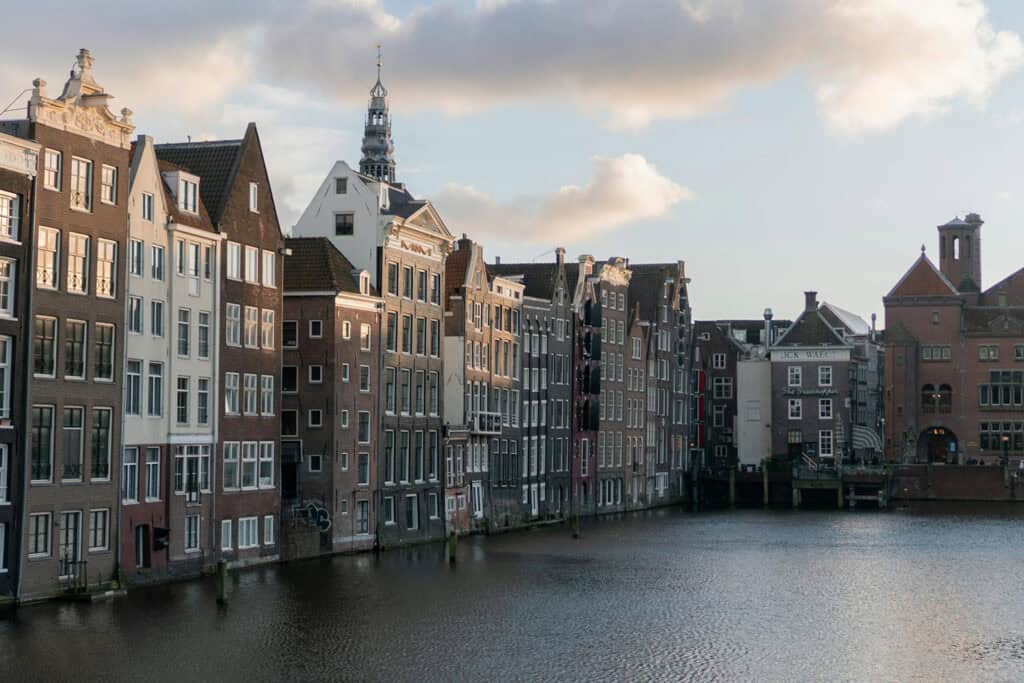

Dutch townhouses have ornate gables. They add elegance and extra attic space. They show the ingenuity of Dutch building traditions.
2. Use of Brick
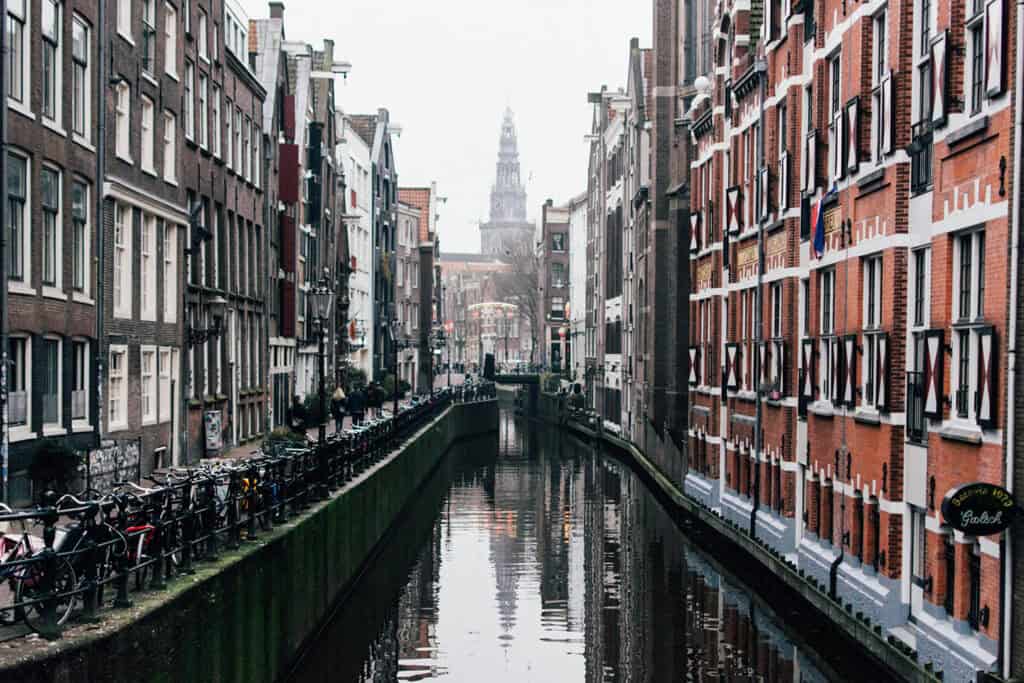

Dutch architects traditionally favored local materials, especially red brick. It is durable and well-insulated. This choice was due to resource availability and a desire for durability.
Brick is common in historic colonial settlements. It helps homes blend with their surroundings. It also reflects a sense of stability and permanence.
3. Large Windows
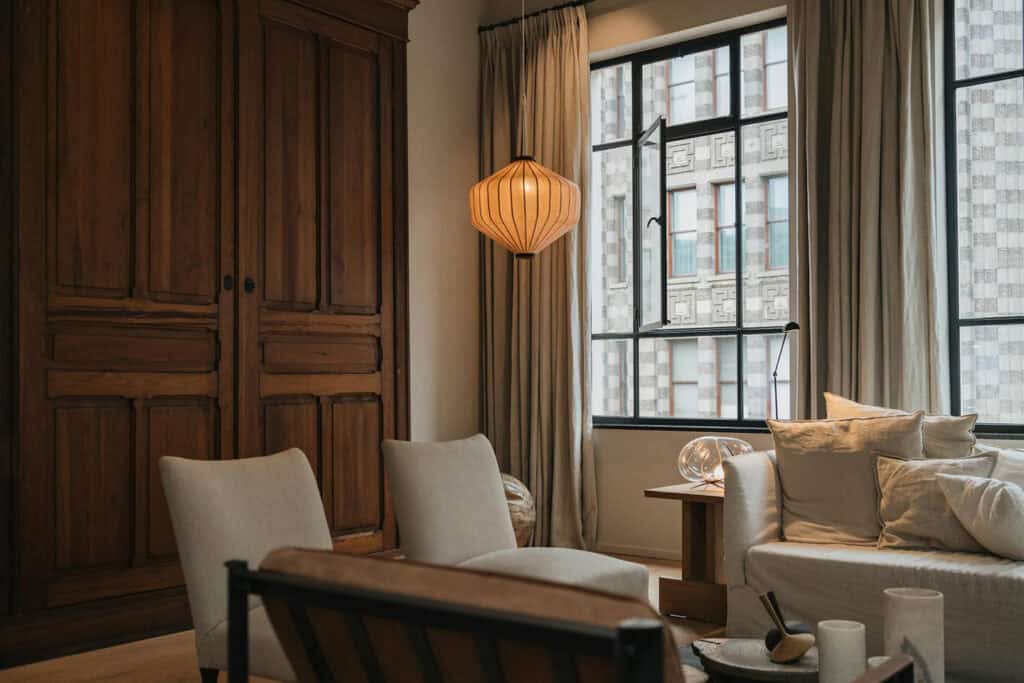

Dutch architecture emphasizes large windows to maximize natural light and promote openness. These expansive openings enhance airiness and connect interiors with the outdoors.
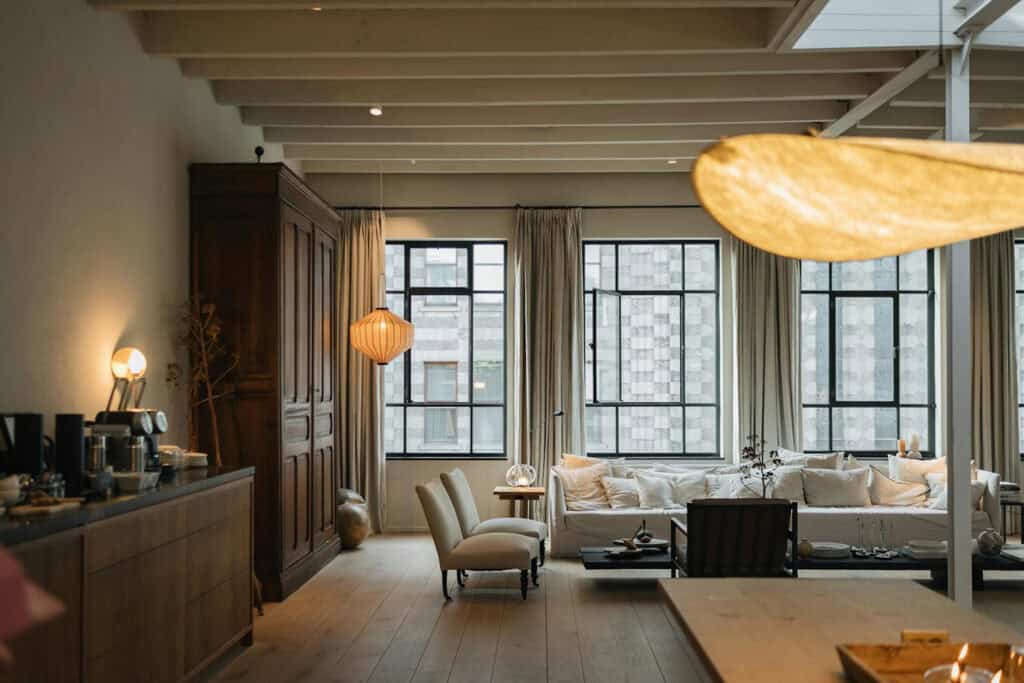

This design reflects a cultural preference for spacious, airy living areas. The window designs use straight lines and symmetry. They create a balanced, pleasing look.
4. Tall, Narrow Houses
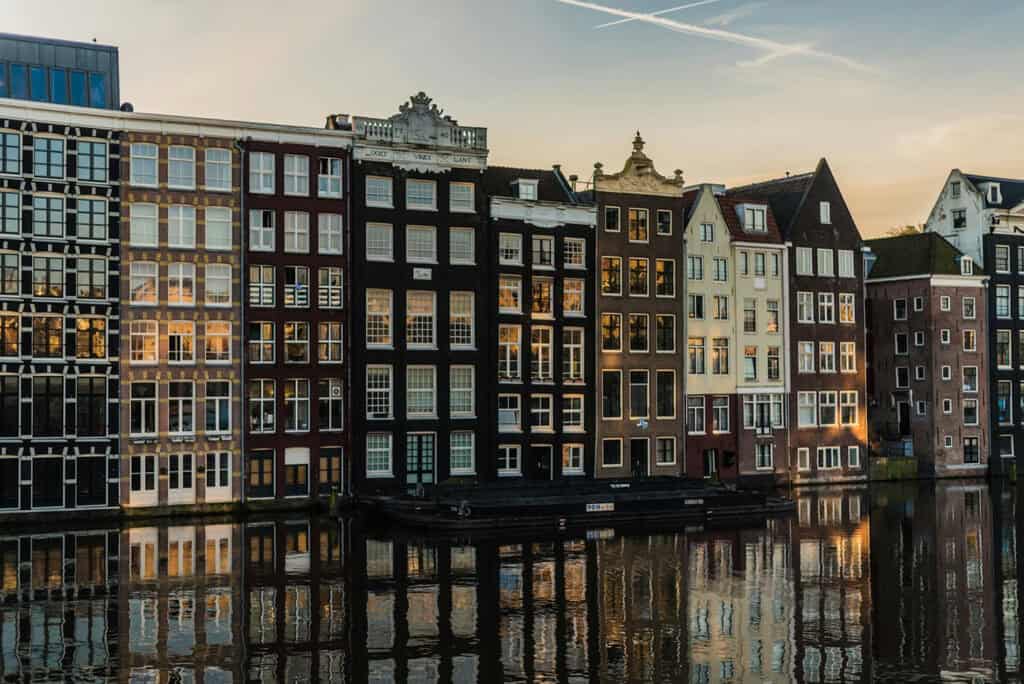

Urban areas have a history of space constraints. So, Dutch architecture favors tall, narrow houses. These structures often reach two stories, maximizing living space on limited plots. This efficient structure meets the needs of city living. In crowded areas, verticality is vital for functional living spaces.
See also: Santa Barbara’s Architectural Style: 10 Key Features to Know
Famous Examples of Dutch Architecture
Dutch architecture is famous for its mix of history and new design. Key examples include:
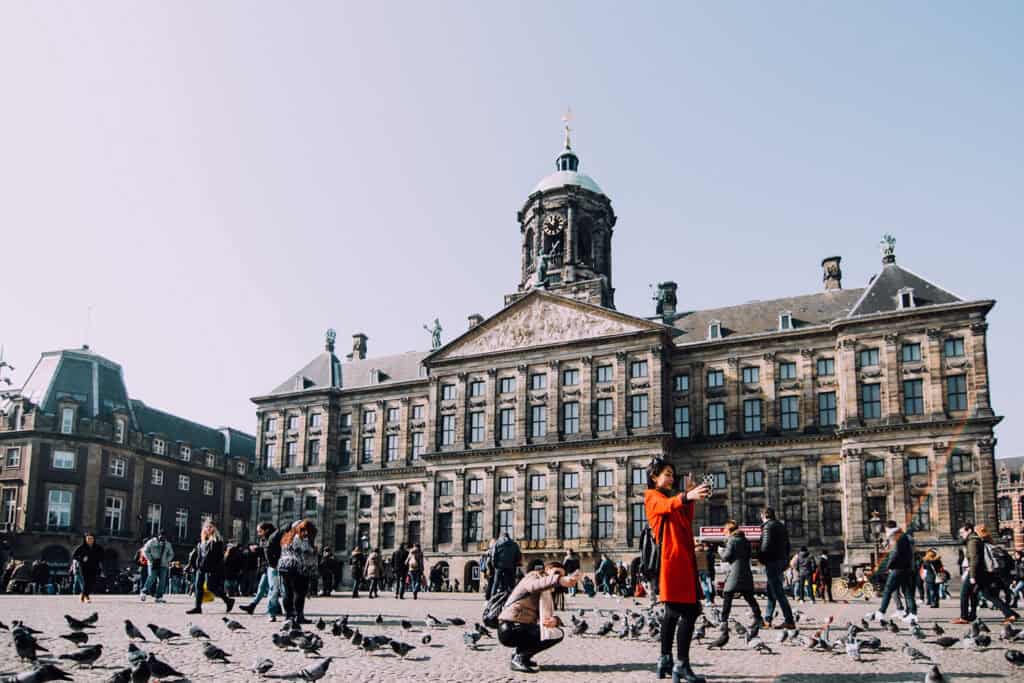
1. The Royal Palace of Amsterdam
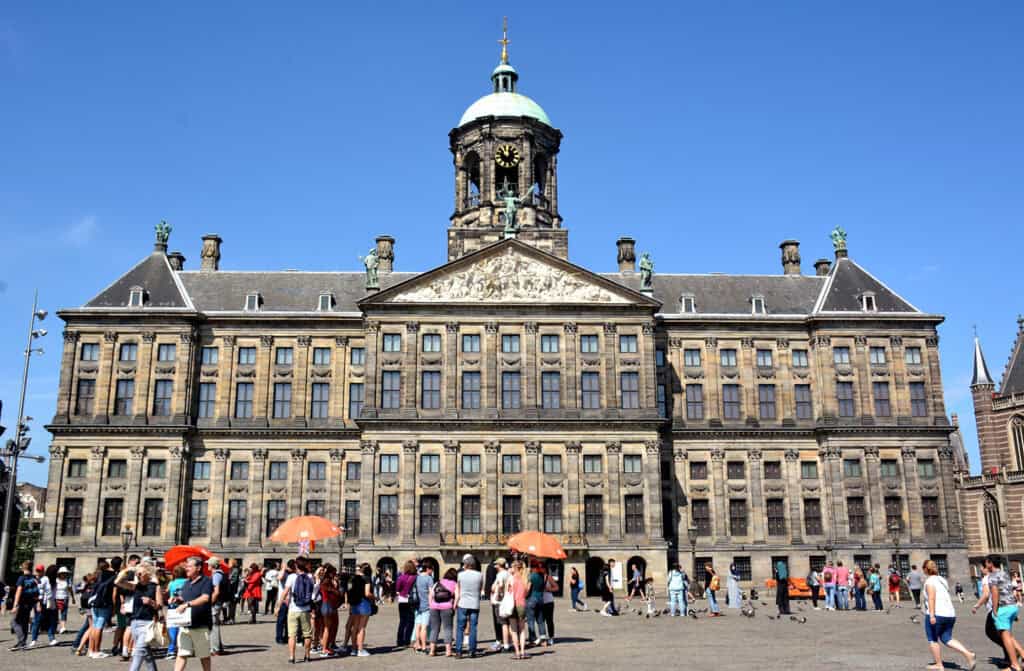

The Royal Palace of Amsterdam exemplifies Dutch Classicism. Built in the 17th century, this impressive structure reflects the wealth of the Dutch Golden Age. Originally a city hall, it was later converted into a royal residence.
2. The Cube Houses in Rotterdam
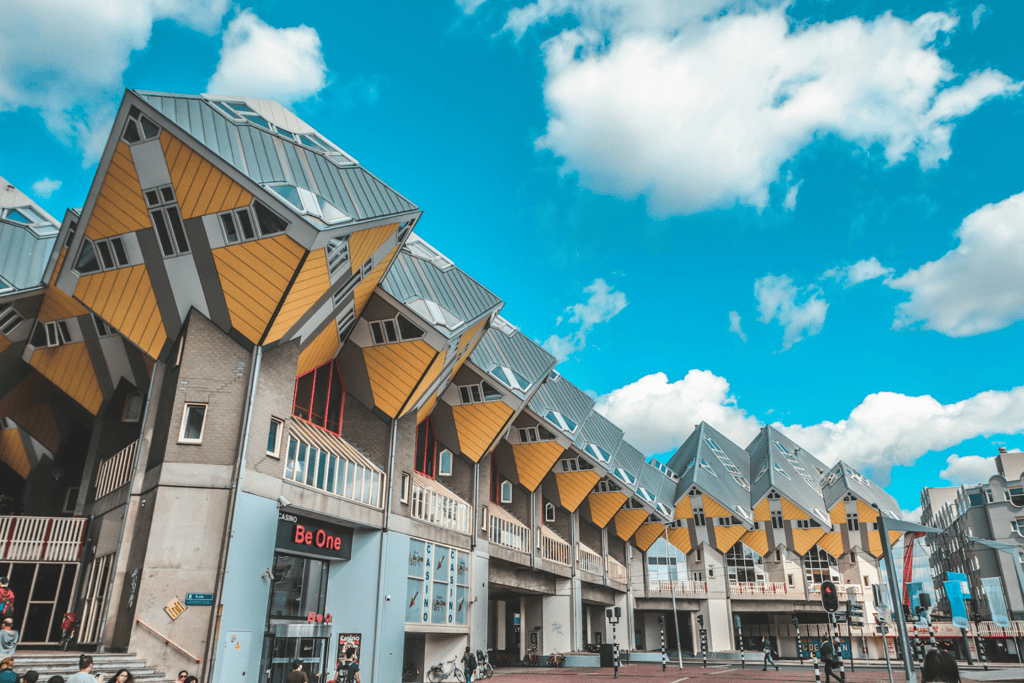

The Cube Houses represent a bold departure from traditional architecture. These asymmetrical structures sit on slanted pillars. They create a unique living space that redefines urban housing.
3. The Rietveld Schröder House
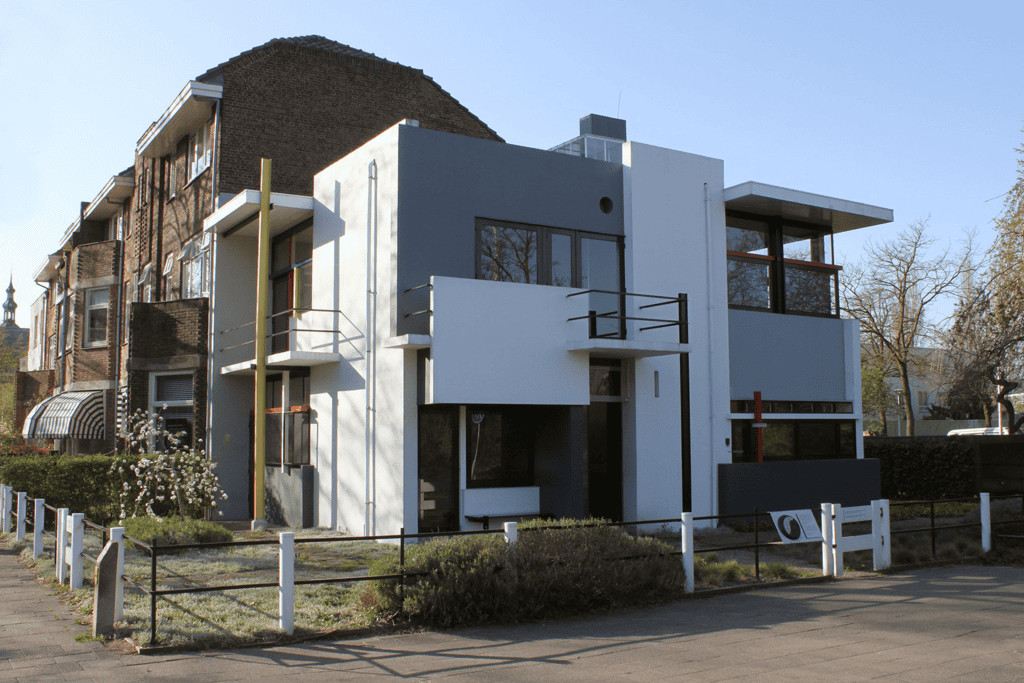

The Rietveld Schröder House, designed by Gerrit Rietveld in 1924, is a masterpiece of Dutch Modernism. The house is noteworthy for its open floor plan and innovative use of space, reflecting the ideals of the De Stijl movement.
See also: Cubic Architecture Style: 6 Features
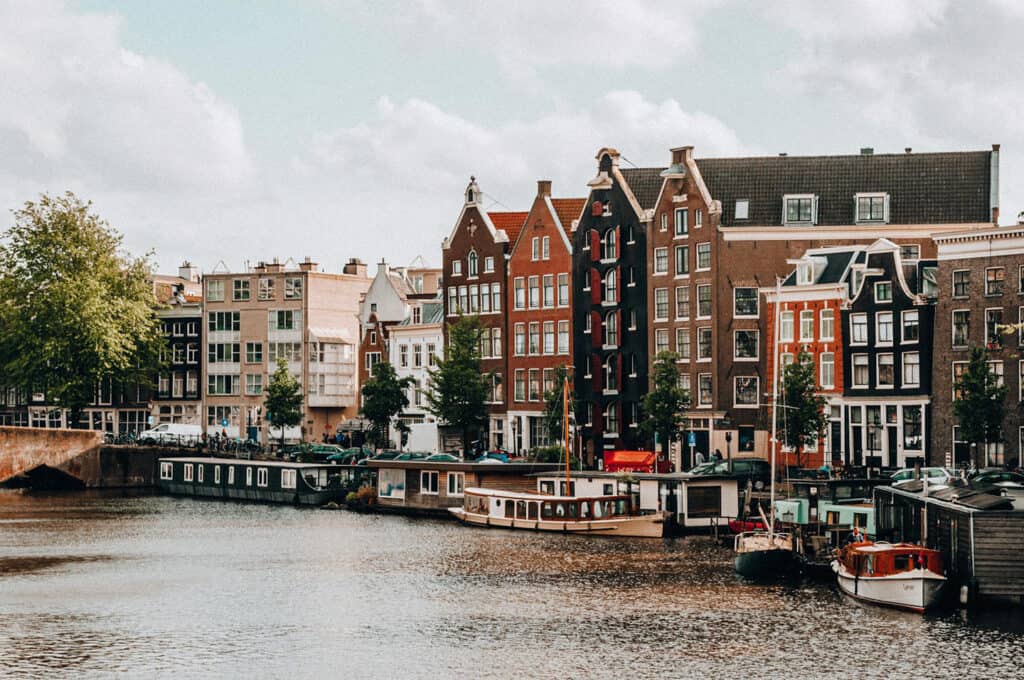
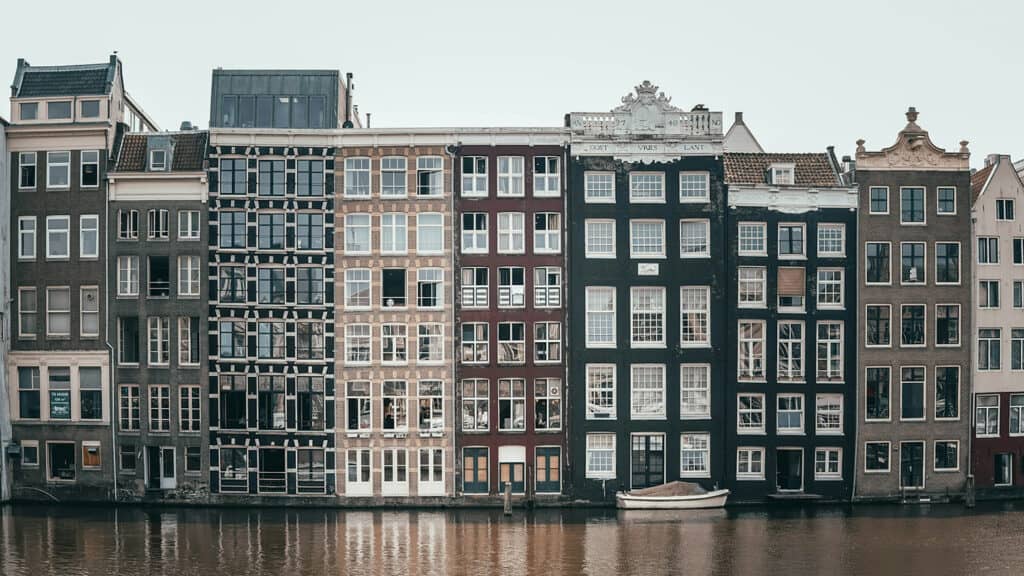
4. Canal Houses in Amsterdam
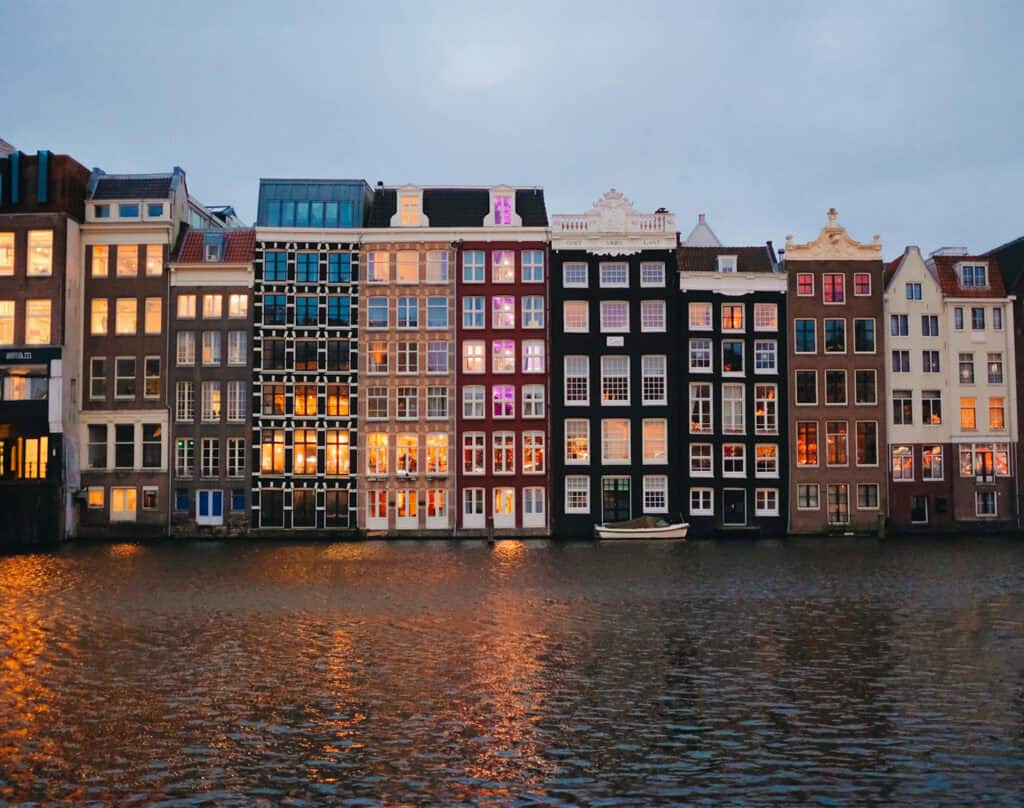

The Canal Houses of Amsterdam are iconic examples of Dutch urban architecture from the 17th century. These slender, multistory buildings line the city’s famous canals. They have gabled roofs, large windows, and ornate façades.

5. Van Nelle Factory
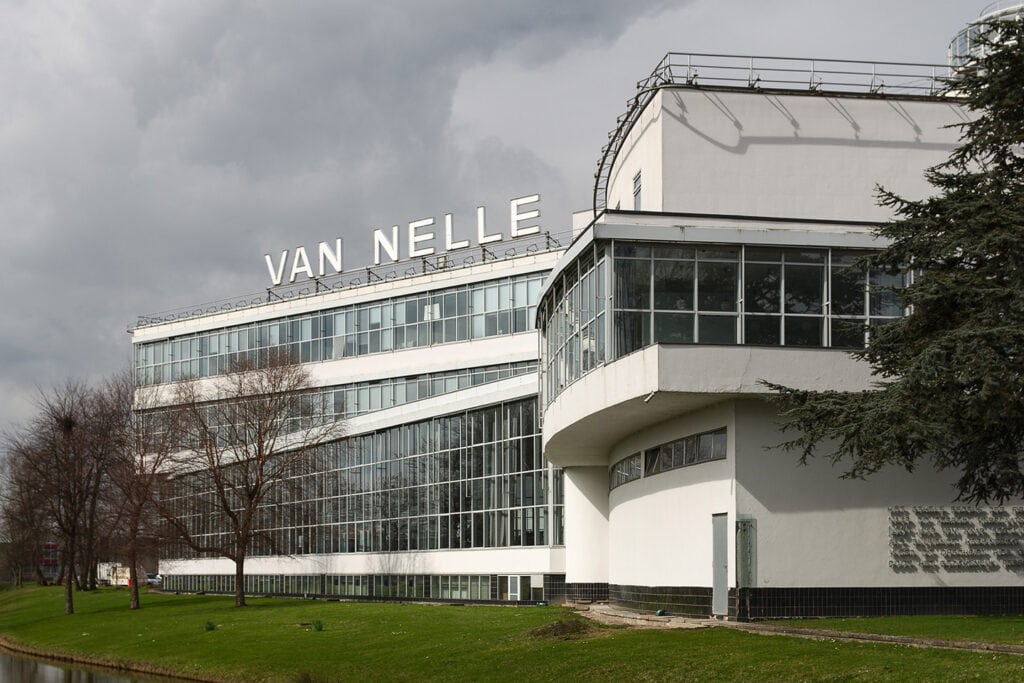

The Van Nelle Factory in Rotterdam is a modern industrial masterpiece. Built from 1929 to 1931, the factory is an example of the International Style. It emphasizes functionality and minimalism.
See also: Best Cities for Architecture in the USA: 9 Cities to Explore
Dutch Style Architecture: A Recap

Dutch architecture has greatly impacted the world. It blends classic styles with modern designs that meet today’s needs. Dutch Colonial homes are an example of this.
Societies evolve. So, future trends in Dutch architecture will focus on sustainability and innovation. There is a push to use local materials and eco-friendly methods. It aligns with global movements for greener buildings. This evolution of styles shows the lasting impact of Dutch architecture. It adapts to a changing world.