Curious about how traditional Bahamian architecture blends history with modern trends? The architecture of the Bahamas combines practical designs suited to the tropical climate with colonial influences, offering both beauty and functionality.
At Landmarks Architects, we guide you through the fascinating world of traditional Bahamian architecture. Learn how historical influences continue to shape contemporary designs.
In this article, we explore:
- Limestone and Wood Construction: Durable and aesthetic local materials.
- Steep Gabled Roofs: Efficient rainwater shedding and ventilation.
- Wrap-Around Porches: Shaded, airy outdoor spaces.
- Sash Windows and Shutters: Maximizing light and airflow control.
Let’s start this journey together!
Architectural Features
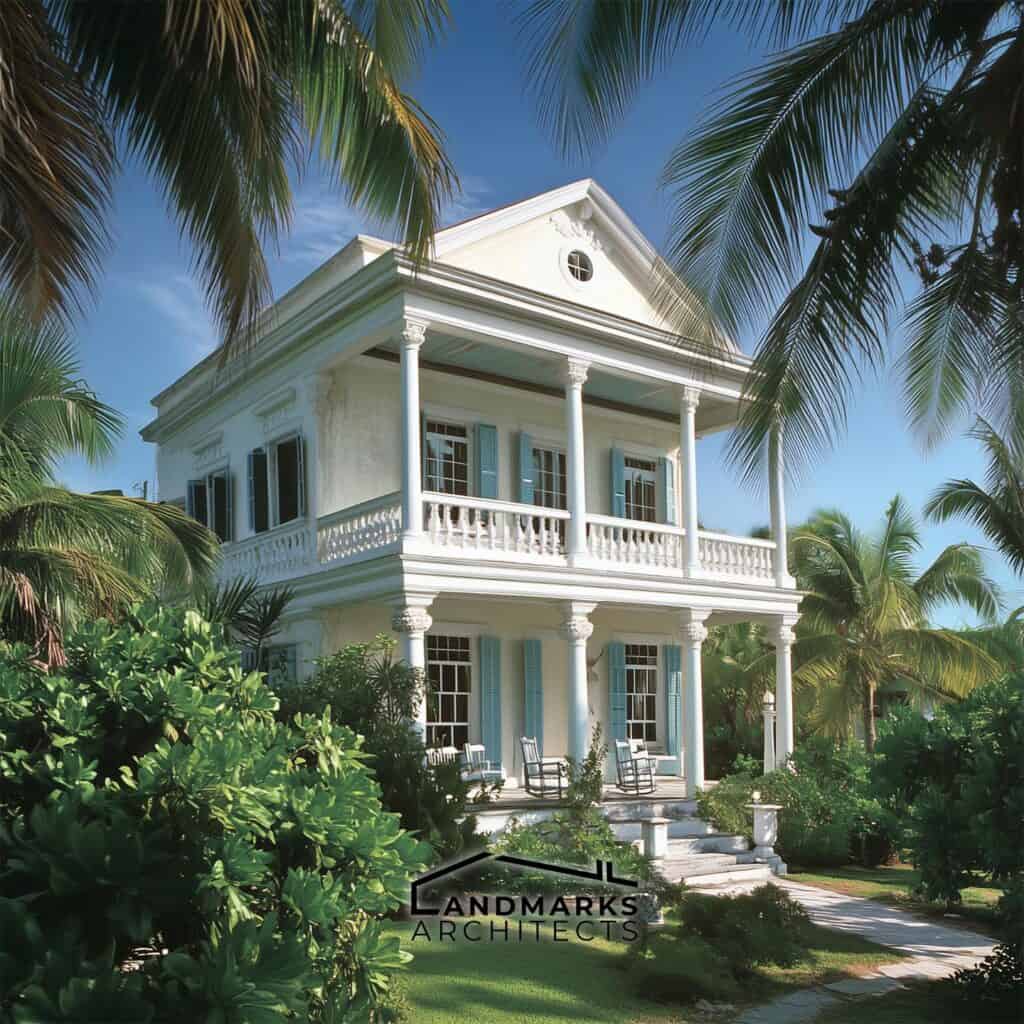

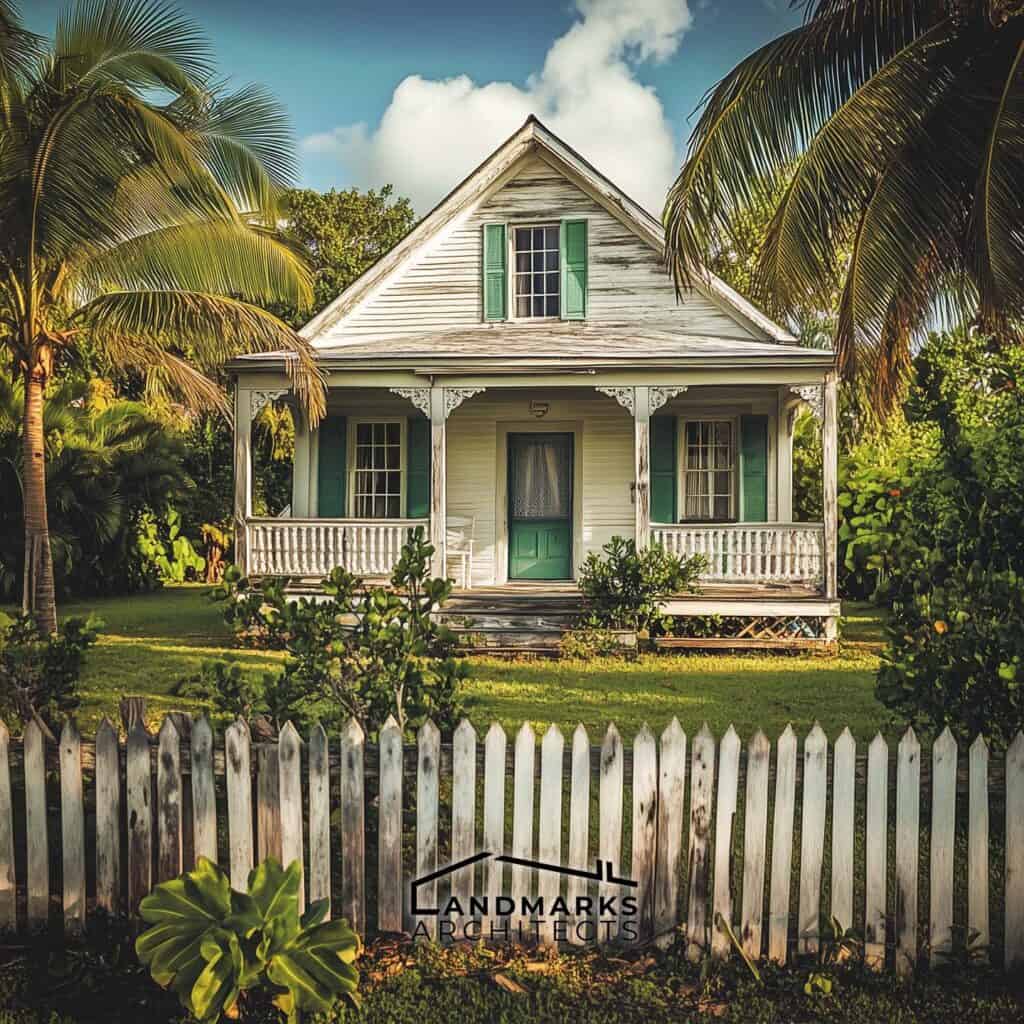
Traditional Bahamian architecture showcases a harmonious blend of practical designs suited to the tropical climate and influences from the region’s colonial past. Key architectural elements help structures withstand the elements while enhancing beauty and functionality.
1. Limestone and Wood Construction
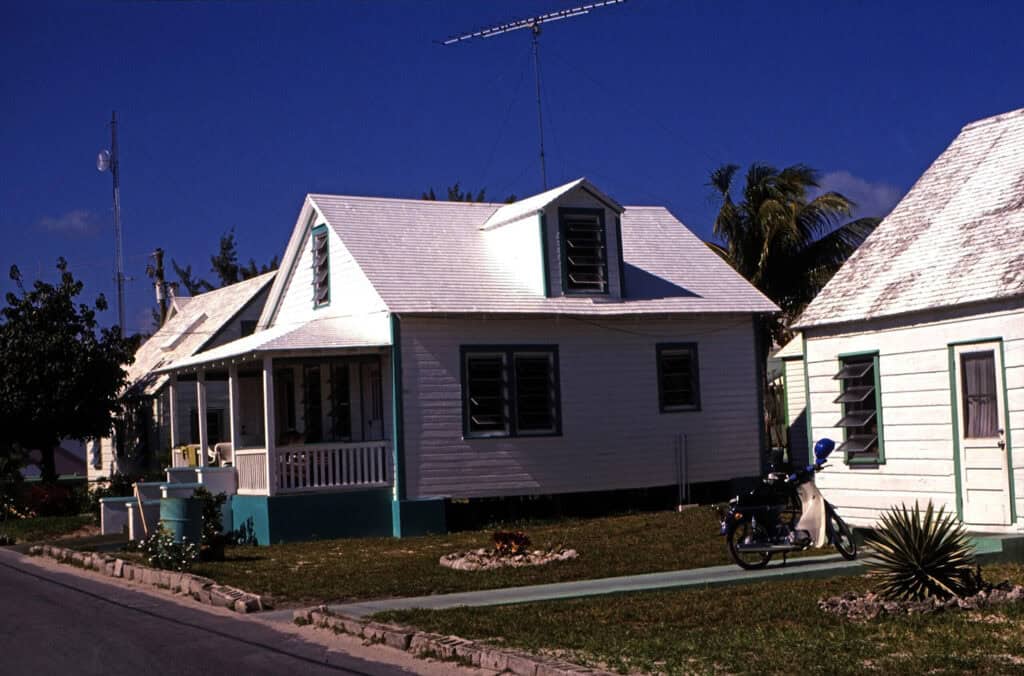


Most traditional Bahamian buildings utilize local materials such as limestone and wood. Limestone, abundant in the islands, provides durability and insulation. Wood, often sourced from Caribbean cedar, is favored for its natural resistance to insects and humidity.
Famous examples include the colonial houses on Harbour Island, featuring intricate wooden detailing. These materials reflect the country’s history and enable airy designs that promote air circulation and comfort in home life.
See Also Traditional Bulgarian Architecture
2. Steep Gabled Roofs
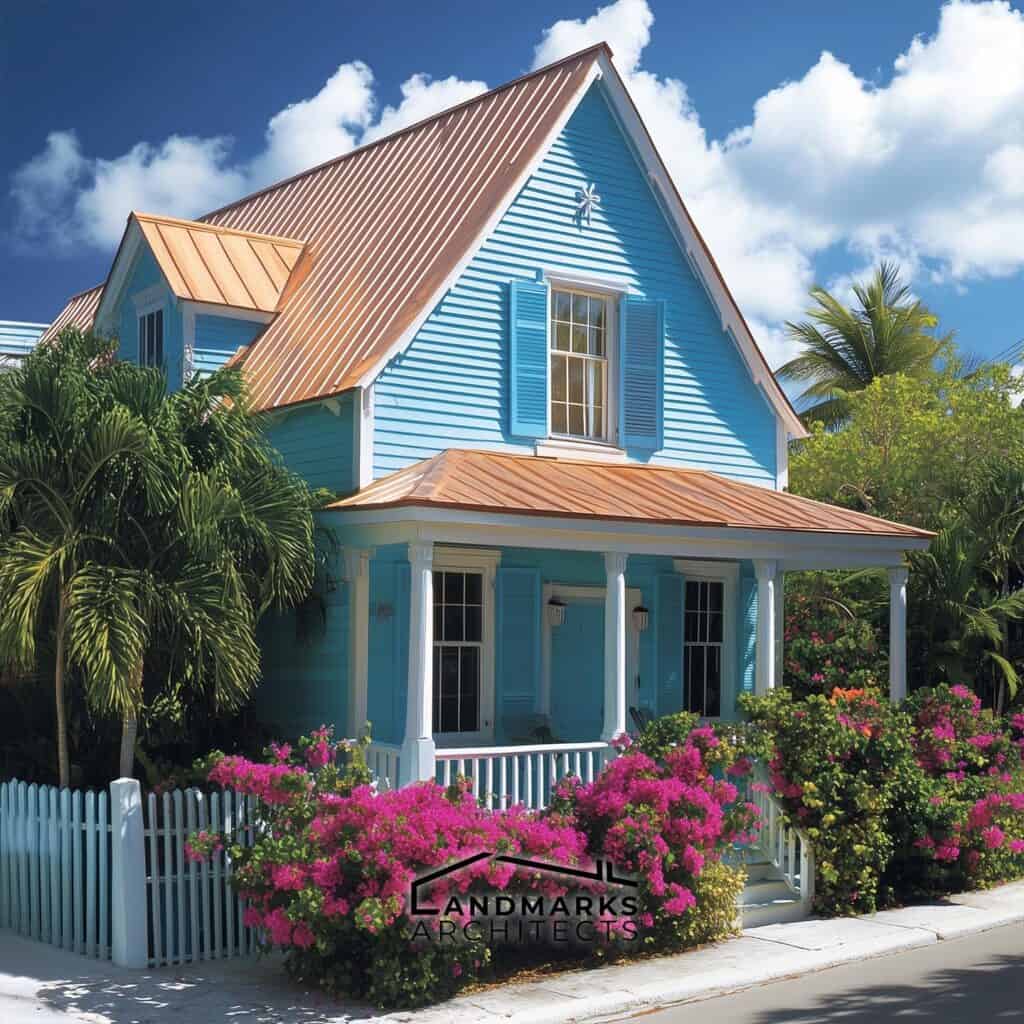
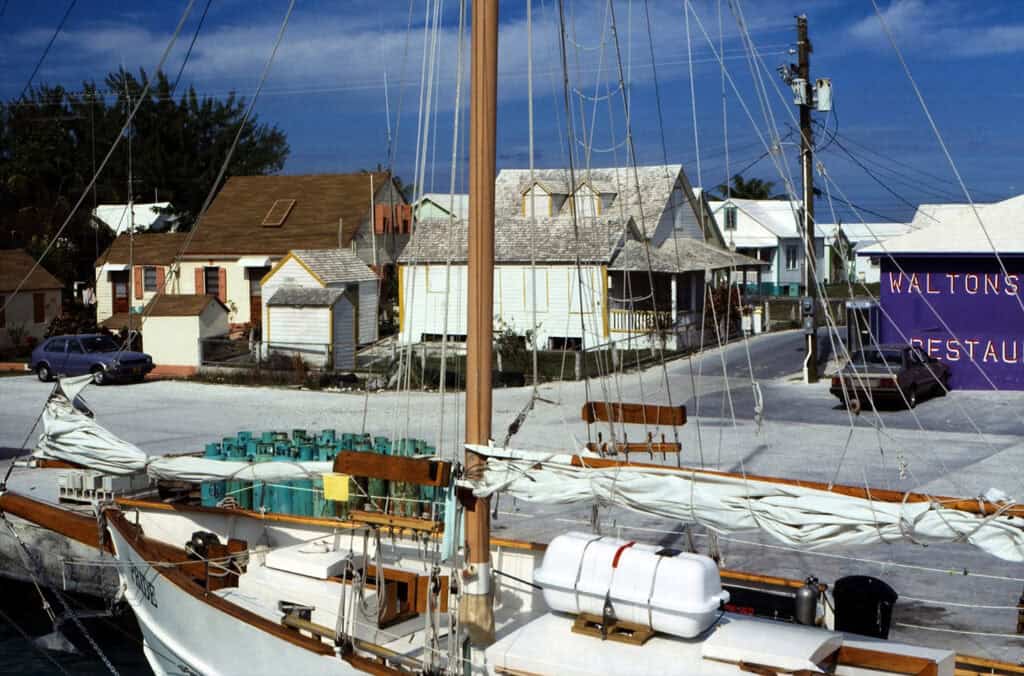


Steep gabled roofs are a hallmark of Bahamian architecture, designed to quickly shed rainwater. The angle of these roofs facilitates the circulation of direct breezes from the trade winds through the spaces below, essential for maintaining a cool interior climate.
Prominent structures showcasing this feature include the clapboard cottages of Spanish Wells. These higher-peaked roofs not only enhance functionality but also contribute to the aesthetic appeal, drawing the eye upward and enriching the architectural silhouette of the buildings.
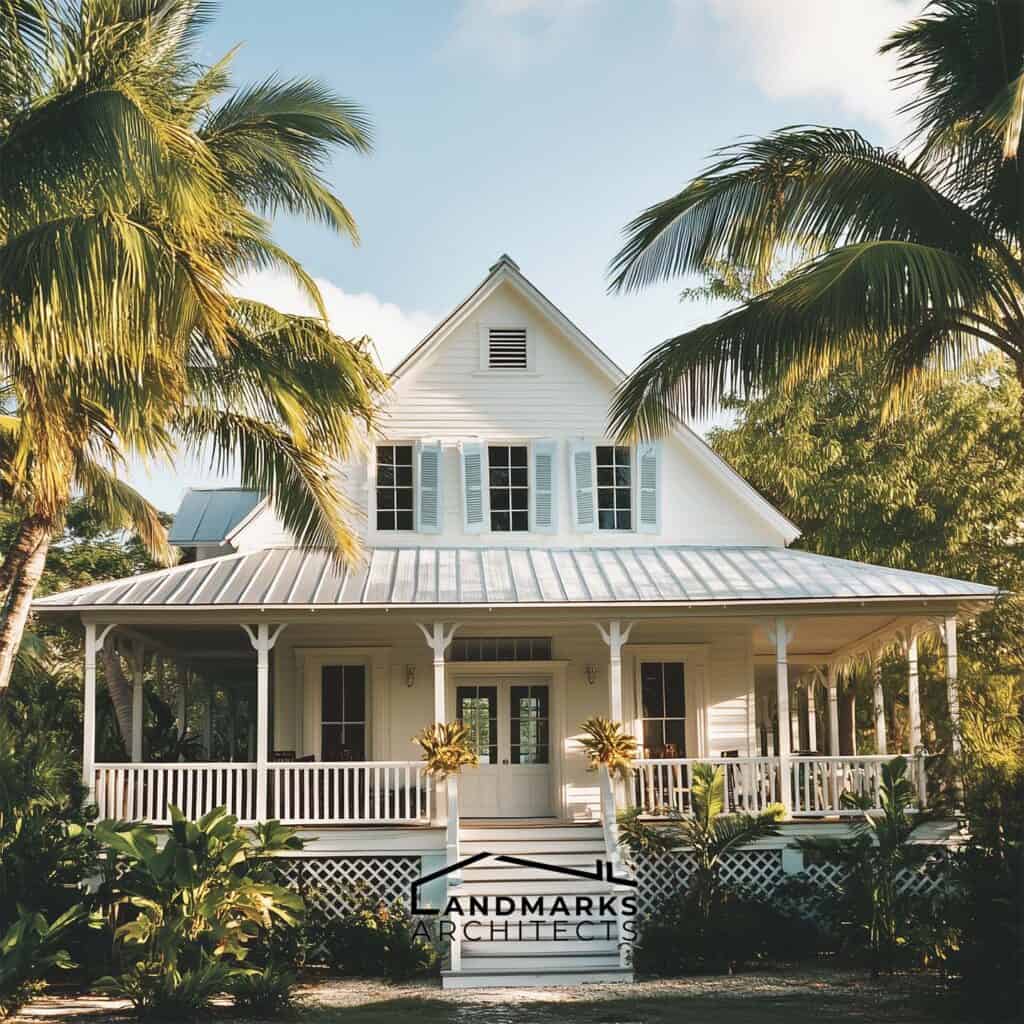
3. Wrap-Around Porches


Wrap-around porches are integral to the Bahamian lifestyle, offering shaded outdoor spaces that connect residents with nature. These porches promote relaxation and social interaction, enabling enjoyment of the outdoors while staying protected from the sun.
Many modern villas and historical homes feature expansive porches. The elevation provided by low stilts enhances landscape views and allows air circulation beneath, offering a cooling effect during the hot months.
See Also Traditional Mexican Architecture
4. Sash Windows and Shutters
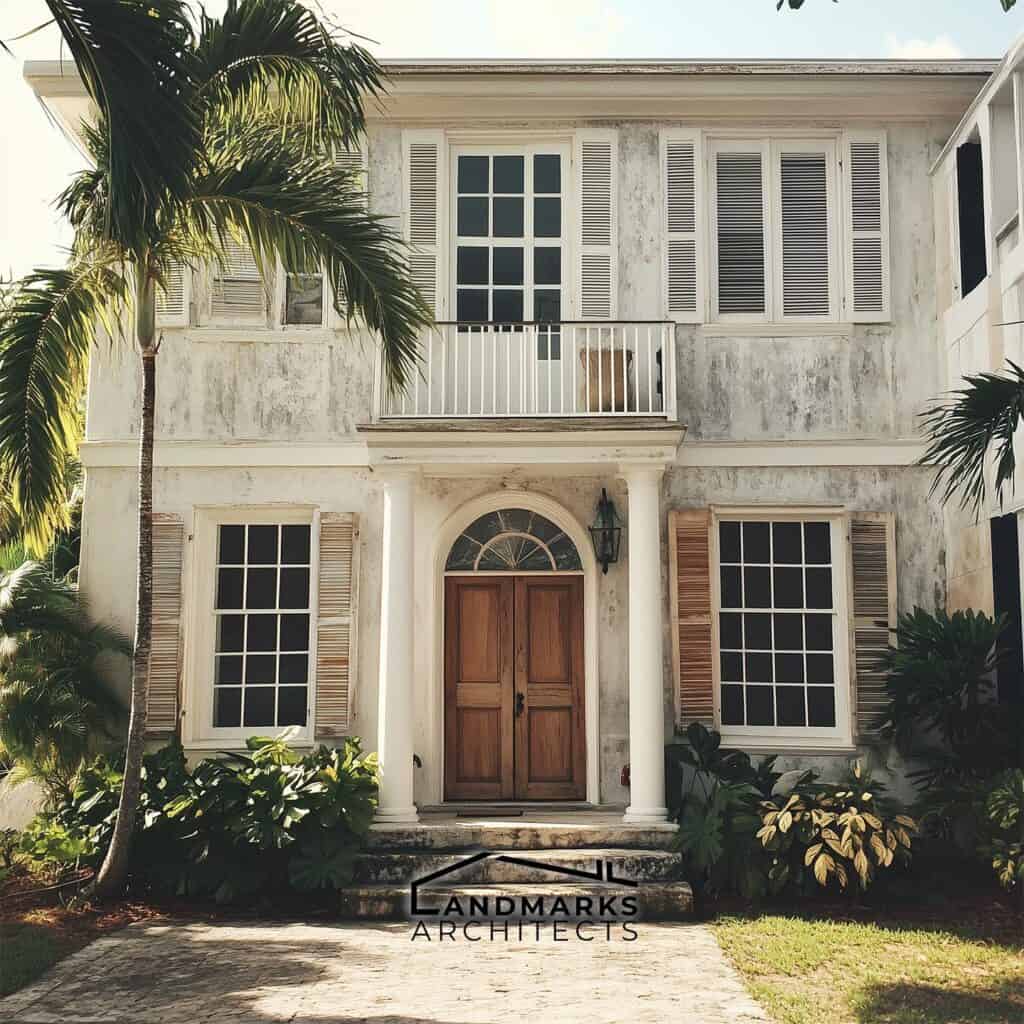


Large sash windows with functional shutters are characteristic of Bahamian architecture. These windows maximize natural light and allow residents to control airflow, which is crucial in the humid climate. Shutters serve both practical and aesthetic purposes, adding visual charm to the structures.
Buildings in Nassau exemplify how these features enhance both aesthetics and functionality. The ability to adjust openings creates a versatile living space, seamlessly blending comfort with the outdoor beauty unique to the Bahamas.
Materials and Techniques
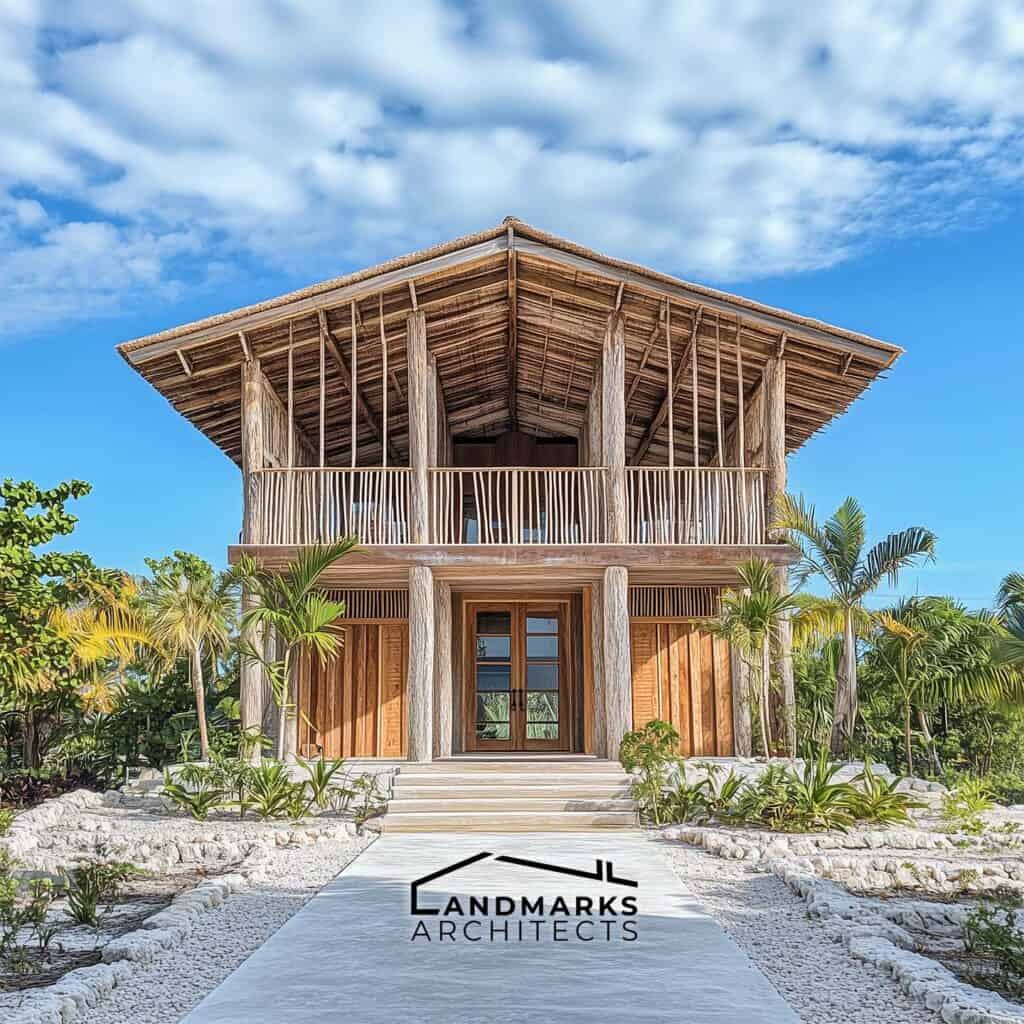

Bahamian architecture showcases unique building methods and materials that reflect the region’s culture and environment. Utilizing local resources and sustainable practices highlights the ingenuity of traditional construction.
Abaco Pine Utilization


Abaco pine is a significant material in traditional Bahamian architecture, valued for its durability and resistance to decay. Commonly used in clapboard cottages and colonial houses, it withstands the tropical climate effectively. Buildings often feature large windows and high ceilings, promoting airflow and natural light.
The use of low stilts elevates structures, preventing water damage and utilizing the space underneath for storage or leisure. Traditional designs, especially in places like Harbour Island, emphasize harmony with the environment, using materials that reflect local aesthetics and functional needs.
Sustainable Sourcing Practices


Sustainable sourcing is integral to Bahamian architecture, balancing development with environmental conservation. Builders use local materials to minimize transportation costs and reduce carbon footprints.
Techniques such as using coral and reclaimed wood provide aesthetic appeal while respecting the islands’ natural resources. Building orientation often leverages trade winds, directing breezes through angled porches and large windows.
These practices preserve architectural heritage while adapting to modern needs, exemplifying the blend of tradition and innovation in the Bahamas.
Historical Preservation and Modern Interpretations

Preserving traditional Bahamian architecture involves safeguarding its rich history while adapting to contemporary needs. Key efforts focus on maintaining architectural integrity and reflecting the aesthetic values that define the islands.
Conservation Efforts



In The Bahamas, conservation focuses on restoring colonial houses and clapboard cottages across the islands. Organizations partner with local communities to protect structures that feature large windows, high ceilings, and low stilts.
Efforts strive to preserve the unique character of traditional buildings, ensuring they resonate with local culture. These initiatives also consider the architecture’s interaction with the environment, designing structures to capture breezes and circulate air, addressing the tropical climate while reflecting historical styles.
Contemporary Bahamian Architects
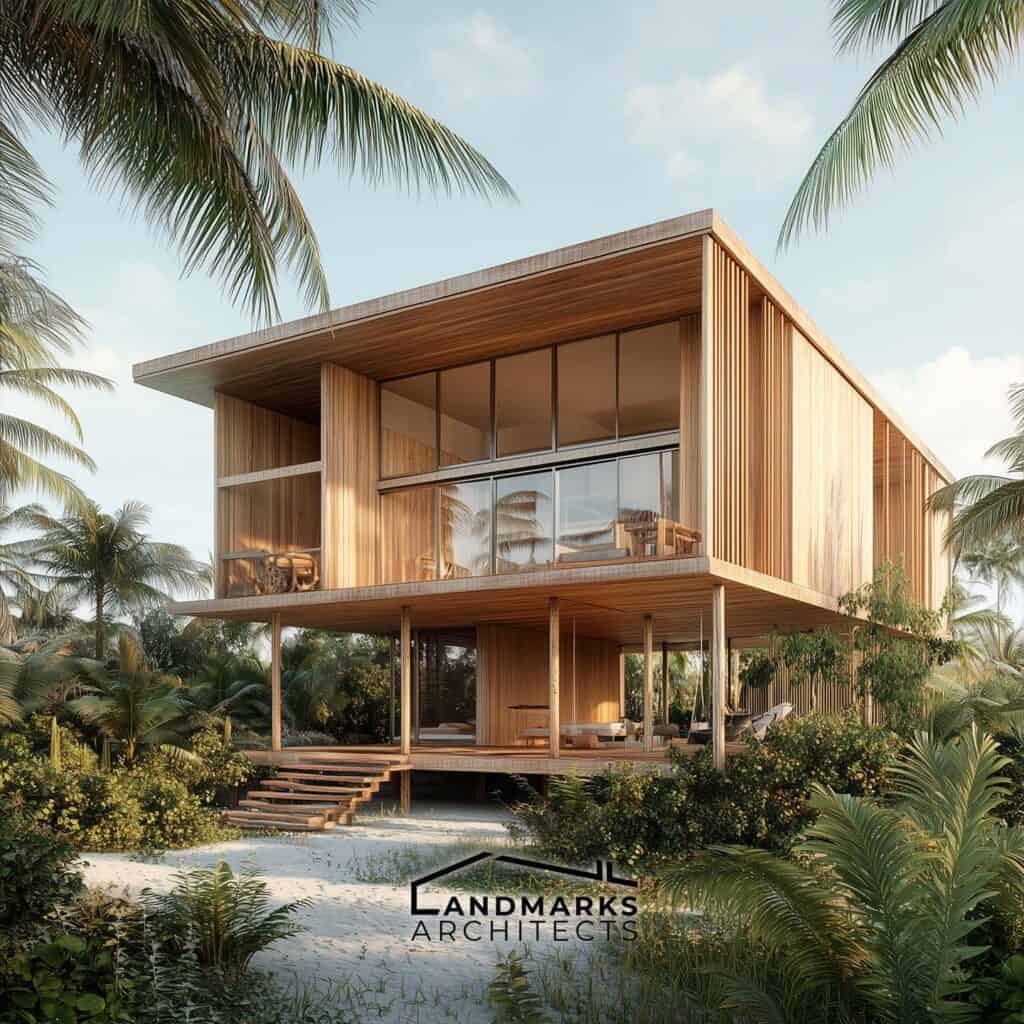
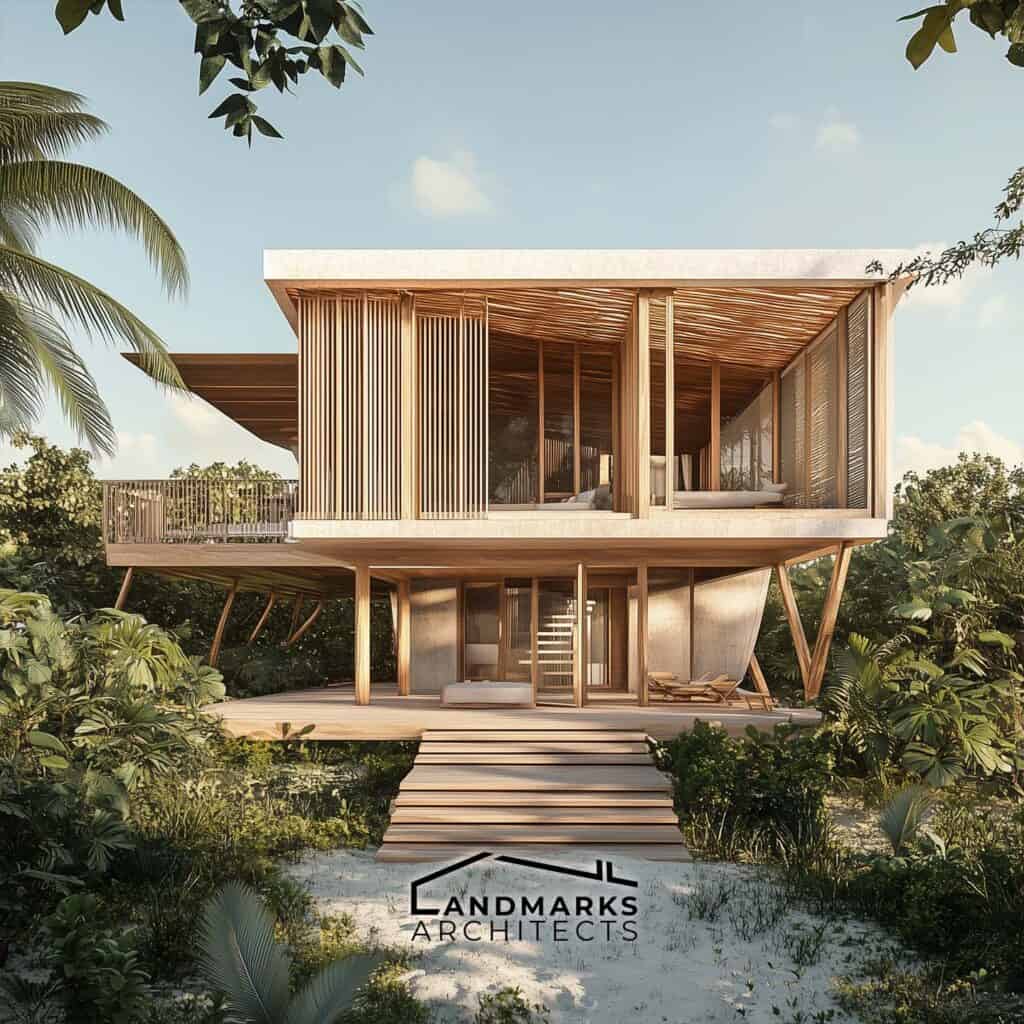


Modern Bahamian architecture blends traditional influences with innovative design. Contemporary architects create villas that honor established aesthetics while incorporating new materials and technologies.
Sustainability is emphasized, with the use of coral and locally sourced materials.
Buildings feature angled porches and elevated structures to enhance ventilation and maintain visual connections to the landscape. This fusion of old and new preserves architectural heritage while enriching Bahamian life. Exploring these projects reveals the islands’ evolving architectural narrative.
See Also Famous Architecture in Brazil
Traditional Bahamian Architecture: A Recap
Traditional Bahamian architecture is types of architectural styles which is defined by its use of local materials like limestone and Abaco pine, practical features such as steep gabled roofs and wrap-around porches, and the integration of large sash windows and shutters.
Modern interpretations honor these elements while following sustainability. Preservation efforts ensure the unique blend of heritage and innovation continues to enhance the Bahamian landscape.